Updated May 6, 2023
Difference Between Kotlin Object vs Class
Kotlin supports both objects and classes in functional applications developed using Kotlin. Object and class is the basic concept in every object-oriented programming language, as we know that kotlin supports object-oriented and functional programming language. While providing support in object-oriented programming, kotlin will support the inheritance, object class, and encapsulation. Object and class are very important in kotlin.
Kotlin is the statistically typed language; kotlin was built into Java to inherit all the object-related Java concepts from Java. In kotlin, class is nothing but the blueprint of the entity that was showing in runtime. The kotlin object is nothing but a state, including state behavior. We declare a class in Kotlin using a class header and body enclosed in curly braces. This same functionality is available in Java. When defining any class in kotlin, we use the class keyword and then need to specify the class name. We need to define a unique class name for the whole project.
Kotlin does not allow duplicate class names within the same project. In kotlin, different classes are available, like nested and inner classes. As we are creating several objects from the same category, also in kotlin, we can create multiple objects by using a single class. After creating the class and objects, we are free to include the members and functions of a class. In kotlin, we can control the visibility of class member variables by using different keywords. Kotlin almost supports the JVM so kotlin will introduce the concept of the object at the top level. In Kotlin, a class describes a structure that can be instantiated as needed, allowing us to create multiple instances. In kotlin, the object will represent a single static instance.
What is Kotlin Object?
This feature is very useful in multiple techniques in packaging and singleton objects. In kotlin, the object is very useful and important for sharing the common properties of the class. To create an object in Kotlin, we use a Kotlin class. The object shares the common properties and behaviors defined by the class through its member functions and data members. We can access the properties and methods of a class by using the (.) operator. The below syntax shows to declare the class object as follows. In the example below, var and val are used to declare the variable used in a kotlin object. By using var and val, we are displaying the specified variable. By using the class, we are creating the object.
Syntax:
var name_of_var = name_of_class()
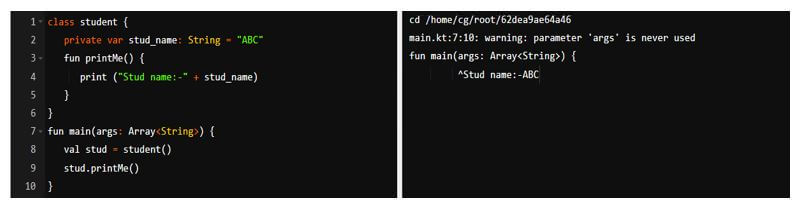
val name_of_var = name_of_class()The below example shows the kotlin object as follows. In the below example, we are creating kotlin and its object from which we are accessing the data from the class.
Example:
class student{
private var stud_name: String = "ABC"
fun printMe (){
print ("Stud name:-" + stud_name)
}
}
fun main(args: Array<String>) {
val stud = student()
stud.printMe ()
}Output:
What is the Class?
The class defines the blueprint for an object, which serves as the template for creating the necessary objects. In kotlin, classes are the building block; a class is defined by using the keyword as a class. The below syntax is showing to create a class in kotlin as follows. The class declaration of kotlin is similar to Java, consisting of the class body and header surrounded by curly braces.
Syntax:
class name_of_class
{
…..
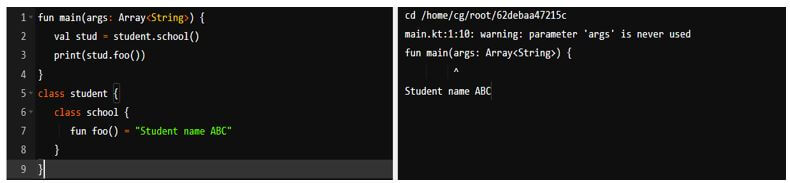
}By default, the classes of kotlin are public. We can control class visibility by using different modifiers. The below example shows Kotlin’s class as follows.
Example:
fun main(args: Array<String>){
val stud = student.school()
print (stud.foo())
}
class student {
class school {
fun foo() = "Student name ABC"
}
}Output:
Head-to-Head Comparison Between Kotlin Object vs Class (Infographics)
Below are the top 11 differences between Kotlin Object vs Class:
Key Difference Between Kotlin Object vs Class
Let’s see the key differences between Kotlin Object vs Class:
- The class in kotlin its object contains similar properties. At the time of class, using kotlin, we need to define some before creating the object. When creating a class, we need to define the class’s name, the class’s header, and the class body. The header and the class body are optional in the class declaration. If suppose nothing into curly braces, then the body of the class is omitted.
- An object is a basic unit of object-oriented programming that will represent the entities in real life that contain the behavior and states. Kotlin object is used to access the member function properties from the class. While using kotlin language, we can create multiple objects from a single class.
- Every class contains its specific name in kotlin. The class header in the kotlin class consists of constructors and parameters of the class. Curly braces surround the body of the class. If suppose we want to provide a class name as a constructor, then we only need to write the constructor keyword just after the name of the class.
- State in kotlin object will represent the object attribute. It was also reflecting the object’s properties. The behavior will represent the object method. It is also reflecting the object’s response to other objects. The object identity will give the unique name of the object which was interacting with another object.
Kotlin Object vs Class Comparison Table
Let’s discuss the top comparison between Kotlin Object vs Class:
| Kotlin Object |
Kotlin Class |
| Kotlin supports the class object while developing the application. | While developing applications, Kotlin supports different types of classes. |
| Kotlin object is similar to the objects in Java. | Kotlin classes are similar to the objects in Java. |
| We can create multiple objects from a single class. | We can create multiple nested classes in a single code. |
| In kotlin, we are using object declaration to create a singleton class. | We are creating multiple objects by using a single class. |
| The object contains only one type in kotlin language. | Kotlin class contains multiple types. |
| Kotlin object contains a single object which was created by the class. | We create the singleton class in kotlin language. |
| Kotlin compiler will translate singleton objects into the class. | Kotlin class is not translated after declaring the same in our code. |
| We can create unique objects in a single class. | For creating the class, we need to define a unique name. |
| We can instantiate the object from a concrete class. | In kotlin, we cannot instantiate the class. |
| We cannot inherit the object by using a class in kotlin. | We can inherit the class from the parent class by using inheritance. |
| An object is a fundamental concept while using kotlin. | Class is a fundamental concept when using kotlin. |
Conclusion
In kotlin, class is nothing but the blueprint of the entity that was showing in runtime. Object and class is the very basic concept in every object-oriented programming language. Kotlin object vs class is supporting in the functional application, which was developed into the kotlin.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “Kotlin Object vs Class” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.