Updated July 21, 2023

Definition of Loss Ratio
Loss Ratio can be defined as the losses incurred by an insurer as a result of claims that are already paid in comparison to the premiums that are already earned and it represents how well an insurance company is actually performing, i.e., whether the insurance company is able to collect sufficient premiums for meeting its debt obligations as well as other commitments or it is merely under-charging its customers to the point that the same is suffering from losses.
The formula used for calculating is as follows:
Example of Loss Ratio (With Excel Template)
Let’s take an example to understand the calculation in a better manner.
Example #1
ABC Insurance Company has paid a total of $60 million in claims during the last year and has received a premium of $75 million during the same year. Calculate the loss ratio for ABC Insurance Company.
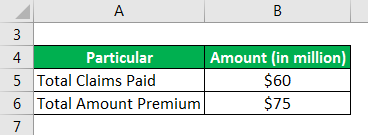
Solution:
Loss Ratio is calculated using the formula given below
Loss Ratio = (Losses Incurred in the Claims + Adjustment Expenses) / Premiums Earned for the Period
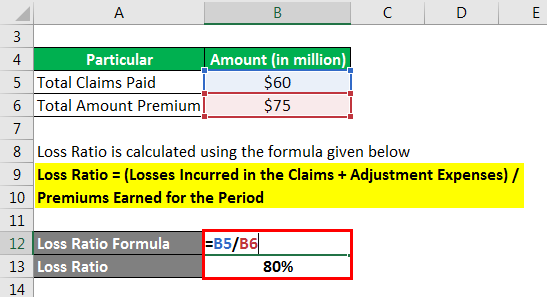
- Loss Ratio = $ 60 million / $ 75 million
= 80%
Hence, loss for ABC Insurance Company is 80 %.
Example #2
An insurance company collected $600,000 in premiums in the year 2019. In the same year, the company had paid a total claim and adjustment expenses of $300,000. Calculate the loss ratio for this company.
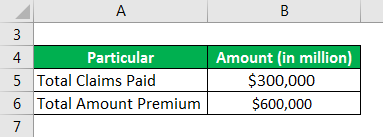
Solution:
Loss Ratio is calculated using the formula given below
Loss Ratio = (Losses Incurred in the Claims + Adjustment Expenses) / Premiums Earned for the Period
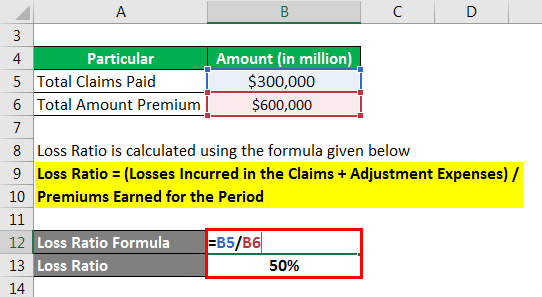
- Loss Ratio = $ 300,000 / $ 600,000
= 50%
Therefore, the loss of the aforesaid insurance company is 50 %.
Explanation
This is merely a percentage of the overall claims that are paid by a particular insurance company in comparison to the overall premiums that are already received within a time period of 1 year. This signifies how effectively a company is performing. This represents if an insurance company is being able to collect a sufficient amount of premiums for meeting all its expenses or not. This is highly useful for assessing the financial wellbeing of an insurance company and identifying the efficiency level of each and every product line.
Importance of Loss Ratio
Computation of loss ratio is really important for insurance companies. It helps in evaluating the financial wellness of an insurance company. This indicates the fact that whether an insurance company is successfully collecting sufficient premiums by itself so that it can take care of all the claims and adjustment expenses or not. It is a very effective tool in calculating the percentage of losses in comparison to the premiums earned by an insurance company. In other words, the ratio helps in determining the profit earning ability of an insurance company. It also helps in determining the premiums of the upcoming policies as the insurance companies will be able to gather feedback for already issued policies and that too on a regular basis and tweak their pricing so that it remains competitive as well as profitable.
Difference Between Loss Ratio vs Combined Ratio
Both Ratios are taken into use for the purpose of measuring the profit earning ability of an insurance company. However, both differ from each other on multiple parameters. It is used for measuring the total losses incurred by the insurance companies in comparison to the insurance premiums actually collected by the same. The losse borne by an insurance company in a loss ratios is computed by adding up the total claims and adjustment expenses paid by the same and dividing it with the total premiums that it has paid in the same year. On the other hand, the combined ratio is used for measuring the losses and expenses incurred in comparison to the total premiums actually collected.
Benefits
The benefits for the same are provided and discussed as follows-
- This helps in determining the profit earning ability of an insurance company.
- This helps in determining the financial wellbeing of insurance companies.
- This helps in determining the efficiency level of a particular product line.
- This also helps in determining the premiums of upcoming policies as it allows the companies to take feedback for policies that are already issued from time to time. This allows the insurance companies to stay competitive and at the same time earn sufficient profits.
Conclusion
Loss Ratio is a very important metric used for tracking the financial performance of an insurance company. It is a very important ratio for insurance companies as it helps them in evaluating their profitability and financial wellness and also lets them stay competitive in their industry. Users must always use the same along with combined ratios in order to measure the overall outflows in comparison to the total inflows. This is calculated by summing up the total claims and adjustment expenses for a particular year and dividing the same with the total premiums that are earned during that same year.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to the Loss Ratio. Here we discuss how to calculate Loss Ratio along with practical examples. We also provide a downloadable excel template. You may also look at the following articles to learn more –


