Updated June 3, 2023

Definition of MariaDB Delete User
- MariaDB Delete User command in MariaDB server is responsible to remove a MariaDB user account that may run either on a Unix or Linux type of servers with the help of the mysql command.
- This Delete User is a Maria query statement which deletes the privilege row records for the specified account from all the grant tables. Therefore, to implement this MariaDB Delete user command, one should hold the global privilege of CREATE USER or the privilege of DELETE for the MySQL database.
- Basically, suppose any user needs to delete any account present in the MariaDB database that may be idle or non-operational. In that case, we must get liberated of it, which is the finest option available using the MariaDB delete user query execution.
Syntax:
The syntax for the MariaDB Delete User is defined as follows:
DROP USER {IF EXISTS} UserName {, UserName} … ;- In the above syntax, the term IF EXISTS has been used since the MariaDB 10.1.3 version started. If this IF EXISTS option is implemented with the syntax, suppose the user does not present so the MariaDB may yield a note rather than an error.
- Whereas the UserName denotes the name of the MariaDB user account available.
- If we use the syntax for MariaDB Delete User, the one should have the global privilege for CREATE USER and the privilege for DELETE for the server MySQL database. Here, every account is termed by using the identical format structure as for the CREATE USER statement, such as ‘myuser@localhost’. When the user state just the user name of the account name in MariaDB, a hostname part of ’%’ is implemented. We need to refer to the CREATE USER query for extra information or details about stating the account names.
- It should be noted that when we identify an account that is presently connected, therefore then it may not be removed until the connection is shut, and thus the user may be able to execute query commands until the end of the session. After that, if the session ends, the user will be removed and unable to log in to the MariaDB server. But the databases and related objects which the user has created will not be spontaneously deleted.
- If any of the particular user accounts is not present, it results in ERROR 1306 i.e. HY000. If any error happens, the DROP USER statement working as the MariaDB Delete User command will still remove the user accounts in the server that will not output, producing an error. Simply one error will be generated for all users that have not been released as:
ERROR 1396 (HY000): Operational DROP USER failed for 'v1'@'%', 'v2'@'%'Remember that failed DROP or CREATE operations associated with both roles and users generate the identical error code.
How to delete a user in MariaDB using various ways?
For removing the available user account, the user or admin needs to initially login as the root account for the user on either MySQL or MariaDB server, followed by some more steps to conclude the query execution. But the most important warning is that you need to have taken a backup of the database or related tables which is a good procedure to follow before anyone types any of this kind of command.
When you are deleting the user account, you should know that with this all the associated grants/permissions will also be dropped from the database server. This process of dropping any user in MariaDB or MySQL can be speedy and easy. Also, observing a minimal number of MariaDB user accounts will help to keep the database server safer against any malicious attacks.
Examples
Let us describe how the command MariaDB Delete User query statement works in the server. Firstly, view the user accounts list in the user accounts tab in the phpmyadmin wamp localhost as shown here:
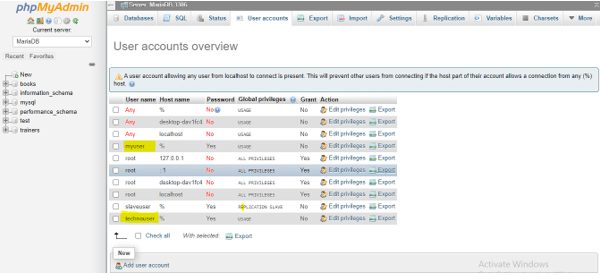
Suppose we have to execute a statement for deleting the user as a demo like myuser, which is the current account the user holds in the MariaDB database, then the command works as:
DROP USER myuser;Use of IF EXISTS:
DROP USER myuser;Output:
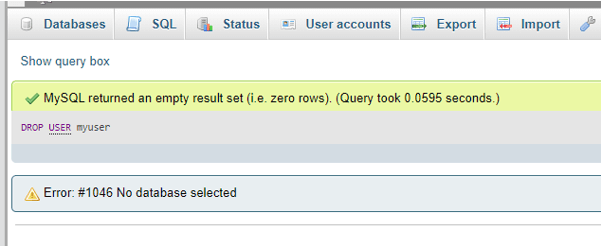
If the command succeeds, it will return: Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec). You can also view the error or any warnings provided on query execution with the following command:
SHOW WARNINGS;If any user requires to check what grants the specific user account, then you need to enter the succeeding command:
SHOW GRANTS FOR 'root'@'localhost';Output:
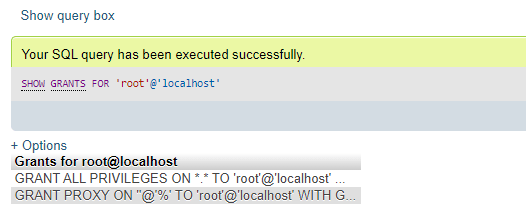
Where,
- Myuser: MariaDB/MySQL user name
- Localhost: MariaDB/MySQL hostname
- : Name of Database
We can also revoke all privileges stated for a MySQL user account by typing the SQL query command scripted as below:
REVOKE ALL PRIVILEGES, GRANT OPTION FROM 'myuser'@'localhost';Dropping more than single user:
In MariaDB, a user can delete more than a single account user at a time. But yes, we can apply the DROP USER query statement to remove multiple user accounts by separating the specifically selected users with comma as a symbol which a user wants to delete from the MariaDB server.
For instance, we can type the following query as below:
DROP USER 'myuser'@'localhost', 'technouser'@'localhost';This command typed above will execute to drop an available couple of users created using CREATE USER command in MariaDB – myuser and technouser.
Hence, MariaDB permits the implementation of the DROP command to multiple user accounts and applies for related grant applicable privileges, which further helps the user accounts connect and regulate the databases.
If the user no longer requires any long, they may consider it a good idea to either delete the account privileges or completely remove the user account.
Conclusion
- The MariaDB Delete User command is useful if a user requires to acquire the release of any unwanted or outdated MariaDB user account in the database server.
- Because holding any extra account in the server without any operational tasks can be insecure as any susceptibility or attack may happen in that database through this unmanaged account.
- This article will teach you how to delete a user account from a MariaDB database server using the Linux system or the command line.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “MariaDB Delete User” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.

