Definition of Long-Term Debt in Balance Sheet
Long-term debt is the debt that the company owes to investors, payable after over a year since it is a liability and payable in more than one year. Hence it is shown as a non-current liability in the balance sheet.
Explanation
Long-term debt is a debt item presented on the balance sheet. It is categorized as non-current liabilities because it is payable after more than one year. Long-term debts include 10,20,30 years of bonds, long-term bank loans, etc. Companies may have a portion that requires repayment within one year in long-term debt. That portion is shown as the “Current portion of long term debt” under Current liabilities in the balance sheet. For example, in 10-year bonds, Companies have to pay semiannual coupons to the debt holders. The coupon amount that needs to be paid in 1 year is kept as a “Current Portion of long term debt” under current liabilities.
Component of Long-Term Debt in Balance Sheet
As mentioned earlier, long-term debt has two components in the balance sheet. One under non-current liabilities and another under current liabilities. We know that long-term debts are payable in more than 1 year, such as 10 or 20 years bonds; As a result, companies categorize bonds under non-current liabilities, but a portion of these bonds is due for payment within a year. Therefore, that specific portion classifies under current liabilities.
Examples of Long-Term in Balance Sheet
Following are the examples are given below:
Example #1
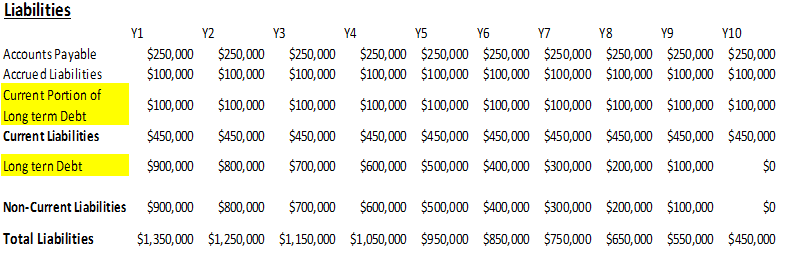
Let’s assume Company XYZ was an unleveled company. It has just now taken a bank loan of $1,000,000 for 10 years. This bank loan will be equally amortized over 10 years. That means in the next 1 year, $100,000 must be paid, and the rest must be paid over 10 years. So below can be the liabilities portion of its balance sheet:
| Liabilities | Amount |
| Accounts Payable | $250,000 |
| Accrued Liabilities | $100,000 |
| Current Portion of Long-term Debt | $100,000 |
| Current Liabilities | $450,000 |
| Long term Debt | $900,000 |
| Non-Current Liabilities | $900,000 |
| Total Liabilities | $1,350,000 |
Pic: Liabilities portion of Company XYZ
Example #2
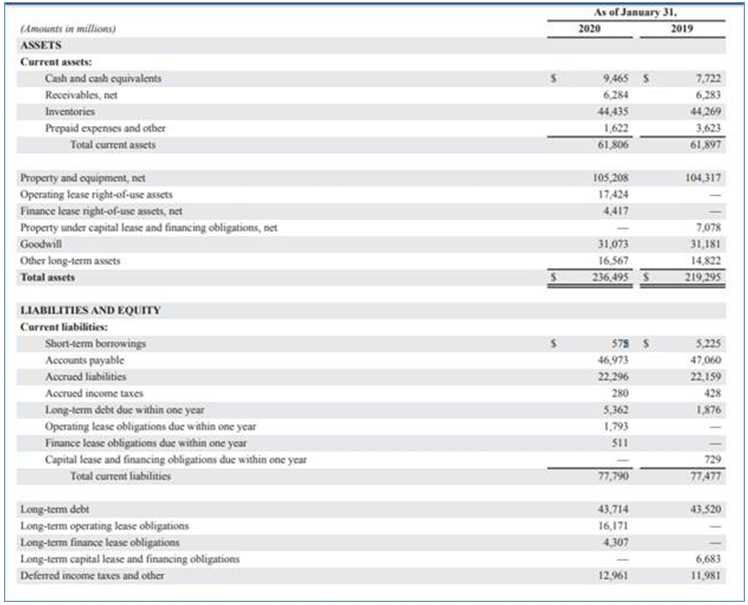
Walmart is a US multinational retail organization headquartered in Bentonville, Arkansas. Walmart was founded in 1962. Below is a snippet of its balance sheet from its 2020 annual report.
Source: Wallmart Inc Annual Report
As we can see here, as of 31st January 2020, it has a long-term debt of $43,714 million, which is almost similar to the long-term debt on 31st January 2019. However, the Current portion of long-term debt increased from $1,876 million to $5,362 million.
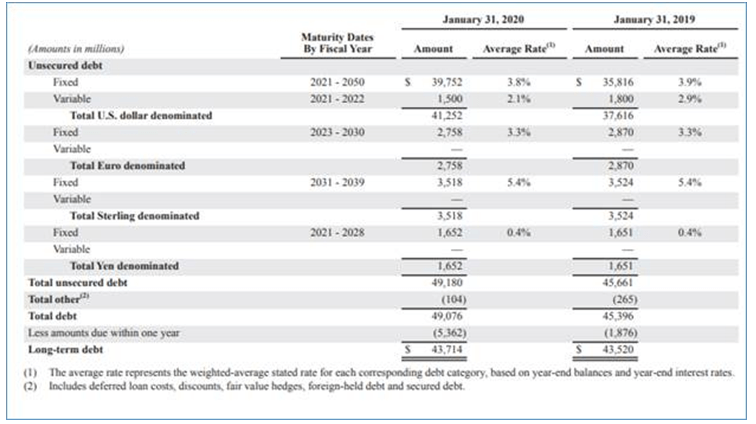
Below is the break up of its long-term debt:
Source: Wallmart Inc Annual Report
Modeling of Long Term in Balance Sheet
We will take the above example of Company XYX to understand how the company will model a $1,000,000 bank loan over 10 years. This bank loan will get amortized over 10 years. We can see below how the company will model that loan over 10 years:
As we have seen, the company will pay back $100,000 from the loan each year. So that amount will be shown in the “Current portion of long term debt”. Long-term debt will also get reduced by $100,000 each year. This process repeats until year 10, when there is only $100,000 remaining to be paid, and since that amount will be paid in the 10th year, that amount will be shown under current liabilities, and the long-term debt amount will be zero.
Use of Long-Term Debt in Balance Sheet
The main purpose of any kind of financing, whether that is equity or debt, is to raise capital to buy assets. That asset will eventually generate revenue for the business. Long-term debt can also be used to leverage the company, buy back the shares, and convert the company from public to private. Also, debt financing is cheaper than equity financing, so the company can prefer to raise capital via debt and not by equity.
Conclusion
Companies use long-term debt for various purposes that align with their strategy. Companies benefit from long-term debt as it can be repaid gradually over the years, and the cost of debt is lower than the cost of equity. However, companies must remain cautious to avoid becoming overleveraged, as this can make it challenging for them to fulfill their obligations and repay investors.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Long Term Debt in Balance Sheet. Here we also discuss the definition and component of long-term debt in the balance sheet, along with examples. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –