Updated May 23, 2023

Definition of Linux Untar
Untar is a command that enables users to extract compressed files with tar, tar.gz, and tar.bz2 compression formats. This command is used for 2 specific utilities in file operations. It first helps the user to extract or, in other words, unpack files in the compressed mode, and once the unpacking or extraction is done, the command helps the user to uncompress the same. Listing content and extracting a single file or directory are some of the widely used utilities of the command untar. In this article, we will go through all the command utilities and take deep dive using some examples to understand them in even greater detail!
Syntax:
In Linux, there are fewer options available for untar compared to other extensively used commands, and we will discuss all of those in detail here in this section later in the article, take a dig at the working of untar commands in Linux.
1. Extraction of the tar file
Syntax:
tar -xvf <tar file name with .tar extension>2. Extraction of the tar.gz file
Syntax:
tar - xvzf <tar file name with .tar.gz extension>3. Extraction of tar.bz2 file
Syntax:
tar -xvjf <tar file name with .tar.bz2 extension>4. Untar tar archive File at the desired location
Syntax:
tar -xvf <full location of tar file> -C <location to specified directory>5. List Content of tar Archive File
Syntax:
tar -tvf <full location of tar file>
6. List Content of tar.gz Archive File
Syntax:
tar -ztvf <full location of tar file>7. List the Content of tar.bz2 Archive File
Syntax:
tar -jtvf <full location of tar file>8. Extract a single file from the tar Archive File
Syntax:
tar -xvf <full location of tar file> <file name to be extracted>9. Extract all files from the tar Archive File matching a particular file regex
Syntax:
tar -xvf <full location of tar file> --wildcards ‘<file type>’How does Untar Command work in Linux?
Recently, most of our files downloaded from the internet have been compressed using a particular compression format, where a few formats are tar, tar.gz, and tar.bz2. The history behind tar is; in early times, the tar file format was used to create archives to store files on magnetic tape, and hence the full form of tar is Tape ARchive. Untar is a process of reversion of the process which leads to the formation of the tar file.
In the computation world, there are two different versions of tar, namely BSD tar and GNU tar. By default, most Linux is pre-installed with GNU tar. Another similar process of untar is gzip utility with the command gunzip. Now, talking about the different options of utility of untar, they are the following 4 options:
x – provides an option to the tar command to extract files from the given tar file.
v – commands the tar to list out the files as they get extracted.
z – commands the tar command to decompress, without which, by default, the tar command will compress instead of decompressing.
f – helps specify the filename that needs to be worked on for the untar process.
In the above few options, we look at all the widely used utilities. Apart from this, we also have other utilities like:
- wildcard option: This option allows the user to search for a type of file extraction. For example, one would like to untar only the .jpeg extension in a tar file containing other file types. Using the –wildcards ‘<file type>’ will allow the user just to extract the specified file type.
- C option: This option helps untangle the specified files to a particular path location; in case one needs this utility.
- Delete option: Though not a part of untar option, a utility closely associated with untar is the removal of a file from a tar archive. Using the –delete option assists the user in deleting a specific file in a tar archive.
With all the utilities mentioned above, this command becomes an inadvertent skill set any Linux developer possesses.
Examples
Let us discuss examples of Linux Untar.
Example #1
Extraction of tar file
Syntax:
tar -xvf eduCBA-demo.tarOutput
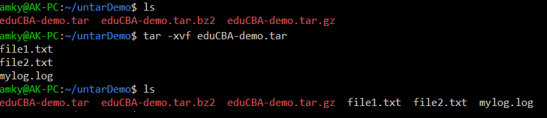
Here we see that at first, there are no such files present while we have the directory, but as we untar the file, all the file contents get extracted and uncompressed to the location where we are running the command from. A similar explanation goes for the below 2 examples (for tar.gz and tar.bz2).
Example #2
Extraction of the tar.gz file
Syntax:
tar - xvzf eduCBA-demo.tar.gzOutput:

Example #3
Extraction of tar.bz2 file
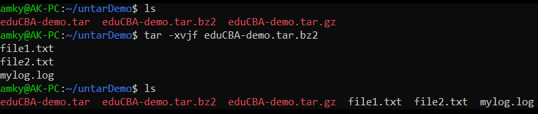
Syntax:
tar -xvjf eduCBA-demo.tar.bz2Output:
Example #4
Untar tar archive File at the desired location
Syntax:
tar -xvf eduCBA-demo.tar -C desiredLocOutput:
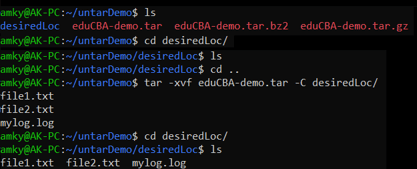
Here we see that the location desiredLoc has no files under it, and as we extract the file, all the file contents get extracted to the location specified i.e. desiredLoc.
Example #5
List Content of tar Archive File
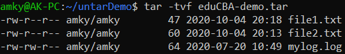
Syntax:
tar -tvf eduCBA-demo.tarOutput:
Example #6
List Content of tar.gz Archive File
Syntax:
tar -ztvf eduCBA-demo.tar.gzOutput:
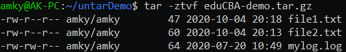
Example #7
List the Content of tar.bz2 Archive File
Syntax:
tar -jtvf eduCBA-demo.tar.bz2Output:
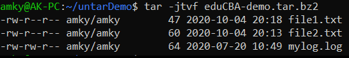
Example #8
Extract single file from tar Archive File
Syntax:
tar -xvf eduCBA-demo.tar file1.txtOutput:
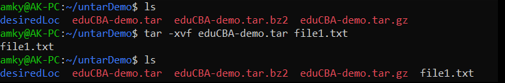
Example #9
Extract all files from tar Archive File matching a particular file regex
Syntax:
tar -xvf eduCBA-demo.tar --wildcards '*.txt'Output:
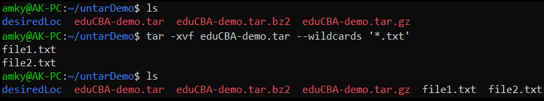
In this example, we see that only the files with “txt” as an extension get untarred in the location!
Conclusion
With the set of examples and explanation of the way of working for untar command, the usage and utilizes are even more clear for the readers, and now we leave it up to you to experiment more with the different permutation combinations possible with the options present in the command utility. Though not mandatory, advisable to use untar command for any of the uncompressing processes of a tar, tar.gz, tar.bz2 file types as these will always have the latest options available at its disposal.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “Linux Untar” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.


