Updated February 20, 2023
Introduction to JUnit 5 Parameterized Test
JUnit 5 parameterized tests are one of these features of JUnit; we can use this functionality to run the same test method numerous times with varied settings. JUnit 5, the next version of JUnit, adds a slew of new capabilities to make developing developer tests easier. The JUnit Platform is a foundation for testing frameworks to run on the JVM; It will also define the Test Engine API, which can be used to create a platform-based testing framework. The platform also includes a Console Launcher for starting the platform from the command line of the platform’s test engines.
Overview of JUnit 5 Parameterized Test
- Popular IDEs also provide first-class support for the JUnit Platform. For example, in JUnit 5, JUnit Jupiter combines the new programming paradigm with the extension concept for test writing and extensions.
- The Jupiter sub-project provides a Test Engine for performing Jupiter-based tests on the platform.
- JUnit Vintage comes with a Test Engine that allows us to run JUnit 3, and JUnit 4 tests must be installed on the classpath or module path.
- We must first guarantee on the classpath before we can build parameterized tests with JUnit 5.
- We don’t need to do anything if we use the JUnit-Jupiter aggregator artifact because all of the essential dependencies are already added to the classpath.
- JUnit 5, Jupiter Parameterized tests allow us to run the same test numerous times with various parameters. They are declared similarly to conventional @Test methods, except instead of using the @Test annotation, they use the @ParameterizedTest annotation.
- Parameterized tests allow us to run the same test with various parameters numerous times. We can rapidly validate various situations without having to write a test for each one. We can create a data source in a parameterized test.
- We’ll also need to declare a test argument source. These argument sources are annotated with various argument source annotations.
- In JUnit 5, parameterized tests allow us to execute a test many times with varied parameters. It saves time for developers when writing and running tests. We can construct parameterized JUnit 5 tests the same way we do standard JUnit 5 tests.
- JUnit 5 parameterized test is used to test the application values by using JUnit. It is a very important tool to test our application.
JUnit 5 Parameterized Test Create a Class
The below example shows create a class for the JUnit 5 parameterized test class is as follows.
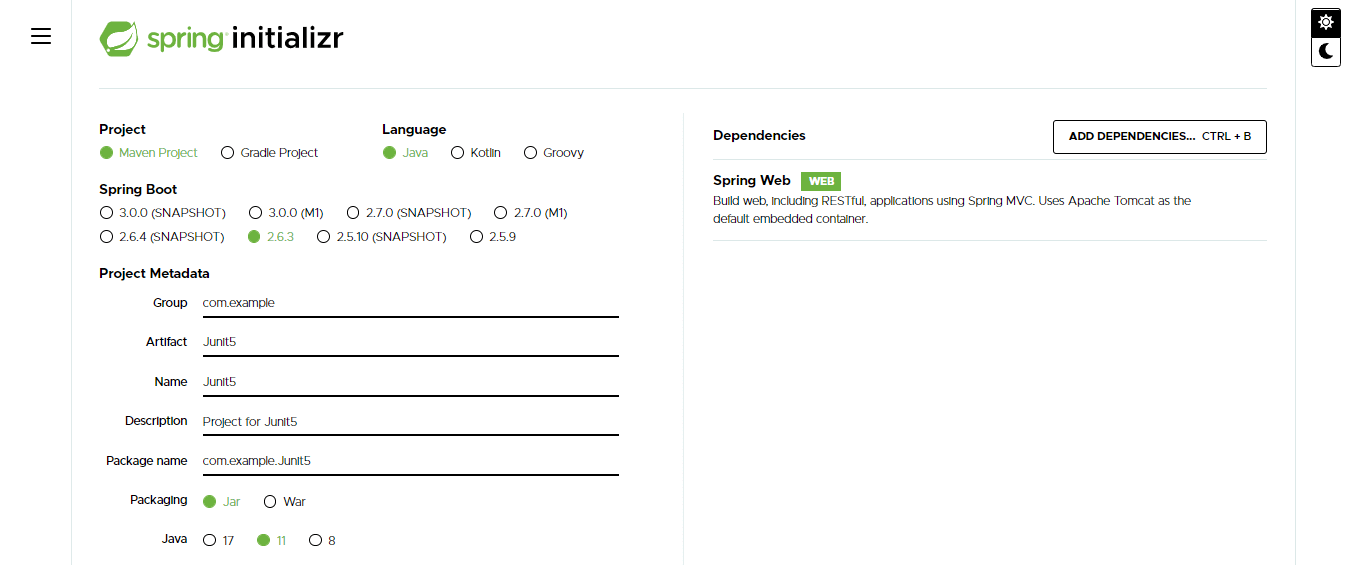
1. In the first step, we are creating a spring tool suite project template to create a JUnit 5 parameterized test class.
In this step, we have provided project group name as com.example, artifact name as JUnit5, project name as JUnit5, and selected java version as 8. Also, we have defined the spring boot version as 2.6.3; We are creating a project in maven.
We have selected spring web dependency in the below project to create a class.
Group – com.example Artifact name – JUnit5
Name – JUnit5 Spring boot – 2.6.3
Project – Maven Java – 8
Package name – com.example. JUnit5
Project Description – Project for JUnit5
Dependencies – spring web, PostgreSQL driver.
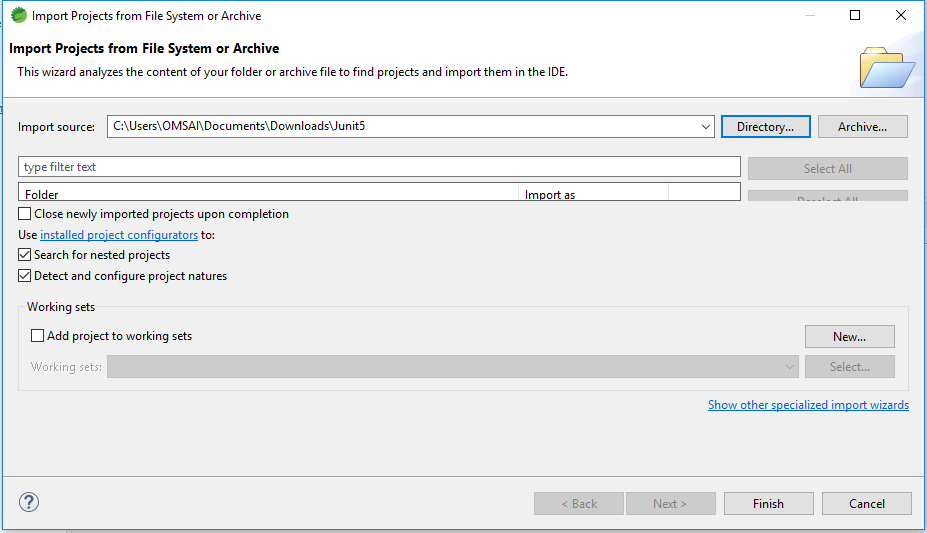
2. In a second step, we are opening the JUnit5 project by using the spring tool suite.
After generating the project using the spring initializer, we are opening the JUnit5 project using the spring tool suite.
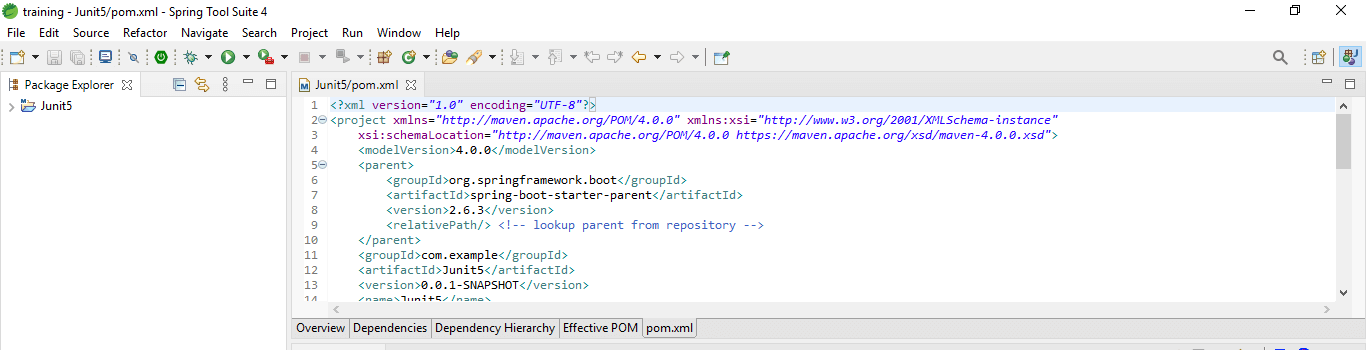
3. Check the dependency packages of a project by using the pom.xml file.
In this step, we are checking all the dependencies of packages by using the pom.xml file.
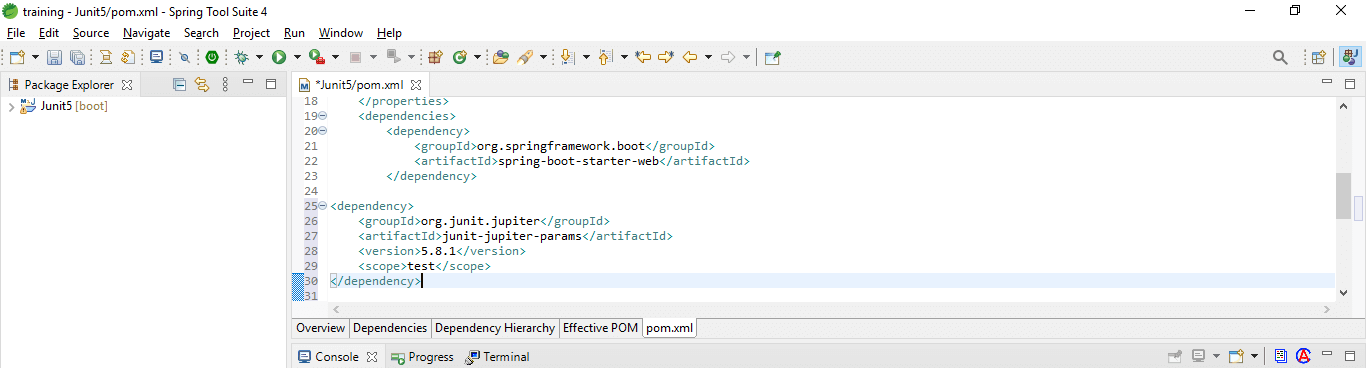
4. Add dependency packages
In this step, we are adding the JUnit 5 dependency package in the pom.xml file.
Code:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.JUnit.jupiter</groupId>
<artifactId>JUnit-jupiter-params</artifactId>
<version>5.8.1</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>5. Check created class file
In this step, we are checking the class file is created in a project which was we have imported.
JUnit 5 Parameterized Test Argument Sources
As we all know, a parameterized test runs the same test numerous times with various parameters.
Below are the argument sources are as follows.
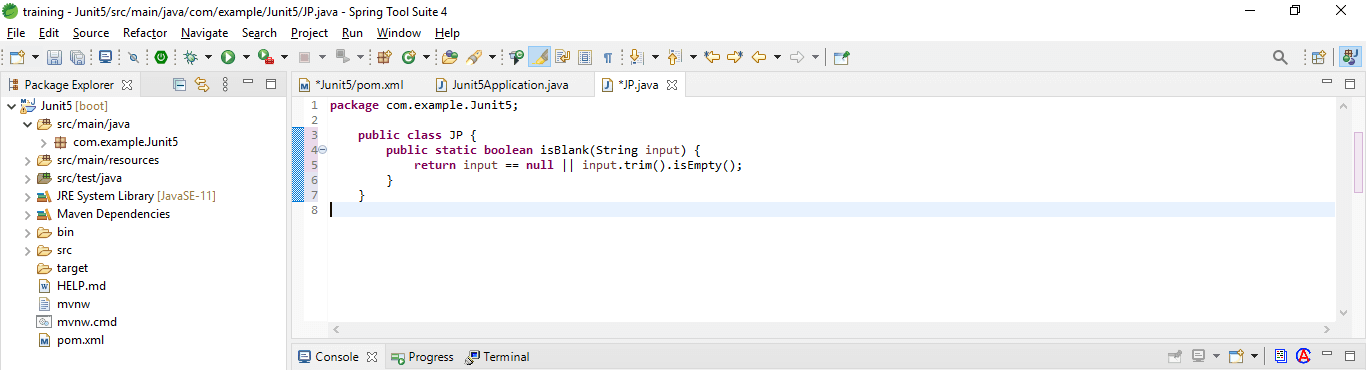
1. Simple values –
We are passing literal values to the method using the @ValueSource annotation.
Code:
public class JP {
return input == null || input.trim ().isEmpty ();
}
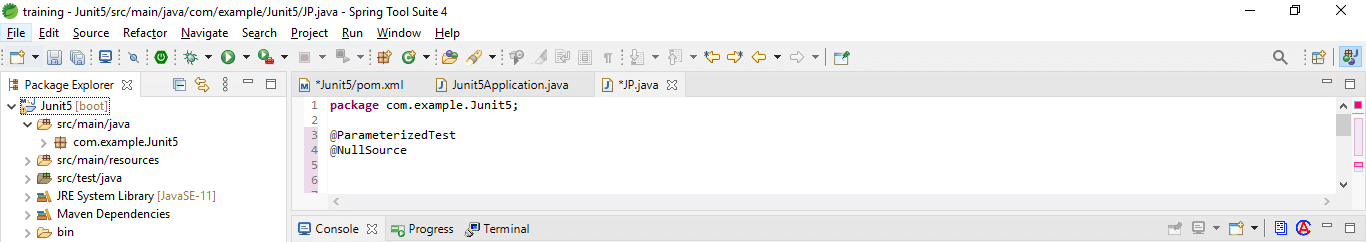
}2. Null and empty values –
In the below example, we are passing single null values to the parameterized test method.
Code:
@ParameterizedTest
@NullSource
void isBlank_ShouldReturnTrueForNullInputs(String input)
{
assertTrue (Strings.isBlank(input));
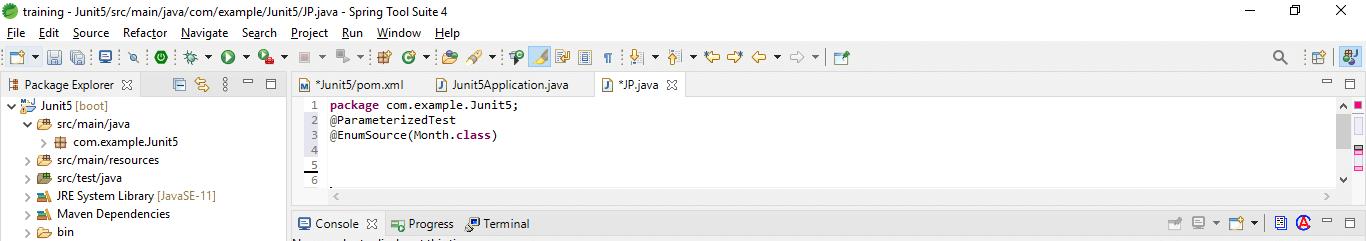
}3. Enum –
We are using the annotation of @EnumSource to run a test with different enumeration values.
Code:
@ParameterizedTest
@EnumSource (Month.class)
void getValueForAMonth_IsAlwaysBetweenOneAndTwelve(Month month) {
int monthNumber = month.getValue ();
assertTrue (monthNumber >= 1 && monthNumber <= 12);
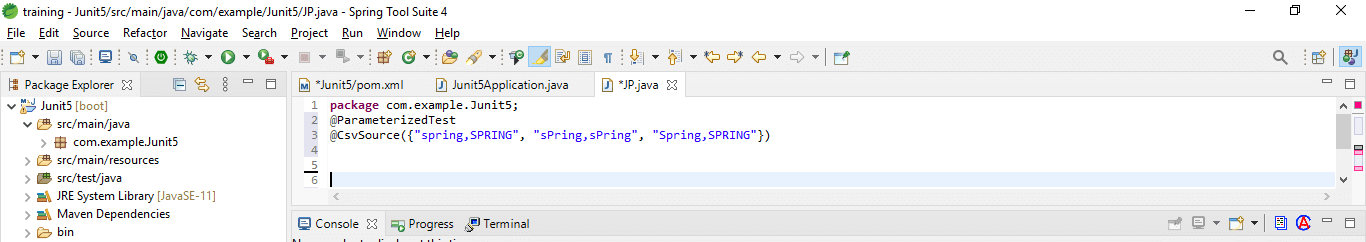
}4. CSV literals –
Assume we want to verify that the String’s toUpperCase method returns the expected uppercase result. @ValueSource will not suffice.
Code:
@ParameterizedTest
@CsvSource ({"spring,SPRING", "sPring,sPring", "Spring,SPRING"})
void toUpperCase_ShouldGenerateTheExpectedUppercaseValue (String input, String expected) {
String actualValue = input.toUpperCase ();
assertEquals (expected, actualValue);
}CSV Files and Method
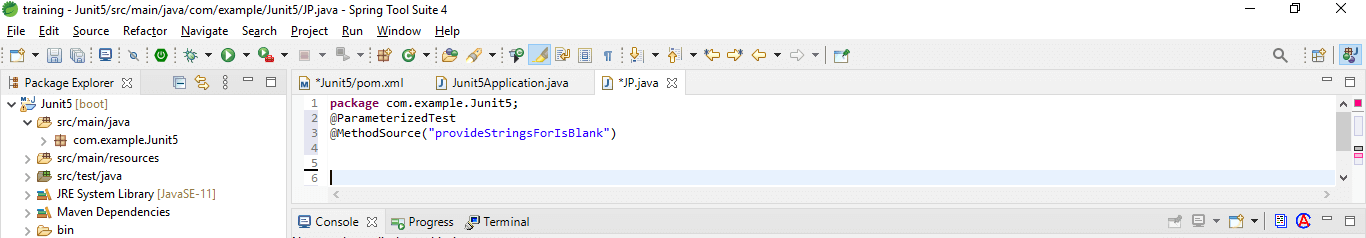
1. Method
Using the source of argument method is one option for delivering more complicated arguments.
Code:
@ParameterizedTest
@MethodSource ("provideStringsForIsBlank")
void isBlank_ShouldReturnTrueForNullOrBlankStrings (String input, boolean expected)
{
assertEquals (expected, Strings.isBlank(input));
}2. CSV files
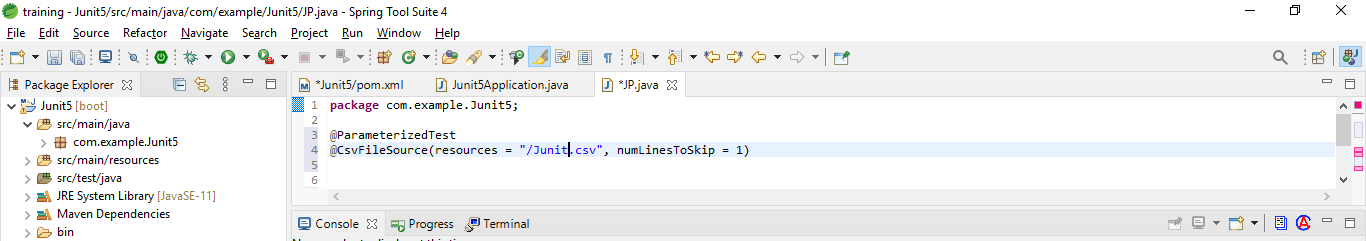
We can refer to an actual CSV file rather than sending values of CSV into code.
Code:
@ParameterizedTest
@CsvFileSource (resources = "https://cdn.educba.com/JUnit.csv", numLinesToSkip = 1)
void toUpperCase_ShouldGenerateTheExpectedUppercaseValueCSVFile (
String input, String expected) {
String actualValue = input.toUpperCase ();
assertEquals (expected, actualValue);
}JUnit 5 parameterized Test Data
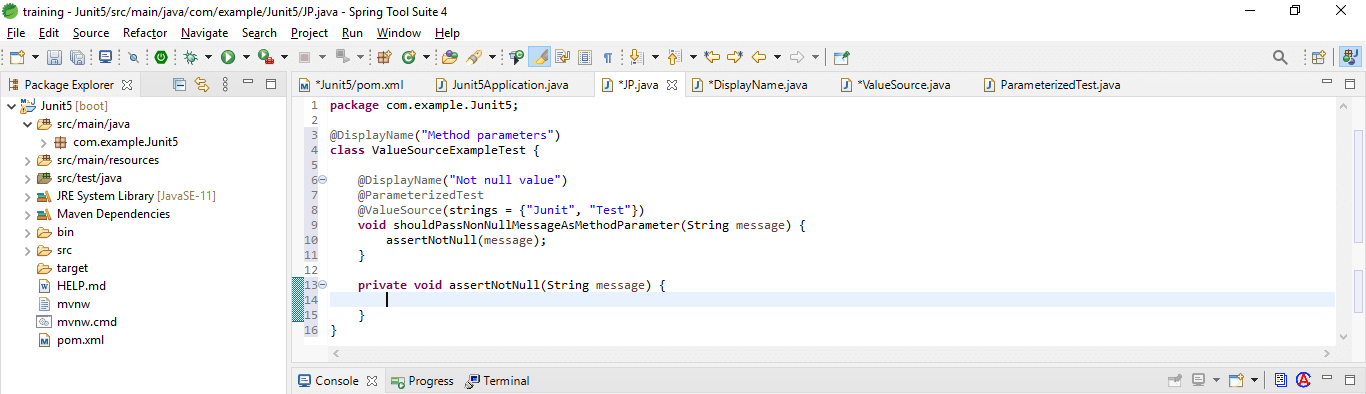
Below is the example are as follows.
Code:
@DisplayName ("Method parameters")
class ValueSourceExampleTest {
@DisplayName ("Not null value")
@ParameterizedTest
@ValueSource(strings = {"JUnit", "Test"})
void shouldPassNonNullMessageAsMethodParameter (String message) {
assertNotNull (message);
}
private void assertNotNull(String message) {
}
}Run the application by using the JUnit test.
Conclusion
In JUnit 5, parameterized tests allow us to execute a test many times with varied parameters. They are one of these features of JUnit; we can use this functionality to run the same test method numerous times with various settings.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to the JUnit 5 Parameterized Test. Here we discuss the definition, overview, and how to create a class along with CSV files and methods. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –