Updated May 3, 2023
Introduction to LEFT OUTER JOIN in PostgreSQL
Left outer join is also known as Left join, it will retrieve all rows from the left table, and matching rows from the right table also retrieve all matching records from both tables if we want to fetch all records from the first table and doesn’t need any record from the second table then we create left to join the second table such as that column has null values, left join or left outer join is a most important type of join in PostgreSQL, PostgreSQL left join comes in a PostgreSQL outer also join it is types of PostgreSQL outer join.
Syntax
The left join will retrieve all rows from the left table and match records from the right table.
Below is the syntax of the left outer join is as follows:
Syntax #1
Select columns from table_name1 LEFT OUTER JOIN table_name2 on table_name1.column = table_name2.column;Syntax #2
SELECT (*) FROM table_name1 LEFT OUTER JOIN table_name2 on table_name1.column = table_name2.column;Working on LEFT OUTER JOIN in PostgreSQL
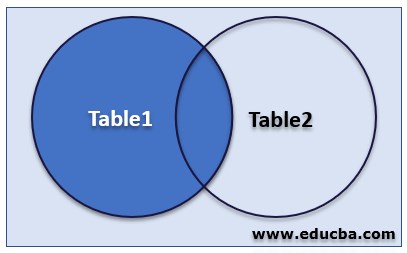
The following diagram shows the virtual representation:
Explanation of the above diagram:
- While joining the table using the left outer join, PostgreSQL first does a normal join and then starts scanning from the left table.
- PostgreSQL left join retrieves all rows from the left table and all matching rows from the right table. If there is no match in both tables, the right tables have null values.
- The above image representation of the left join shows the same as retrieving all rows from table1 and matching rows from table2.
- PostgreSQL left joins two tables and fetches data row based using condition, which matching from both the tables also fetches unmatched rows from the tables before joining clause.
- I suppose the ABC table has a left join with a PQR table with a join condition (We consider ABC as the left table and PQR as the right table).
- PostgreSQL left to join the ABC table depends on the PQR table. Also, all tables depend on ABC, and ABC depends on all tables being used left join condition except table PQR.
- The left join condition will decide how to retrieve rows from the PQR table.
In this case, This PostgreSQL will show below outputs values from ABC and PQR table:
- It will take all the selected values from the ABC table.
- The value will be combined with the column name from the PQR table.
- Retrieves all matching rows from the associated (right table) table.
- Then sets the value for every column from the right table (PQR table) to null, which is unmatched by the ABC table.
- PostgreSQL left join, also known as left outer join. It will fetch all the records from the left table and match records from the right table. If the right table has null values, no matching record will occur.
- PostgreSQL left join selects data from multiple tables in a single query.
- Retrieving data from multiple tables using PostgreSQL left join, we need to have primary key constraints on the first table and foreign key constraints on the second table.
- PostgreSQL left join comes in types of PostgreSQL outer join.
PostgreSQL outer join has three types:
- Left outer join or left join
- Right outer join or right join
- Full outer join.
- In left outer join or left join in PostgreSQL will return all records from table1 and only matching or intersect records from table2.
- PostgreSQL left join or left outer join is used to retrieve all data from one table and match records from the second table.
Examples
Following is the example of a left outer join are as follows. We have used employee and department tables to describe left join in PostgreSQL.
Example #1
Create an Employee and Department table and insert data into it
Code:
CREATE TABLE employee ( emp_id INT NOT NULL, emp_name character(10) NOT NULL, emp_email character(20) NOT NULL, emp_phone character(14), PRIMARY KEY (emp_id));Output:
Code:
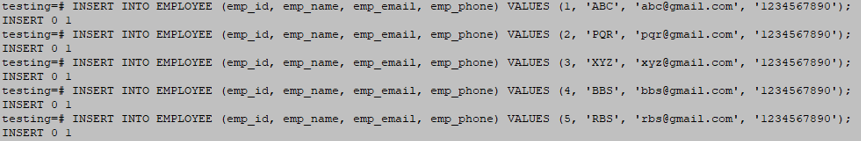
INSERT INTO EMPLOYEE (emp_id, emp_name, emp_email, emp_phone) VALUES (1, 'ABC', '[email protected]', '1234567890');
INSERT INTO EMPLOYEE (emp_id, emp_name, emp_email, emp_phone) VALUES (2, 'PQR', '[email protected]', '1234567890');
INSERT INTO EMPLOYEE (emp_id, emp_name, emp_email, emp_phone) VALUES (3, 'XYZ', '[email protected]', '1234567890');
INSERT INTO EMPLOYEE (emp_id, emp_name, emp_email, emp_phone) VALUES (4, 'BBS', '[email protected]', '1234567890');
INSERT INTO EMPLOYEE (emp_id, emp_name, emp_email, emp_phone) VALUES (5, 'RBS', '[email protected]', '1234567890');Output:
Code:
CREATE TABLE department ( dept_name character(10) NOT NULL, dept_id int NOT NULL, dept_code varchar(10));Output:
Code:
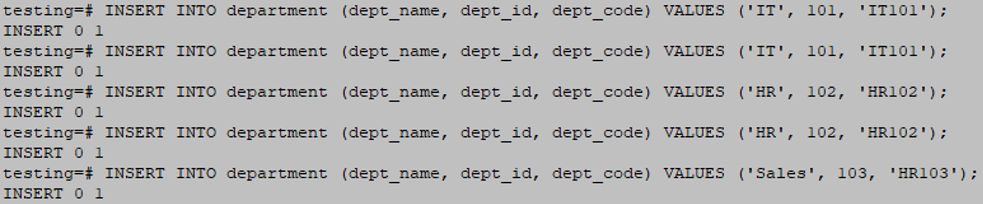
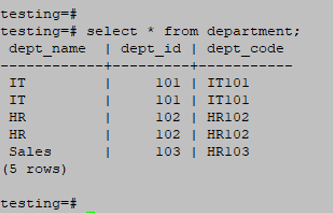
INSERT INTO department (dept_name, dept_id, dept_code) VALUES ('IT', 101, 'IT101');
INSERT INTO department (dept_name, dept_id, dept_code) VALUES ('IT', 101, 'IT101');
INSERT INTO department (dept_name, dept_id, dept_code) VALUES ('HR', 102, 'HR102');
INSERT INTO department (dept_name, dept_id, dept_code) VALUES ('HR', 102, 'HR102');
INSERT INTO department (dept_name, dept_id, dept_code) VALUES ('Sales', 103, 'HR103');Output:
Code:
select * from department;Output:
Example #2
Create a left join between the employee and department table
Code:
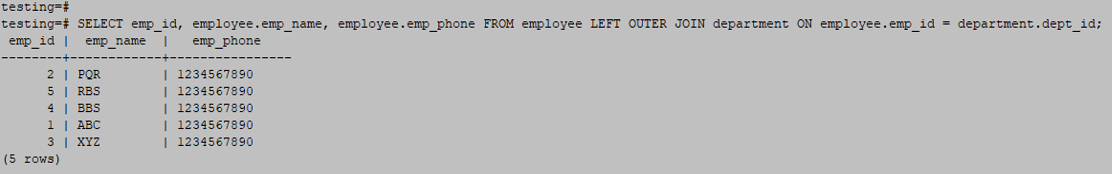
SELECT emp_id, employee.emp_name, employee.emp_phone FROM employee LEFT OUTER JOIN department ON employee.emp_id = department.dept_id;Output:
Code:
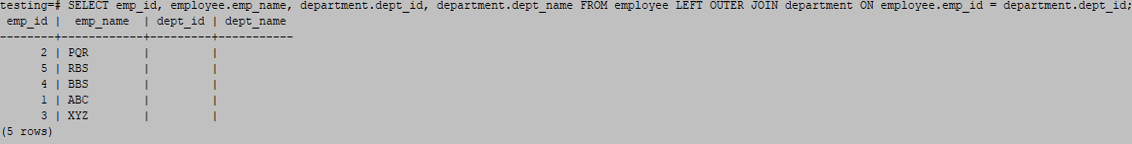
SELECT emp_id, employee.emp_name, department.dept_id, department.dept_name FROM employee LEFT OUTER JOIN department ON employee.emp_id = department.dept_id;Output:
Explanation of the above tables:
- You need to join the employee and department tables from the previous table. The first illustration displays every record from the employee table. In the second example, the employee and department tables have no matching records, displaying an empty set.
- The above example retrieves different outputs from the same table using the same.
- In our example, the employee table has left the table, and the department table is the right table.
- We are joining the table using the employee table as the id column and department tables as the dept_id column.
- The second example of a left join is useful when selecting data from one table and doesn’t have a match from the second table.
Conclusion
A left join is the most important type of join in PostgreSQL. The left join will fetch all rows from the left tables and matching rows from the right table. We need the primary key on the first table for retrieving the data for joining two tables using the left outer join.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “LEFT OUTER JOIN in PostgreSQL” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.