What Are Key Performance Indicators (KPIs)?
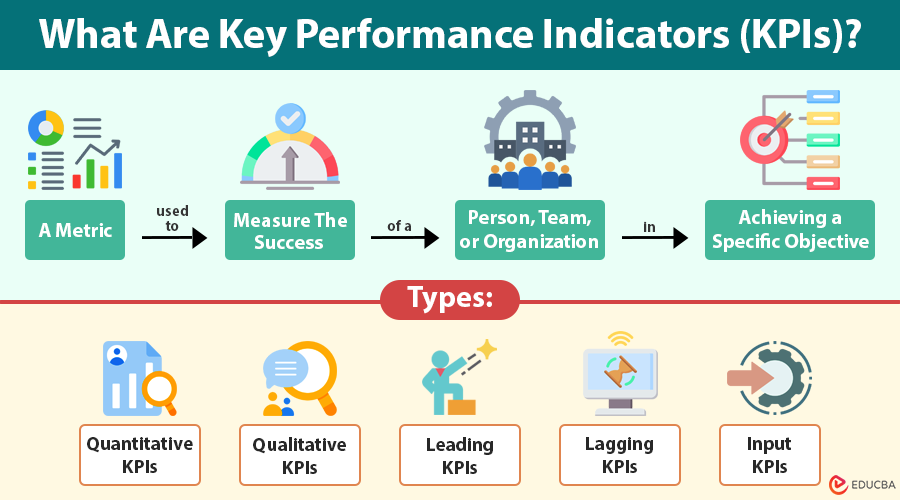
A Key Performance Indicator (KPI) is a metric used to measure the success of a person, team, or organization in achieving a specific objective.
Think of a key performance indicator as the dashboard of your car. Without them, you might keep driving without realizing you are low on fuel, going too fast, or straying off course. KPIs ensure you stay on track toward your strategic destination.
Examples of key performance indicators in real life:
- A retail chain may track daily sales per store.
- A hospital may monitor patient recovery time.
- An HR department may measure employee retention rates.
KPIs are different from simple metrics. Every key performance indicator is a metric, but not every metric qualifies as a KPI. A key performance indicator must be directly tied to a business objective, whereas metrics can be general data points.
Table of Contents
- Meaning
- Why Are KPIs Important?
- Characteristics
- Types of KPIs
- Examples
- How to Develop and Implement KPIs?
- Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Benefits of Using KPIs
- Tools and Software
Why Are KPIs Important?
Organizations without KPIs often operate blindly, relying on assumptions rather than data. Here is why KPIs matter:
- Clarity of direction: KPIs turn abstract goals into tangible targets. Instead of saying “We want to improve customer service,” a KPI makes it measurable: “Achieve a customer satisfaction score of 90% by year-end.”
- Performance monitoring: KPIs help track progress continuously. If a marketing campaign is not generating enough leads, KPIs will flag the issue early.
- Accountability: Employees know what is expected of them when KPIs are clear. For example, a sales manager could be tasked with closing 20 deals every month.
- Resource optimization: KPIs ensure that resources, including time, money, and manpower, are utilized effectively.
- Strategic alignment: KPIs bridge the gap between day-to-day activities and long-term goals. They ensure every effort aligns with the bigger picture.
Characteristics of a Good Key Performance Indicator
Not every measurement qualifies as a key performance indicator. To be meaningful, KPIs should follow the SMART principle:
- Specific: You must clearly define what you are measuring..
- Measurable: Expressed in numbers, percentages, or ratios.
- Achievable: Ambitious yet realistic.
- Relevant: Tied directly to organizational objectives.
- Time-bound: Measured within a defined timeframe.
Example:
Instead of “Improve social media presence”, a SMART KPI would be:
“Increase Instagram follower count by 20% within three months while maintaining engagement above 5%.”
Additional qualities of strong KPIs include:
- Actionable: Provides insights that can trigger corrective measures.
- Simple: Easy to understand for all stakeholders.
- Comparable: Can be benchmarked against industry standards or competitors.
Types of KPIs
KPIs take many forms based on what they measure, how organizations use them, and when they provide insights. Understanding the different types helps organizations select the right mix for balanced performance tracking. Below are the main categories of KPIs:
1. Quantitative KPIs
Organizations express these as numbers, percentages, or ratios. They are straightforward, objective, and easy to track.
- Examples: Monthly revenue, profit margin, website visitors, cost per acquisition (CPA).
- When to use: Ideal for measuring financial performance, sales growth, and operational efficiency.
2. Qualitative KPIs
Unlike quantitative KPIs, these focus on opinions, experiences, or perceptions. They may not always express KPIs in numbers, but KPIs provide valuable context for decision-making.
- Examples: Employee engagement level, customer satisfaction ratings, brand reputation.
- When to use: Helpful in areas like HR, customer service, and brand management where human perception matters.
3. Leading KPIs
Leading KPIs are predictive indicators that give early signals about future performance. Proactive KPIs help businesses make course corrections before outcomes are finalized.
- Examples: Number of qualified leads (predicts future sales), employee training hours (predicts future productivity).
- When to use: Essential for forecasting and strategic planning.
4. Lagging KPIs
Lagging KPIs measure results after they have already occurred. They are outcome-based and confirm whether a strategy has been effective.
- Examples: Quarterly revenue, annual churn rate, customer retention rate.
- When to use: Useful for reporting, historical analysis, and performance reviews.
5. Input KPIs
These measure the resources invested in a process or project. They show what went into achieving a result.
- Examples: Marketing spend, number of employee training sessions, hours worked on a project.
- When to use: Helpful for budgeting, resource allocation, and efficiency tracking.
6. Process KPIs
Process KPIs measure how efficiently and effectively workflows are performing. They highlight bottlenecks and areas for process improvement.
- Examples: Average customer support response time, order fulfillment time, error rate in manufacturing.
- When to use: Best for operations, logistics, and service delivery tracking.
7. Output KPIs
They focus on the results achieved after completing a process. They measure deliverables or outcomes directly.
- Examples: Number of units produced, total number of new customers acquired, and projects completed on time.
- When to use: Effective for assessing productivity and results-driven performance.
8. Directional KPIs
These show whether performance is getting better, worse, or staying the same over time.
- Examples: Month-over-month sales growth, customer satisfaction trends.
- When to use: Good for identifying long-term improvement or decline patterns.
Examples of Key Performance Indicators by Industry
To make this practical, here are industry-specific key performance indicator examples:
1. Healthcare Industry
- Patient wait time: Measures how long patients wait before receiving care.
- Bed occupancy rate: Percentage of hospital beds occupied at a given time.
- Readmission rate: Tracks the number of patients who return for treatment within 30 days of discharge.
- Patient Satisfaction Score (PSS): Surveys to gauge overall patient experience.
2. Retail Industry
- Sales per square foot: Revenue generated per square foot of retail space.
- Inventory turnover ratio: How quickly products are sold and replaced.
- Average Transaction Value (ATV): Average spend per customer transaction.
- Customer retention rate: Percentage of repeat customers over time.
3. Financial Services & Banking
- Net Interest Margin (NIM): Difference between interest earned and interest paid.
- Non-Performing Loan (NPL) Ratio: Percentage of loans that are in default.
- Cost-to-Income Ratio: The ratio of operating costs to income generated.
- Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC): Average cost to gain a new customer.
4. Manufacturing Industry
- Overall Equipment Effectiveness (OEE): Measures the productivity of machines.
- First Pass Yield (FPY): Percentage of products manufactured correctly the first time.
- Production downtime: Hours lost due to equipment or process failures.
- On-time delivery rate: Share of orders delivered on time.
5. Technology & SaaS Industry
- Monthly Recurring Revenue (MRR): Predictable monthly income from subscriptions.
- Churn rate: The proportion of customers who unsubscribe.
- Customer Lifetime Value (CLV): The total amount of money a customer is likely to spend over their relationship with a business.
- Daily Active Users (DAU) / Monthly Active Users (MAU): Tracks user engagement.
How to Develop and Implement KPIs?
A step-by-step roadmap to create effective KPIs:
- Define clear objectives: Determine the exact goals your business, team, or department aims to accomplish.
- Choose relevant KPIs: Select measurable indicators that directly reflect progress toward your objectives.
- Set targets: Establish realistic, time-bound targets for each KPI.
- Collect data: Determine the data sources and tools needed to track each KPI consistently.
- Monitor and analyze: Regularly review key performance indicator data to track performance and identify trends.
- Take action: Use insights from KPIs to make informed decisions and improve processes.
- Review and adjust: Periodically evaluate the KPIs to ensure they remain relevant and adjust targets or metrics if needed.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
Even the best companies sometimes get KPIs wrong. Watch out for:
- Tracking too many KPIs: leads to confusion and diluted focus.
- Using vanity metrics: Instead of business-impact metrics.
- Lack of context: KPIs without benchmarks can be misleading.
- No follow-up actions: Measuring without acting makes KPIs useless.
Benefits of Using KPIs
When done right, KPIs offer massive advantages:
- Clarity: Everyone knows what success looks like.
- Alignment: Ensures employees work toward common goals.
- Efficiency: It pinpoints areas that need process improvement.
- Accountability: Assigns ownership of results.
- Many organizations also integrate employee rewards software with KPI tracking systems to recognize top performers and maintain high engagement levels across teams.
- Competitive edge: Enables quick responses to market changes.
Key Performance Indicator Tools and Software
Tracking KPIs manually can be time-consuming. Fortunately, tools simplify the process:
- Google Analytics: Website and digital marketing KPIs.
- Tableau & Power BI: Data visualization and dashboarding.
- Klipfolio & Databox: Real-time KPI dashboards.
- Salesforce: Sales performance tracking.
- Zoho Analytics: End-to-end business reporting.
Final Thoughts
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) are the backbone of performance management. They transform goals into measurable results, improve accountability, and align day-to-day activities with long-term strategies.
By identifying the right KPIs, regularly tracking them, and avoiding common pitfalls, organizations can stay agile, competitive, and focused.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1. How many KPIs should a company track?
Answer: The optimal number of KPIs depends on the size and complexity of the organization. Focus on a few high-impact KPIs (typically 5–10 per department) rather than tracking dozens, which can dilute focus.
Q2. Should KPIs be the same for every employee?
Answer: No. KPIs should be role-specific to reflect each employee’s contribution to organizational goals. For example, a sales representative and a marketing analyst will have very different KPIs.
Q3. What makes a KPI actionable?
Answer: A KPI is actionable when it provides insight that can influence decision-making or trigger specific actions. For example, tracking customer churn is only valuable if it leads to effective strategies for retaining customers.
Q4. What is the best way to present KPIs to teams?
Answer: Use dashboards, visual charts, and scorecards to make KPIs easy to understand. Tools like Tableau, Power BI, or Google Data Studio help teams quickly track progress and take action.
Q5. How often should KPIs be updated or revised?
Answer: Organizations should review KPIs quarterly or whenever they shift business goals. Outdated KPIs can mislead teams and fail to reflect evolving priorities.
Recommended Articles
We hope this guide to Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) was helpful. Explore our related articles on performance management, business analytics, and effective goal-setting strategies to boost organizational success.
