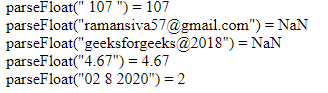Updated June 19, 2023
Introduction to JavaScript Floating
A floating point is a number that has decimal numbers. It dynamically types and frequently converts the numbers into the implicit format between strings and floating-point numbers. These numbers are in the IEEE format, which enforces variable values to be floating-point numbers using the 64-bit format. The script uses globally defined methods, such as parseFloat(), to pass floating-point values into variables.
Syntax and Parameters
The javascript floating is one of the types of representing numbers in the application for using the mathematical operations in the web pages. It has its own features and behaviors in the operations.
<html>
<body>
<script>
var v=12345f;
var v1=123-4f5;
document.getElementById("").innerHTML=v + v1;
--some jaavscript logics---
</script>
</body>
</html>The above codes are the basic syntax for mathematical operations in the scripts. We can use some default methods for reducing the lines of codes in the script because it helps to find the parsed strings, and it will return the numbers in floating point format.
How is Floating Done in JavaScript?
The Javascript, sometimes we have to choose the feature called Numeric conversion. It helps to use the operators and operands like plus +, or we can use them as functions or default methods like Number(), the strict format in script codes. If a value is not matching exactly, the format numbers are to fail using the default method called parseFloat. These units have utilized the values like “203px” or “15pt” in presentation layers called CSS.
Generally, the parseInt() and parseFloat() methods will be used optionally in the second argument. Because it specifies the base of the numerical system under covers all types of numbers in the script. So it requires and accepts the parseFloat method. You can also use the parsing methods for hexa numbers, binary numbers, and octal numbers to parse each string of number types. So that we can parse the parseInt and parseFloat numbers are the “read-only” options, it cannot edit the numbers even though it has to be the string type until they can’t cover all segments. In case of an error, that time, it handles the situations for gathering numbers, and it is returned with different orders. The method parseInt returns the integer, while the parseFloat returns floating-point numbers. It’s the basic difference between both functions of the javascript.
JavaScript has built-in methods for classes like Math objects which contain the small API libraries of mathematical functions and constants. We can use these functions, and default constants are moreover it applicable for both arithmetic and logical operations. Not only these functions, but it also has some other default functions and constants; all it has is the default math object; using these particular instances, it applies trigonometry and other features.
Examples of JavaScript Floating
Following are the examples given below:
Example #1
Code:
<!DOCTYPEhtml>
<html>
<body>
<script>
x = parseFloat(" 107 ")
document.write('parseFloat(" 107 ") = ' +x +"<br>");
y = parseFloat("[email protected]")
document.write('parseFloat("[email protected]") = '
+y +"<br>");
c = parseFloat("geeksforgeeks@2018")
document.write('parseFloat("geeksforgeeks@2018") = '
+c +"<br>");
d = parseFloat("4.67")
document.write('parseFloat("4.67") = '
+d +"<br>");
e = parseFloat("02 8 2020")
document.write('parseFloat("02 8 2020") = '
+e +"<br>");
</script>
</body>
</html>Output:
Example #2
Code:
<!DOCTYPEhtml>
<html>
<body>
<script>
x = parseFloat(" 107 ")
document.write('parseFloat(" 107 ") = ' +x +"<br>");
y = parseFloat("[email protected]")
document.write('parseFloat("[email protected]") = '
+y +"<br>");
c = parseFloat("geeksforgeeks@2018")
document.write('parseFloat("geeksforgeeks@2018") = '
+c +"<br>");
d = parseFloat("4.67")
document.write('parseFloat("4.67") = '
+d +"<br>");
e = parseFloat("02 8 2020")
document.write('parseFloat("02 8 2020") = '
+e +"<br>");
f=parseFloat(3.14);
document.write('parseFloat("3.14") = '
+f +"<br>");
g=parseFloat('3.14');
document.write('parseFloat("3.14") = '
+g +"<br>");
h=parseFloat(' 3.14 ');
document.write('parseFloat("3.14") = '
+h +"<br>");
i=parseFloat('314e-2');
document.write('parseFloat("3.14e-2") = '
+i +"<br>");
j=parseFloat('0.0314E+2');
document.write('parseFloat("0.0314E+2") = '
+j +"<br>");
k=parseFloat('3.14some non-digit numbers ad characters are also apploicables');
document.write('parseFloat("3.14") = '
+k +"<br>");
l=parseFloat({ toString: function() { return"3.14" } });
document.write('parseFloat("3.14") = '
+l +"<br>");
</script>
</body>
</html>Output:
Example #3
Code:
<!DOCTYPEhtml>
<html>
<head>
<style>
div.second {
background-color:green;
font-family: "Times New Roman", Times, serif;
}
div.third {
background-color:red;
font-family: Arial, Helvetica, sans-serif;
}
div.four {
background-color:pink;
font: 80% sans-serif;
}
div.five {
background-color:yellow;
font: 13px/11px sans-serif;
}
div.six {
background-color:orange;
font-weight: 500;
font: 1rem monospace;
white-space: nowrap;
}
</style>
</head>
<body bgcolor="blue">
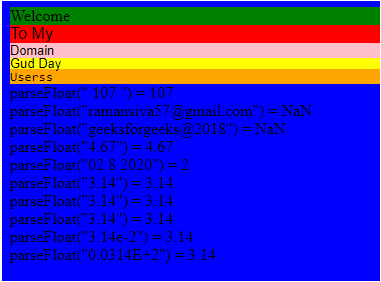
<div class="second">Welcome</div>
<div class="third">To My</div>
<div class="four">Domain</div>
<div class="five">Gud Day</div>
<div class="six">Userss</div>
<script>
x = parseFloat(" 107 ")
document.write('parseFloat(" 107 ") = ' +x +"<br>");
y = parseFloat("[email protected]")
document.write('parseFloat("[email protected]") = '
+y +"<br>");
c = parseFloat("geeksforgeeks@2018")
document.write('parseFloat("geeksforgeeks@2018") = '
+c +"<br>");
d = parseFloat("4.67")
document.write('parseFloat("4.67") = '
+d +"<br>");
e = parseFloat("02 8 2020")
document.write('parseFloat("02 8 2020") = '
+e +"<br>");
f=parseFloat(3.14);
document.write('parseFloat("3.14") = '
+f +"<br>");
g=parseFloat('3.14');
document.write('parseFloat("3.14") = '
+g +"<br>");
h=parseFloat(' 3.14 ');
document.write('parseFloat("3.14") = '
+h +"<br>");
i=parseFloat('314e-2');
document.write('parseFloat("3.14e-2") = '
+i +"<br>");
j=parseFloat('0.0314E+2');
document.write('parseFloat("0.0314E+2") = '
+j +"<br>");
</script>
</body>
</html>Output:
Conclusion
We have used the floating point of values in the web pages with different scenarios in scripting languages. Whenever the default method for handling floating-point values is used, it is important to validate these values on both the client and server sides.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to JavaScript Floating. Here we also discuss the introduction and how floating is done in javascript. along with different examples and code implementation. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –