Updated July 5, 2023
Introduction to JQuery Progress Bar
JQuery progress bar is a user interface feature specifically for jQuery that is used as an indicator for the status or completion level of the processes. There are two types of jQuery progress bar forms, namely ‘determinate progress bar’ and ‘indeterminate progress bar’, which can be functional using three different parameter options disabled, max, and value. A few of the actions performed in the jQuery progress bar are enable, disable, destroy, option, option (option), option (options), value, option (option, value) & widget. The corresponding events are create (event, ui), complete (event, ui) & change (event, ui).
We can show the progress bar in two forms, such as the “determinate progress bar” and “indeterminate progress bar”.
- Determinate progress bar- Determinate progress bar we use in a scenario where we can show the task’s exact progress or status. For example, the numbers of files send the percentage of the data copy, the percentage of the file download, etc. The Determinate progress bar can show progress in the form number percentage, like 54%, or the line filled the form from left to right.
- We use the indeterminate progress bar in a scenario where the task’s exact progress or status is unknown or can not be determined. For example, we cannot determine progress when the request to connect the server proceeds.
Syntax of the progressbar() method
You can use the progressbar() method in two forms.
- $(element, cont). progressbar(option)method
- $(element, cont). progressbar(“action”, params)method
We can apply $ (element, cont) to the element for which we need to manage the progress; we can apply $(element, cont). progressbar(opt) method on the html element to and managed as a progress bar. Whereas option is a parameter that passes the different values to specify how the progress bars behave and appear. For example, $(“#elementid”).progressbar({ value : 30 }), here value is an option, and 30 is the provided value for the value option.
Similarly, we can pass not only one option, but we can also pass more than one option, just each option separated by the comma as given below –
$( selector, context).progressbar({option1: value1, option2: value2..... });The different options which we can pass to the progressbar are given below –
- disabled – The disabled option, if set to true, disables the progress bars, and false is a default value of disabled.
- max – The max option sets the maximum value for a progress bar. The default value of the max is 100.
- value – The value option used to set the initial value of the progress bar. The default value of value is 0.
Examples of JQuery Progress Bar
The default functionality of progressbar() method –
Next, let’s start with some examples of the progress bar to understand its functionality. First, we write some examples to see the progress bar’s default functionality without passing any parameters to the progressbar() method. As the progress bar is an element of the ui jQuery, the first step is to include the jquery external files by specifying the src attribute of the < script > element.
Example #1
<!doctype html>
<head>
<meta charset = "utf-8">
<title> My first jQuery UI Progress Bar example program </title>
<script src = "https://code.jquery.com/jquery-1.10.2.js"></script>
<script src = "https://code.jquery.com/ui/1.10.4/jquery-ui.js"></script>
<link href = " https://code.jquery.com/ui/1.10.4/themes/ui-lightness/jquery-ui.css"
rel = "stylesheet">
<style>
.ui {
background: blue;
border: 2px solid #DDDDDD;
color: #333333;
font-weight: bold;
}
</style>
<script>
$(function() {
$( "#pbid" ).progressbar({
});
});
</script>
</head>
<body>
<h1> This is the default functionality of the progressbar </h1>
<div id = "pbid"> </div>
</body>
</html>Output:
Next, we use the value option and pass it 40, which indicates that the progress is 40% in the progress bar as given in the below code –
Example #2
<!doctype html>
<head>
<meta charset = "utf-8">
<title> My first jQuery UI Progress Bar example program </title>
<script src = "https://code.jquery.com/jquery-1.10.2.js"></script>
<script src = "https://code.jquery.com/ui/1.10.4/jquery-ui.js"></script>
<link href = " https://code.jquery.com/ui/1.10.4/themes/ui-lightness/jquery-ui.css"
rel = "stylesheet">
<style>
.ui {
background: blue;
border: 2px solid #DDDDDD;
color: #333333;
font-weight: bold;
}
</style>
<script>
$(function() {
$( "#pbid" ).progressbar({ value : 40
});
});
</script>
</head>
<body>
<h1> This is the default functionality of the progressbar </h1>
<div id = "pbid"> </div>
</body>
</html>Output:
Next, we set to max and value options as 400 and 40% value, respectively, in the progressbar method of JqueryUI.
Example #3
<!doctype html>
<head>
<title> My first jQuery UI Progress Bar example program </title>
<script src = "https://code.jquery.com/jquery-1.10.2.js"></script>
<link href = " https://code.jquery.com/ui/1.10.4/themes/ui-lightness/jquery-ui.css"
rel = "stylesheet">
<script src = "https://code.jquery.com/ui/1.10.4/jquery-ui.js"></script>
</style>
<script>
$(function() {
$( "#pbid" ).progressbar({
value: 40,
max:400
});
var pb = $( "#pbid" );
function progress() {
var v = pb.progressbar( "value" ) || 0;
pb.progressbar( "value", v + 1 );
if ( v < 99 ) {
setTimeout( progress, 100 );
}
}
setTimeout( progress, 4000 );
});
</script>
<style>
.ui{
background: blue;
color: #333333;
border: 2px solid #DDDDDD;
font-weight: bold;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h1> This is the example of the progressbar for max = 400 and values = 40% </h1>
<div id = "pbid"></div>
</body>
</html>Output:
The progress bar starts filling from left to right and stops when it reaches 400. If no value provides for the max option, then the fill only stops at the right end.
We can apply $ (element, cont) to the element for which we need to manage the progress; we can apply $(element, cont).progressbar(“action”, params) method on the html element to manage and perform an action on the progress bar in the form of a progress bar. The action is a parameter specified as a string in the first argument. For example, $(“#elementid”).progressbar(‘disable’), here disable option disable the progress bar.
Some actions can be passed in $(element, cont).progressbar(“action”, params) method are given below –
- destroy – The destroy action to remove an element’s progress bar functionality completely and return to the pre-init state of an element. It is a zero-argument method.
- disable – The disable action disables the element’s progress bar functionality. It is a zero-argument method.
- enable – The enable action enables the element’s progress bar functionality. It is a zero-argument method.
- option( option ) – The option(option) action gets the value from the specified element. It accepts one argument option, which is a String.
- option – The “options” action retrieves a progress bar option in the form of key-value pairs. It is a zero-argument method.
- option( option, value ) – The option( option, value ) action uses to set the progress bar option value associated with the specified option.
- option( options ) – The option( options ) action sets one or more options for the progress bars. It accepts one argument option, which is a map to option-value pairs.
- value – The “value” action retrieves the value of options. The value indicates the percentage of fill in the progress bar.
- value( value ) – The value( value ) action used to set a new value for a percentage to be filled in the progress bar. It accepts one argument value which is a number.
- widget – The widget action used to get the element on which the progress bar is applied. It is a zero-argument method.
Next, we see some examples of the progress bar with some actions mentioned above. Let’s see the below program for the progressbar() method with disable() and option( optionName, value ) action.
Example #4
<!doctype html>
<html lang = "en">
<head>
<meta charset = "utf-8">
<title> My first jQuery UI Progress Bar example program </title>
<link href = "https://code.jquery.com/ui/1.10.4/themes/ui-lightness/jquery-ui.css"
rel = "stylesheet">
<script src = "https://code.jquery.com/jquery-1.10.2.js"></script>
<script src = "https://code.jquery.com/ui/1.10.4/jquery-ui.js"></script>
<script>
$(function() {
$( "#pbid1" ).progressbar({
value: 40
});
$( "#pbid1" ).progressbar('disable');
$( "#pbid2" ).progressbar({
value: 40
});
var pb = $( "#pbid2" );
$( "#pbid2" ).progressbar( "option", "max", 400 );
function progress() {
var v = pb.progressbar( "value" ) || 0;
pb.progressbar( "value", v + 1 );
if ( v < 99 ) {
setTimeout( progress, 100 );
}
}
setTimeout( progress, 400 );
});
</script>
<style>
.ui {
background: blue;
border: 1px solid #DDDDDD;
font-weight: bold;
color: #333333;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h1> This is the example of the progressbar for Disable action </h1>
<div id = "pbid1"></div><br>
<h1> This is the example of the progressbar for max and value action </h1>
<div id = "pbid2"></div>
</body>
</html>Output –
The above progress bar is disabled; that’s why it is not showing up the progress, and the below progress bar set up the max and value option with some values, so the progress in the form of fill shows from left to right.
Progress bar element manage events –
In addition to the above, the event can also manage the progress bar. The jQuery UI provides an event method; the event gets triggered for a particular event. Some of the events which can be used to manage the progress bar are given below –
- change(event, ui) – This event triggers whenever the progress bar value or progress changes.
- complete(event, ui) – This event is generated when the progress reaches the end or reaches the maximum value.
- create(event, ui) – This event triggers whenever a progress bar is created.
Next, write some examples of the above event action. The following example demonstrates the event method usage during progress bar functionality. This example demonstrates the use of events to change and complete.
Example #5
<!doctype html>
<html lang = "en">
<head>
<meta charset = "utf-8">
<title> My first jQuery UI Progress Bar example program </title>
<link href = "https://code.jquery.com/ui/1.10.4/themes/ui-lightness/jquery-ui.css"
rel = "stylesheet">
<script src = "https://code.jquery.com/jquery-1.10.2.js"></script>
<script src = "https://code.jquery.com/ui/1.10.4/jquery-ui.js"></script>
<script>
$(function() {
pl = $( ".pbc" );
var pb = $( "#pbid" );
$( "#pbid" ).progressbar({
value: false,
change: function() {
pl.text(
pb.progressbar( "value" ) + "%" );
},
complete: function() {
pl.text( "Loading Completed!" );
}
});
function progress() {
var v = pb.progressbar( "value" ) || 0;
pb.progressbar( "value", v + 1 );
if ( v < 99 ) {
setTimeout( progress, 100 );
}
}
setTimeout( progress, 3000 );
});
</script>
<style>
.ui-widget-header {
background: blue;
border: 2px solid #DDDDDD;
color: #333333;
font-weight: bold;
}
.progress-label {
position: absolute;
top: 13px;
left: 50%;
font-weight: bold;
text-shadow: 1px 1px 0 #fff;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
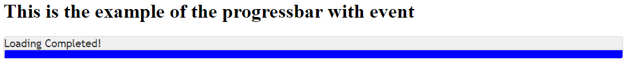
<h1> This is the example of the progressbar with event </h1>
<div id = "pbid">
<div class = "pbc">
Loading...
</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>Output:
The progress bar starts filling from left to right and stops when it reaches the end.
Conclusion
1. Progress bars are a jQueryUI element.
2. The progress bar shows the task or process completion state in percentage.
3. The progressbar() method can be used in two forms −
- $(element, cont). progressbar(option) method
- $(element , cont). progressbar(“action”, params)method
4. The different options which we can pass to the progressbar() method are –
disabled
- max
- value
5. Some actions can be passed in $( element, cont).progressbar( “action”, params ) method are –
- destroy
- disable
- enable
- option
- option( option, value )
- option( options )
- value
- value( value )
- widget
6. The event which can be used to manage the progress bar is given below –
- complete( event, ui )
- create( event, ui )
- change( event, ui )
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on the “JQuery Progress Bar” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.