Updated March 29, 2023
Definition of JUnit Assert
It is a method that was used for determining the pass and fail status of the test cases. This method was provided by class name as org.JUnit.Assert which was used to extend the java.lang.Object class. There are multiple types of assertions available in JUnit like null, identical, and Boolean. Basically, JUnit is providing the class name as assert which is providing the methods of assertion.
Overview of JUnit Assert
- Basically, JUnit is providing the class method name as assert which will provide the bunch of assertion methods which was useful in writing the test cases and used to detect the test.
- It is the utility used for supporting the assert condition in a test. All the methods are accessible through the class of assert. The class of assert is accessible in the version of JUnit4 and assertions are accessible in JUnit5.
- To increase the readability of the test and assertions we are using JUnit. We need to import the respective class statistically.
Using JUnit Assert
- In the version of JUnit4, the library of assertions will be available for all primitive data types. Arrays and objects are available in JUnit4 assertions.
- The order of parameters within the assertion is the value expected and followed by the actual value. The first parameter optional message is which represents the output of the message.
- We can say that assert is the API of JUnit or function of the library on which we can verify if a particular condition or logic will return either true or false at the time of execution of the test. If suppose the value will return false, then the error of assertion will throw.
- It is an important feature that was used to do good unit testing. We can say that it helps us for validating the actual output with the expected output for a specified test case that we have defined in the application.
- Writing the JUnit assert is a very effective and fast way to fix and detect bugs. It will give us confidence that our assumptions on a particular condition are right.
- Many times assertion will work as a precondition of a function call or it also works in the condition. The JUnit 4 and JUnit 5 will contain different classes which contain different methods.
- JUnit 4 will contain all assert methods within the class of assert while JUnit 5 contains all assert methods within the assertion class.
- The package of JUnit 5 is imported by using org.JUnit.jupiter.api.assertions and the package of JUnit 4 is imported by using org.JUnit.assert.
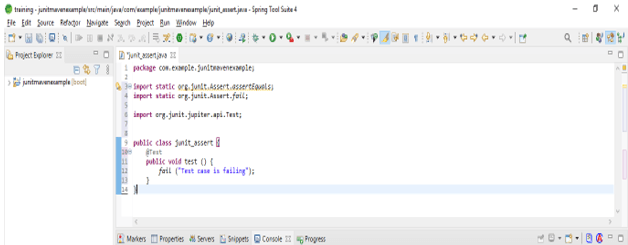
In the below example, we are using the JUnit 4 assert class. In the below example we are using the @Test method to test the classes. In the below example we are using JUnit 4 assert so we are using package name as org.JUnit.assert.
Code –
public class JUnit_assert {
@Test
public void test () {
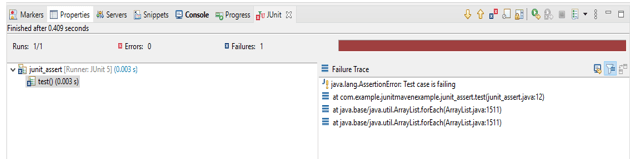
fail ("Test case is failing");
}
}JUnit Assert Methods
- This class provides a number of assertion methods, which are useful for writing the test cases. We are recording only failed assertions by using this method. In JUnit, all the assertions contain the assert class.
- At the time of testing applications by using assert methods we are using the fail method to test the application.
Below are the method available as follows.
- Void assertEquals – This method is used to check whether the two objects are equal or not. This method contains the actual and expected boolean object.
- Void assertTrue – This method is used to check the true condition. This method contains the boolean condition object.
- Void assertFalse – This method is used to check the false condition. This method contains the boolean condition object.
- Void assertNotNull – This method is used to check the object is not null. This method contains the object condition.
- Void assertNull – This method is used to check the object is null. This method contains the object condition.
- Void assertSame – This method will test the two object references which point to the same object. This method contains two objects.
- Void assertNotSame – This method will test the two object reference which is not pointing to the same object. This method contains two objects.
- Void assertArrayEquals – This method is used to check whether our two arrays is equal to each other or not. This method contains the actual and expected array object.
JUnit assert Example
- The below example shows JUnit’s assert example as follows. We are creating the project name as JUnit_assert.
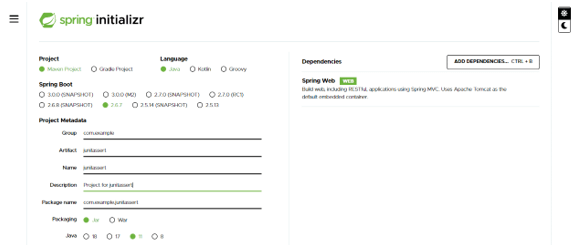
- In this step, we are creating the project template in spring boot. We have provided project group name as com. example, artifact name as JUnitassert, project name as JUnitassert, and selected java version as 11. We are defining the version of spring boot as 2.6.7.
Group – com.example Artifact name – JUnitassert
Name – JUnitassert Spring boot – 2.6.7
Project – Maven Java – 11
Package name – com.example. JUnitassert
Project Description – Project for JUnitassert
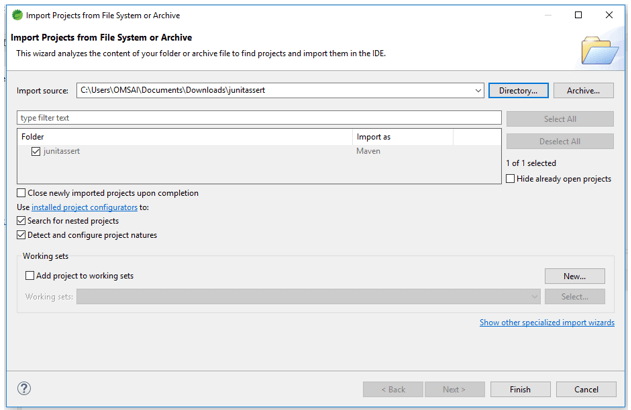
- In this step, we are extracting the downloaded project and opening the same by using the spring tool suite.
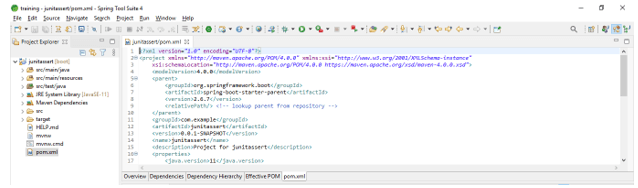
- In this step, we are checking all project structures and their files are as follows. Also, we are checking whether that pom.xml file is created or not.
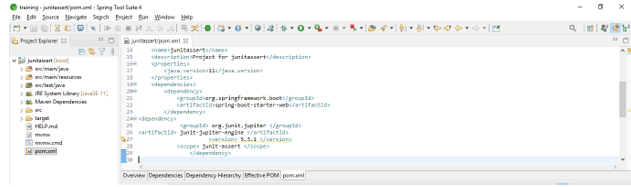
- Add the JUnit dependency in JUnit assert project. We are adding JUnit dependency as follows.
Code:
<dependency>
<groupId> org.JUnit.jupiter </groupId>
<artifactId> JUnit-jupiter-engine </artifactId>
<version> 5.3.1 </version>
<scope> JUnit-assert </scope>
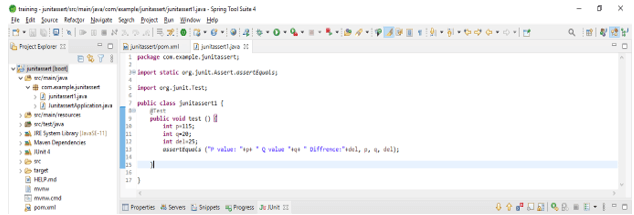
</dependency>- The below example shows the equal method as follows.
Code:
public class JUnitassert1 {
@Test
public void test () {
int p=115;
int q=20;
int del=25;
assertEquals ("P value: "+p+ " Q value "+q+ " Difference:"+del, p, q, del);
}
}
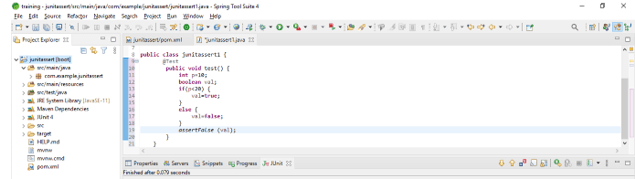
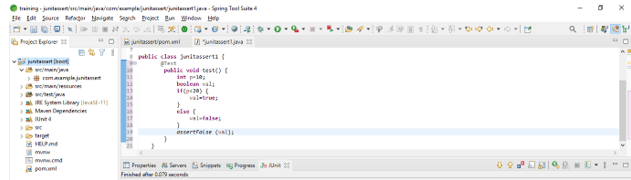
- The below example shows the false method as follows.
Code:
public class JUnitassert1 {
@Test
public void test() {
int p=10;
boolean val;
if(p<20) {
val=true;
}
else {
val=false;
}
assertFalse (val);
}
}
Conclusion
It is the utility used for supporting the assert condition in a test. All the methods are accessible through the class of assert. This is a method that was provided by class name as org.JUnit.Assert which was used to extend the java.lang.Object class.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to JUnit Assert. Here we discuss the Definition, overviews, how to use, methods, and examples with code implementation. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –