Updated March 27, 2023
Introduction to Kruskal’s Algorithm
It is the algorithm for finding the minimum spanning tree for a graph. This tries to provide a localized optimum solution to a problem that can provide a globally optimized solution to a problem, known as the Greedy approach. In this topic, we are going to learn about Kruskal’s Algorithm here the graph is taken as an input in this algorithm and the output includes one of the subsets of nodes of the graph that has the following features:-
- A tree can be formed that includes every vertex of the graph.
- The sum of weights is minimum among all other possible subsets of the tree.
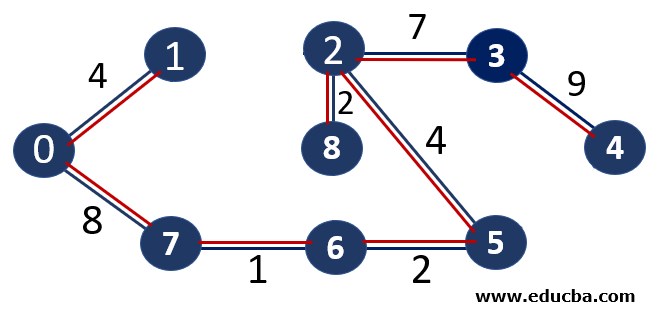
Example of Kruskal’s Algorithm
For better understanding we must understand some below terminologies:-
- Cost of graph: This is the sum of the weights of all the edges in the tree of the graph. This can be used to represent the cost estimated to implement the link between the two vertices.
- Minimum Spanning tree: It is a subgraph or a tree that connects all the graph vertices with the minimum cost possible.
Given, a graph having V vertices and E edges then T is said to be a Minimum spanning tree of that graph if and only if T contains all vertices in V and number of edges in T = n(V) -1 And the sum of weights of the all the edges in the graph is minimum.
KRUSKAL’S ALGORITHM
Below is the algorithm for KRUSKAL’S ALGORITHM:-
1. All the edges of the graph are sorted in non-decreasing order of their weights.
2. Start picking the edges from the above-sorted list one by one and check if it does not satisfy any of below conditions, otherwise, add them to the spanning tree:-
- Including the edge in MST, forms a cycle.
- The number of edges in MST is greater than or equal to V-1, where V is the number of vertices.
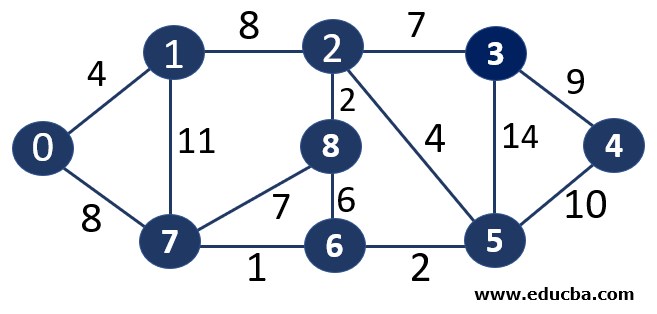
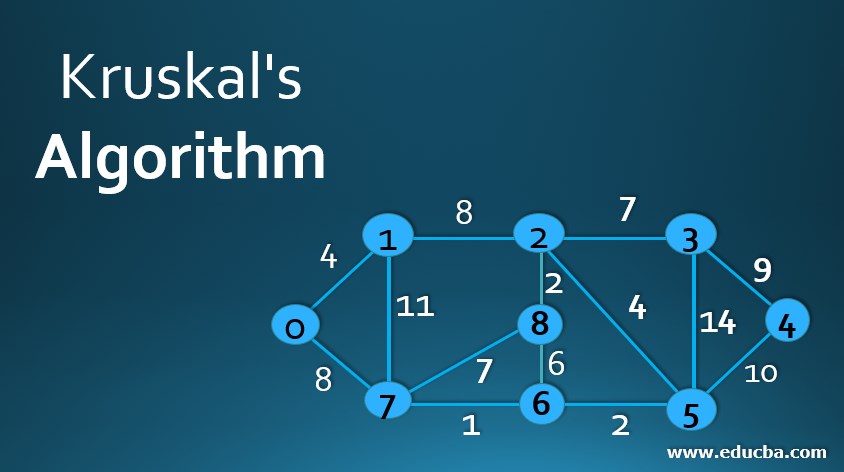
Consider the graph G=(V, E) where V is the set of 9 vertices and E is the set of 14 edges. We need to apply the KRUSKAL algorithm to find the minimum spanning tree out of this graph.
Let’s represent the edges in a table with their respective weights.
| Edge | Weight |
| V0V1 | 4 |
| V0V7 | 8 |
| V1V7 | 11 |
| V1V2 | 8 |
| V7V6 | 1 |
| V7V8 | 7 |
| V2V8 | 2 |
| V8V6 | 6 |
| V2V3 | 7 |
| V6V5 | 2 |
| V5V3 | 14 |
| V2V5 | 4 |
| V3V4 | 9 |
| V5V4 | 10 |
Step 1 – Sort the above edges in non-decreasing order of their weights:-
| Edge | Weight |
| V7V6 | 1 |
| V2V8 | 2 |
| V6V5 | 2 |
| V0V1 | 4 |
| V2V5 | 4 |
| V8V6 | 6 |
| V7V8 | 7 |
| V2V3 | 7 |
| V0V7 | 8 |
| V1V2 | 8 |
| V3V4 | 9 |
| V5V4 | 10 |
| V1V7 | 11 |
| V5V3 | 14 |
Step 2 – We will pick the edges one by one and add it to the spanning tree if it does not result in a cycle.
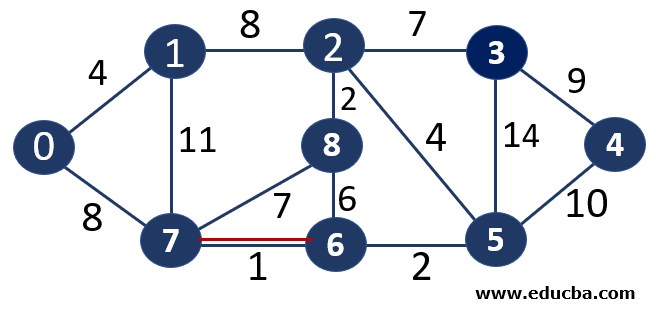
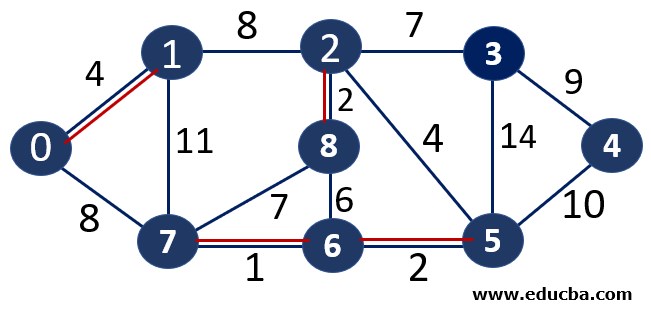
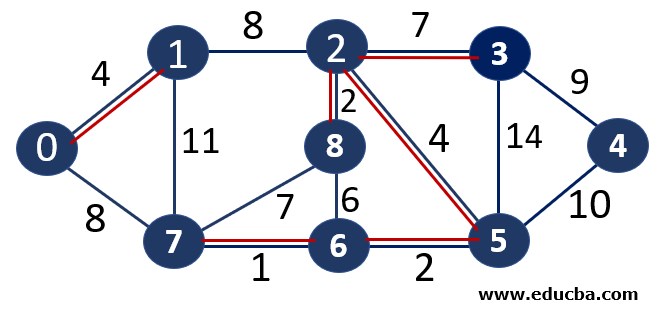
Since edge V7V6 is not forming any cycle, thus can be added to MST.
Thus number of edges is MST = 1 ( < number of vertices-1 i.e 8) and Weight of the edge = 1
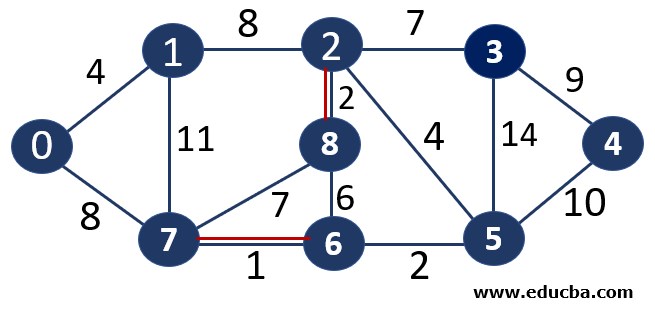
Since edge V2V8 is not forming any cycle, thus can be added to MST.
Thus number of edges is MST = 2 ( < number of vertices-1 i.e 8) and Weight of the edge = 1+2 =3
Since edge V6V5 is not forming any cycle, thus can be added to MST.
Thus number of edges is MST = 3 ( < number of vertices-1 i.e 8) and Weight of the edge = 1+2 +2 =5
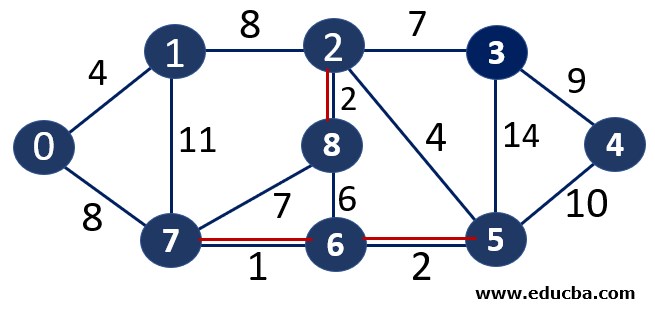
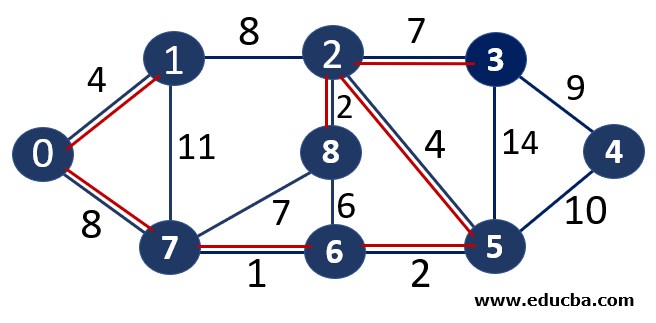
Since edge V0V1 is not forming any cycle, thus can be added to MST.
Thus number of edges is MST = 4 ( < number of vertices-1 i.e 8) and Weight of the edge = 1+2 +2+4=9
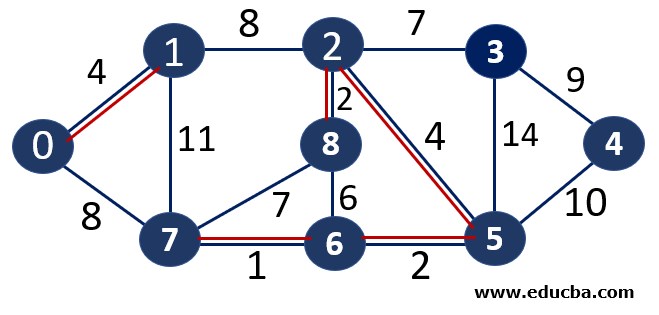
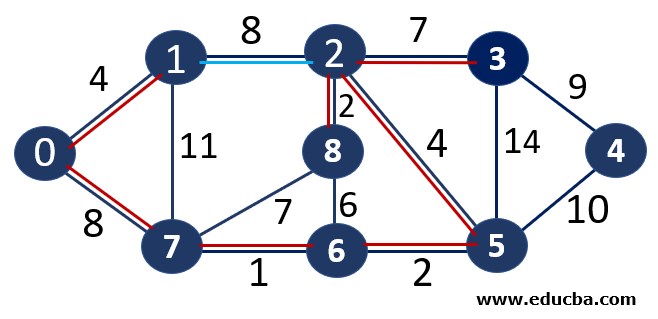
Since edge V2V5 is not forming any cycle, thus can be added to MST.
Thus number of edges is MST = 5 ( < number of vertices-1 i.e 8) and Weight of the edge = 1+2 +2 +4+4 =13
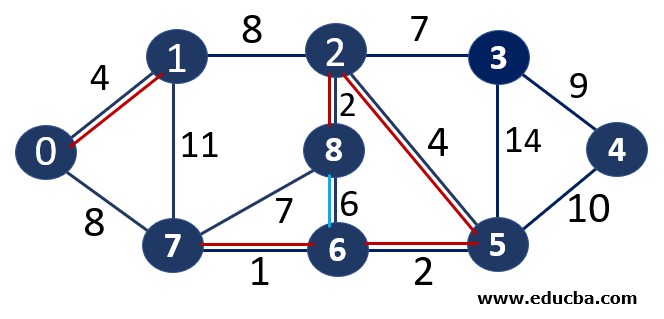
Since edge V8V6 is forming a cycle thus can not be added to MST.
Since edge V8V7 is forming a cycle thus can not be added to MST.
Since edge V2V3 is not forming any cycle, thus can be added to MST.
Thus number of edges is MST = 6 ( < number of vertices-1 i.e 8) and Weight of the edge = 1+2 +2 +4+4+7 =20
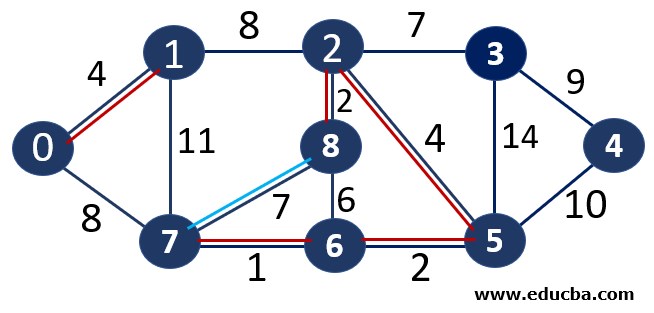
Since edge V0V7 is not forming any cycle, thus can be added to MST.
Thus number of edges is MST = 7 ( < number of vertices-1 i.e 8) and Weight of the edge = 1+2 +2 +4+4+7 +8=28
Since edge V8V7 is forming a cycle thus can not be added to MST.
Since edge V0V7 is not forming any cycle, thus can be added to MST.
Thus number of edges is MST = 6 ( < number of vertices-1 i.e 8) and Weight of the edge = 1+2 +2 +4+4+7 +8 +9= 37
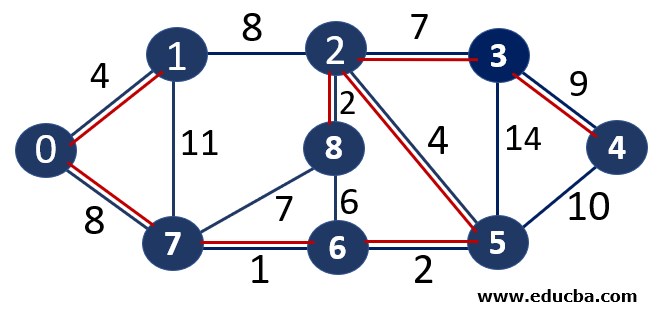
The number OF vertices in MST = 8 Thus one of the stopping conditions have been met. Thus below is our minimum spanning tree.
Weight of the above-spanning tree = 37.
In such a way, one can easily find the minimum spanning tree for a given graph.
Below is the pseudo-code for this algorithm:-
Pseudo Code
KRUSKAL(G,w)
1.A = NULL.
2.for each vertex v in G.V
MAKE-SET(v)
1.Sort the edges G.E into non-decreasing order by weight w.
2.For each edge (u,v) in G.E, taken in non decreasing order
a.If FIND-SET(u) != FIND-SET(v)
A= AU{(u,v)}
UNION(u,v)
3.Return A.
This disjoint set of vertices of a graph is required at most network cable companies to spread their cables across the city within different cities. Thus KRUSKAL algorithm is used to find such a disjoint set of vertices with minimum cost applied.
Conclusion
Kruskal’s Algorithm is one technique to find out minimum spanning tree from a graph, a tree containing all the vertices of the graph and V-1 edges with minimum cost. The complexity of this graph is (VlogE) or (ElogV). The disjoint sets given as output by this algorithm are used in most cable companies to spread the cables across the cities.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Kruskal’s Algorithm. Here we discuss the Examples of Kruskal’s Algorithm along with terminologies and pseudo code. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –