Updated February 17, 2023
Introduction to JUnit BeforeClass
JUnit beforeclass is used when executing a common operation before every test. In junit java, it is preferable to execute the same before running all the tests by using beforeclass. Therefore, junit beforeclass is annotated by using @BeforeClass. The beforeclass method will run before executing the test from the current class. Junit beforeclass is a critical and valuable annotation in the java framework.
What is JUnit BeforeClass?
- Sometimes we need to share the test computationally. So it will compromise the independent test. Sometimes, it is optimization.
- While annotating the @BeforeClass method with the main method, it will cause the method will run before the test methods in a class.
- The @BeforeClass method runs before the current class or will be shadowed in a current class.
- The beforeclass annotation will indicate that the static method is attached and executed once before all tests into the specified class. For example, it will happen when the share method shares an expensive setup computationally.
JUnit BeforeClass Annotation
- The junit beforeclass annotation is used in junit version 4 and junit version 5. The beforeclass annotation method will execute all the test methods when the test class is executing.
- The beforeclass annotation is used when we need to set up test data or resources at the class level.
- The beforeclass method will be annotated with @BeforeClass or @BeforeAll, executing once per test class.
- As we know that beforeclass annotation will be executed once in class, and the copy of the beforeclass annotation method will be shared across the class. Therefore, the way we are using beforeclass annotation is static.
- If suppose in beforeclass, we are using 5 test cases and annotating the same using @BeforeClass. It will execute the test class once before any TestCase initiates its execution.
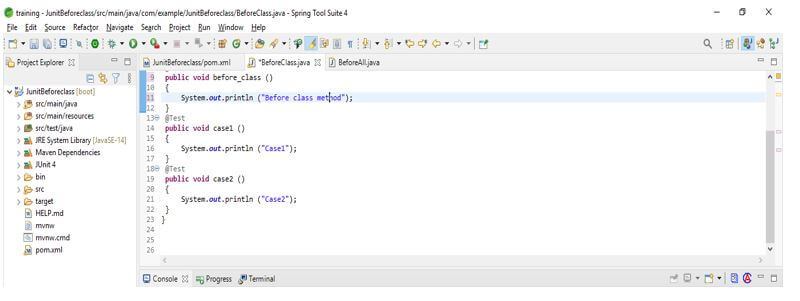
- Below is an example that shows how we are using junit beforeclass annotation in our code. In the below example, we have created a class name as BeforeClass. First, we are creating a name as before_class; we have defined the @BeforeClass method in that method. Also, we are creating two test cases with method names case1 and case2. In both methods, we are using the @Test method annotation.
Code:
public class BeforeClass
{
@BeforeClass
public void before_class ()
{
System.out.println ("Before class method");
}
@Test
public void case1 ()
{
System.out.println ("Case1");
}
Test
public void case2 ()
{
System.out.println ("Case2");
}
}
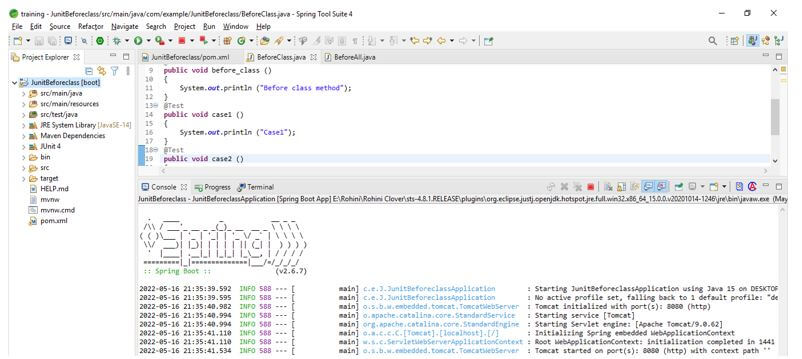
Output:
JUnit BeforeClass Type
- When writing test cases, it is common to find several tests similar to the object created before it runs.
- While annotating the public void method with the beforeclass method will run before the test method.
- The before-class superclass method runs before the class, which was current unless it was overridden as an existing class.
- The beforeclass type method is executed only once in a code. The before annotation is used in a method containing java code running before the test case.
- All the junit method is annotated with the beforeclass method. Junit beforeclass will run before the test class, but it will run as per order.
- When working with beforeclass annotation, it’s possible to run the method once per the entire class before test execution. However, it is time-consuming to open and close the resources in every test after opening servers and communication. It happens by using @BeforeClass annotation.
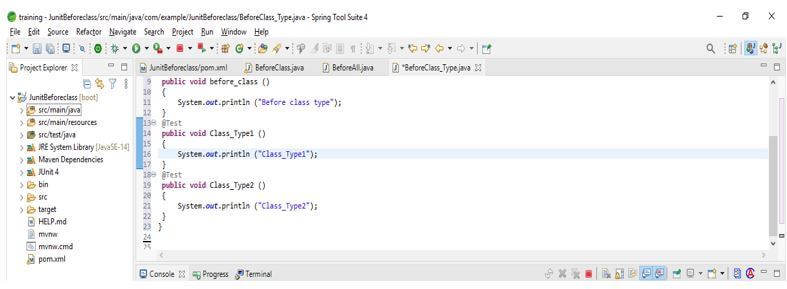
- The below example shows junit beforeclass types as follows. In the below example, we have created a class name as BeforeClass_Type. First, we are creating a name as before_class; we have defined the @BeforeClass method in that method. Also, we are creating two test cases with method names Class_Type1 and Class_Type2. In both methods, we are using the @Test method annotation.
Code:
public class BeforeClass_Type
{
@BeforeAll
public void before_class ()
{
System.out.println ("Before class type");
}
@Test
public void Class_Type1 ()
{
System.out.println ("Class_Type1");
}
@Test
public void Class_Type2 ()
{
System.out.println ("Class_Type2");
}
}
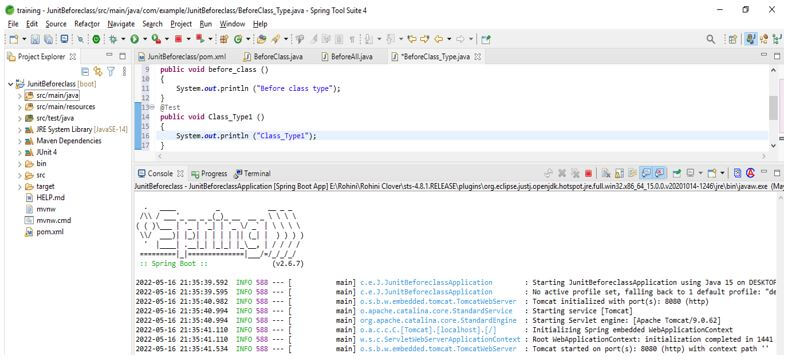
Output:
Examples of JUnit BeforeClass
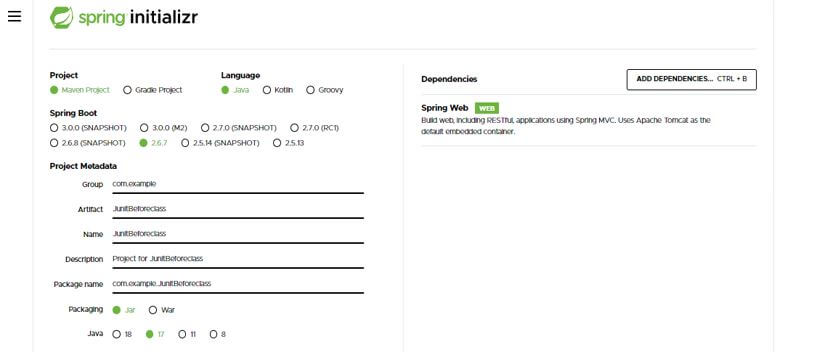
Below are steps shown to create junit beforeclass as follows. We are making the project name as JunitBeforeclass.
In this step, we create the project template of junit JunitBeforeclass in spring boot. We provide the project group name as com. For example, the artifact name is JunitBeforeclass, the project name is JunitBeforeclass, and the selected java version is 11. We are defining the version of spring boot as 2.6.7.
Group – com.example
Artifact name – JunitBeforeclass
Name – JunitBeforeclass
Spring boot – 2.6.7
Project – Maven
Java – 11
Package name – com.example.JunitBeforeclass
Project Description – Project for JunitBeforeclass
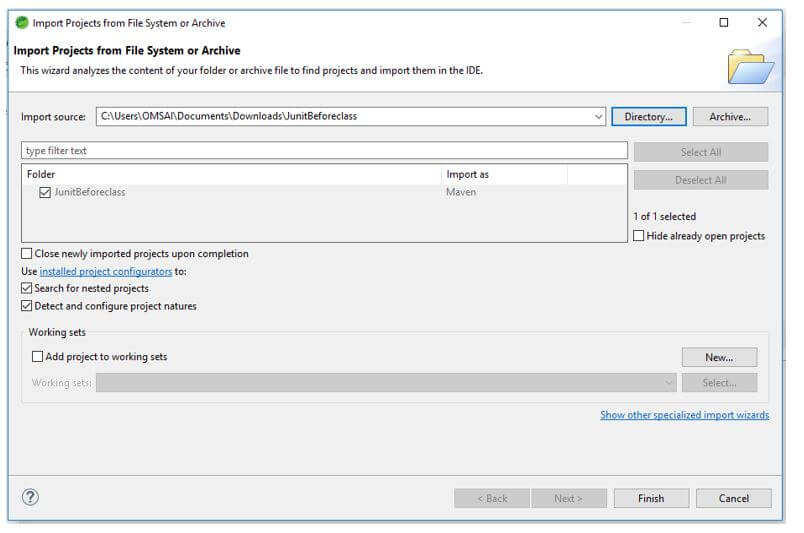
In this step, we extract the downloaded project and open the same by using the spring tool suite.
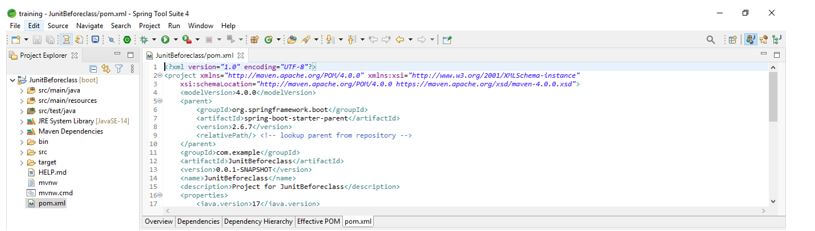
In this step, we check all the project structure and its files. Also, we are checking whether that pom.xml file is created or not. If this file is not created, we need to create the same manually. However, this file is created in the below example, so we do not need to create it manually.
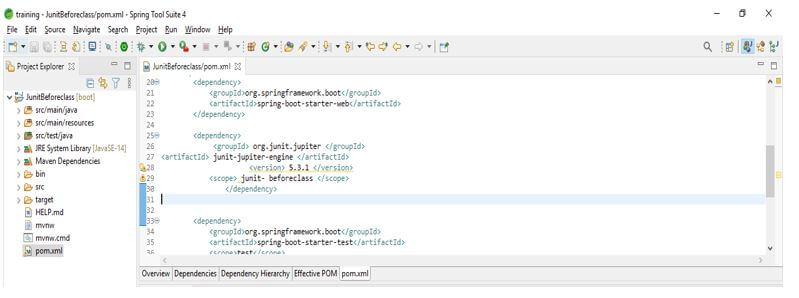
In this step, we add the junit dependency in junit beforeclass; we add the junit dependency as follows.
Code:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.junit.jupiter</groupId>
<artifactId> junit-jupiter-engine </artifactId>
<version> 5.3.1 </version>
<scope>junit- beforeclass </scope>
</dependency>
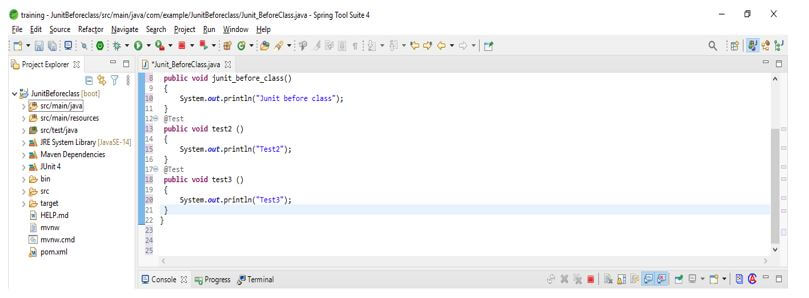
The below example shows junit beforeclass as follows. In the below example, we have created a class name as Junit_BeforeClass. First, we create a name as junit_before_class; in that method, we define the @BeforeClass method. Also, we are creating two test cases with method names test2 and test3. In both methods, we are using the @Test method annotation.
Code:
public class Junit_BeforeClass
{
@BeforeAll
public void junit_before_class ()
{
System.out.println ("Junit before class");
}
@Test
public void test2 ()
{
System.out.println ("Test2");
}
@Test
public void test3 ()
{
System.out.println ("Test3");
}
}
Output:
Conclusion
The @BeforeClass method runs before the current class or will be shadowed in a recent class. It is used when executing a common operation before every test. For example, sometimes, we need to share the test computationally.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to JUnit BeforeClass. Here we discuss the introduction, JUnit BeforeClass annotation, type, and examples. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –