Updated February 15, 2023
Definition of JUnit 5 Parameterized Tests
Junit 5 parameterized tests are used to run the test multiple times by using different arguments. Sometimes in junit, we may need to run a test using different arguments and values; junit 5 parameterize tests will make it simple to run the test multiple times using different arguments. Therefore, we can declare this test the same as a standard test method like @Test, but we need to use @ParameterizedTest instead of @Test annotation.
Overview JUnit 5 Parameterized Tests
- We need to use the @ParameterizedTest annotation to execute the test multiple times and use different arguments. However, we do not need to use @Test annotation; instead of using @Test annotation, we are using @ParameterizedTest annotation.
- We need to declare the one argument source that will provide the arguments for the innovation, which will be consumed as a test method.
- Junit 5 parameterized test will make it possible to run the same tests multiple times using different arguments. Using the junit five parameterized test, we can easily verify the condition without writing any test case.
Argument of JUnit 5 Parameterized Tests
- As we know that we are running multiple tests by using the parameterized test. In the following way, we are providing arguments for the test.
- @ValueSource
- @EnumSource
- @MethodSource
- @CsvSource
- @CsvFileSource
- @ArgumentsSource
- The below steps show junit 5 parameterized test arguments as follows. We are creating the project name as Junit5Parameterized.
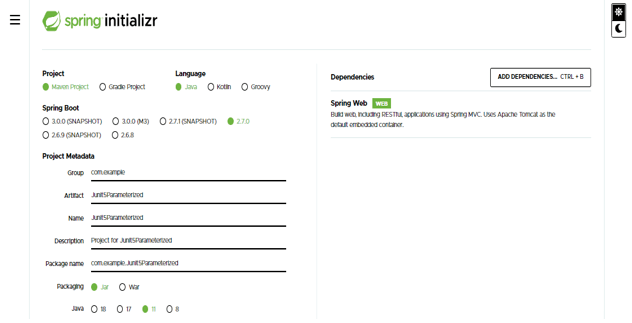
- In this step, we are creating the project template of the junit 5 parameterized test in spring boot. We are providing the project group name as com.example, artifact name as Junit5Parameterized, project name as Junit5Parameterized, and selected java version as 11. We are defining the version of spring boot as 2.7.0.
Group – com.example Artifact name – Junit5Parameterized
Name – Junit5Parameterized Spring boot – 2.7.0
Project – Maven Java – 11
Package name – com.example. Junit5Parameterized
Project Description – Project for Junit5Parameterized
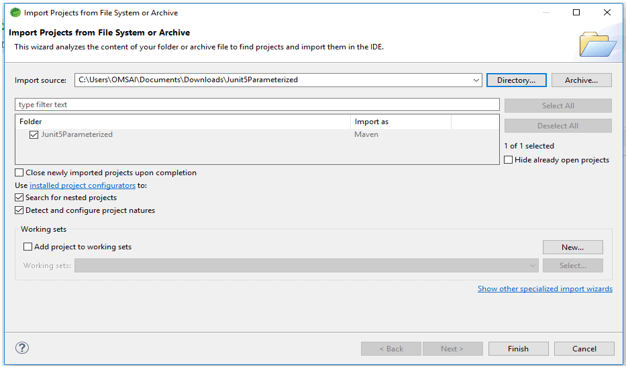
- In this step, we extract the downloaded project and open the same by using the spring tool suite.
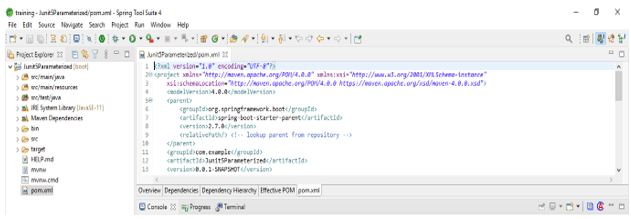
- In this step, we check the project structure and files. Also, we are checking whether that pom.xml file is created or not. If suppose this file is not created, we need to create the same manually. However, this file is created in the example below, so we do not need to create it manually.
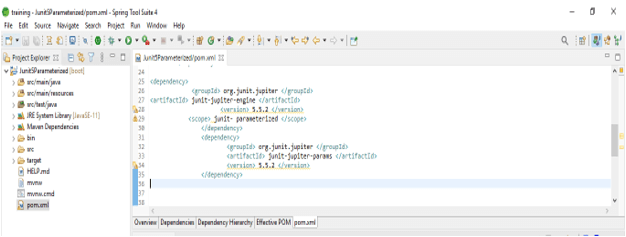
- In this step, we add the junit dependency in the junit 5 parameterized test example. We are adding junit dependency.
Code –
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId> org.junit.jupiter </groupId>
<artifactId> junit-jupiter-engine </artifactId>
<version> 5.5.2 </version>
<scope> junit- parameterized </scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId> org.junit.jupiter </groupId>
<artifactId> junit-jupiter-params </artifactId>
<version> 5.5.2 </version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>- After adding a dependency in the below example, we see that use of each parameter in junit 5 is as follows.
1. @ValueSource
This parameter is used with a single argument list. In the example below, we are using the same in a single parameter list.
Code:
public class ValueSource {
@ParameterizedTest
@ValueSource (int = {11, 21, 31})
void arr (int val) {
assertTrue (val > 0);
}
private void assertTrue(boolean b) {
}
}2. @EnumSource
It will be used to run the test, which was used to take an enum as an argument. The below example shows @EnumSource annotation as follows.
Code:
public class EnumSource
{
@ParameterizedTest
@EnumSource (Size.class)
void enum (Size size) {
assertNotNull (size);
}
}3. @MethodSource
It will be used to run the test, making the static method generate the argument.
Code –
public class MethodSource {
@ParameterizedTest (name = "String method")
@MethodSource ("string")
void method (String method)
{
assertNotNull (method);
}
static Stream string() {
return Stream.of ("junit", "parameterized");
}
}4. @CsvSource
This annotation is used to run the tests, which were used to take the comma-separated value as an argument.
Code –
public class CsvSource {
@ParameterizedTest
@CsvSource ({
"Junit, 41",
"java, 71",
"python, 61"
})
void csv (String str, int len) {
assertEquals (len, str.length ());
}
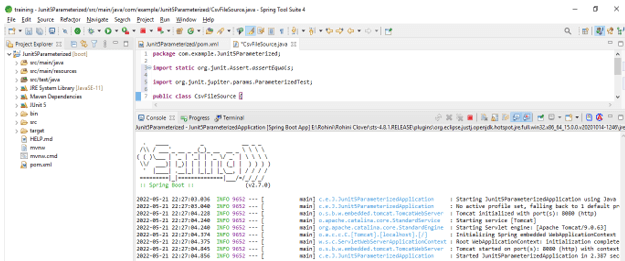
}5. @CsvFileSource
This parameter is used to import the comma-separated values from the file as an argument. The below example shows @CsvFileSource as follows.
Code –
public class CsvFileSource {
@ParameterizedTest
void csvfile (String str, int length) {
assertEquals (length, str.length());
}
}
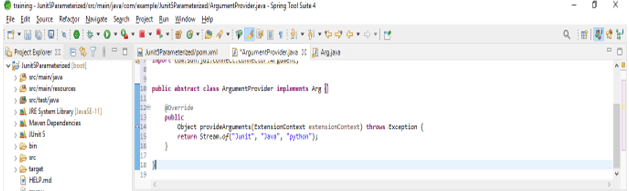
6. @ArgumentsSource
This argument is used to create the argument provider, reusable as follows. The below example shows the argument source.
Code –
public abstract class ArgumentProvider implements Arg {
@Override
public Object provideArguments (ExtensionContext extensionContext) throws Exception {
return Stream.of("Junit", "Java", "python");
}
}Junit 5 tests multiple arguments
- While using the junit 5 multiple arguments, we need to import the junit Jupiter params dependency.
- In junit 5 introduced a new feature named the parameterized test. This will allow the user to run the same test repeatedly using different values. We must follow five tests while creating parameterized tests using multiple arguments.
- Need to annotate class of test by using @RunWith
- We need to create a public static method that was annotated with @Parameters which will return the collection of objects for the test data set.
- We must create the public constructor equivalent to the row’s test data.
- We need to create an instance variable for each column.
- We need to create a test case for the variable of instance for the source data test.
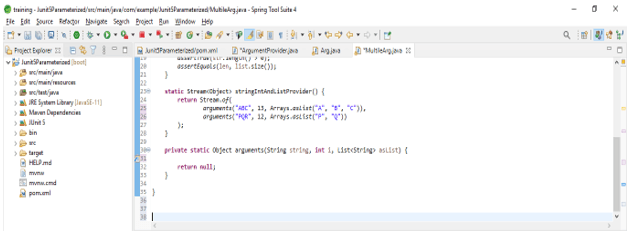
- The below example shows junit 5 tests with multiple arguments as follows. We are using the @MethodSource argument to define the junit 5 multiple arguments.
Code –
public class MultileArg {
@ParameterizedTest
@MethodSource ("multiple arg")
void multiple (String str, int len, List<String> list) {
assertTrue (str.length() > 0);
assertEquals (len, list.size ());
}
static Stream<Object> stringIntAndListProvider () {
return Stream.of (
arguments ("ABC", 13, Arrays.asList ("A", "B", "C")),
arguments ("PQR", 12, Arrays.asList ("P", "Q"))
);
}
Conclusion
We need to use @ParameterizedTest annotation to execute tests multiple times and use different arguments. We do not need to use @Test annotation; instead of using @Test annotation, we are using @ParameterizedTest annotation. Junit 5 parameterized tests are used to run the test multiple times by using different arguments.
Recommended Article
This is a guide to JUnit 5 Parameterized Tests. Here we discuss the Definition, overview, arguments, introduction, and examples with code implementation. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –