Introduction to JavaScript Delay
In JavaScript, delaying the execution of code is a common requirement, especially when dealing with asynchronous operations or creating user-friendly interfaces. JavaScript provides several methods for implementing delays, allowing developers to control the timing of when certain code blocks or actions occur within their applications. One of the primary ways to introduce a delay in JavaScript is through the use of the setTimeout() function. This function authorizes you to specify a callback function and a time delay in milliseconds. The program executes the provided callback function after the specified delay, allowing for delayed execution of code.
Understanding how to implement delays in JavaScript is crucial for building responsive and interactive web applications. Whether creating animations, handling user input, or fetching data from remote servers, effectively managing timing and delays is essential for delivering a smooth and engaging user experience.
Table of Contents:
Basic Syntax
Code:
setTimeout(callback, delay, argument1, argument2, ...);Explanation:
- callback: The function or code block to execute after the specified delay.
- delay: The time, in milliseconds, to wait before executing the function. (1 milliseconds = 1 second)
- arg1, arg2, …: Optional additional arguments you can pass to the callback
Working of the setTimeout() Function
When we use setTimeout() in our code, we tell the browser to remember a task (callback function) and a time delay. While the browser waits for the specified time, it can do other tasks. Our script doesn’t have to sit idle; it can keep doing things. Once the specified time elapses and the browser is not busy with other tasks, it takes the remembered task and puts it on its to-do list. The program then executes the task (callback function).
We can use the clearTimeout() function to cancel a scheduled timeout. (as shown in example 2)
Examples of JavaScript Delay
Here are a few example programs demonstrating the use of the setTimeout function:
Example 1: Three Second Delay
Code:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Delayed Alert Example</title>
</head>
<style>
body {
font-family: 'Arial', sans-serif;
text-align: center;
margin: 20px;
}
button {
padding: 10px;
font-size: 16px;
cursor: pointer;
}
#instruction {
margin-top: 20px;
}
</style>
<body>
<button id="clickMeButton">Click me</button>
<script src="script.js" defer></script>
<p id="instruction">Please click the button above and see what happens after 3 seconds.</p>
<script>
document.addEventListener("DOMContentLoaded", function () {
var clickMeButton = document.getElementById("clickMeButton");
var instruction = document.getElementById("instruction");
clickMeButton.addEventListener("click", function () {
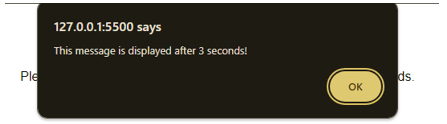
setTimeout(function () {
alert("This message is displayed after 3 seconds!");
}, 3000);
});
});
</script>
</body>
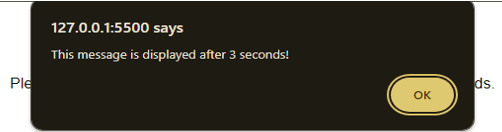
</html>Output 1: Before Click
Output 2: After Click
Explanation:
The “Click me” button triggers an alert after a 3-second delay, displaying “This message is displayed after 3 seconds!”. This page showcases the delayed alert, demonstrating the utilization of the setTimeout function in JavaScript for delayed actions.
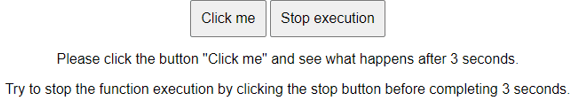
Example 2: Usage of Stop Button
This program displays text after 3 seconds, but if the user clicks the ‘Stop execution’ button before 3 seconds, it halts the execution.
Code:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Delayed Text Display</title>
</head>
<style>
body {
font-family: 'Arial', sans-serif;
text-align: center;
margin: 20px;
}
button {
padding: 10px;
font-size: 16px;
cursor: pointer;
}
</style>
<body>
<button onclick="startExecution()">Click me</button>
<button onclick="stopExecution()">Stop execution</button>
<p>Please click the "Click me" button and see what happens after 3 seconds.</p>
<p>Try to stop the function execution by clicking the stop button before completing 3 seconds.</p>
<script>
let timeoutId;
function startExecution() {
timeoutId = setTimeout(displayText, 3000);
}
function stopExecution() {
clearTimeout(timeoutId);
alert('Execution stopped!');
}
function displayText() {
alert("This message is displayed after 3 seconds!");
}
</script>
</body>
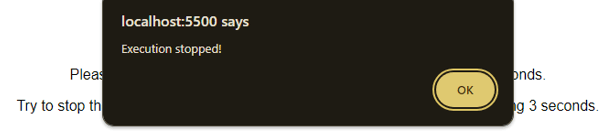
</html>Output 1: Before Click
Output 2: After Click
Explanation:
When you click the ‘Click me’ button, it triggers an alert after a 3-second delay. However, clicking the ‘Stop execution’ button cancels the delay and returns a message saying, ‘Execution stopped!’.
Example 3: Updates After Every Two Seconds
Code:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Timed Text Display</title>
</head>
<style>
body {
font-family: 'Arial', sans-serif;
text-align: center;
margin: 20px;
}
button {
padding: 10px;
font-size: 16px;
cursor: pointer;
}
</style>
<body>
<p>Click the "TIMED TEXT" button and observe the changes every two seconds.</p>
<button onclick="updateTimedText()">TIMED TEXT</button>
<input type="text" id="textt">
<script>
function updateTimedText() {
var textInput = document.getElementById("textt");
setTimeout(function() {
textInput.value = "2 seconds";
}, 2000);
setTimeout(function() {
textInput.value = "4 seconds";
}, 4000);
setTimeout(function() {
textInput.value = "6 seconds";
}, 6000);
setTimeout(function() {
textInput.value = "8 seconds";
}, 8000);
}
</script>
</body>
</html>Output 1:
Output 2:
Explanation
In the program above, it updates the text every two seconds. It uses setTimeout to update the text input’s value at different intervals (2 seconds, 4 seconds, 6 seconds, and 8 seconds).
Example 4: Opening in A New Window
This simple webpage creates a new browser window when you click the button, displays the specified text, and then closes the new window after a 2-second delay.
Code:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>New Window Example</title>
<style>
body {
font-family: 'Arial', sans-serif;
text-align: center;
margin: 20px;
}
button {
padding: 10px;
font-size: 16px;
cursor: pointer;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
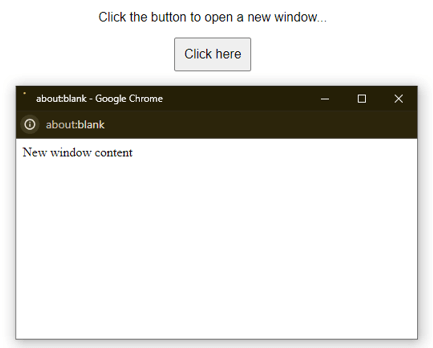
<p>Click the button to open a new window...</p>
<button onclick="openAndCloseWindow()">Click here</button
<script>
function openAndCloseWindow() {
var newWindow = window.open("", "v", "width=500, height=250");
newWindow.document.write("<p>New window content</p>");
setTimeout(function() {
newWindow.close();
}, 2000);
}
</script>
</body>
</html>Output 1:
Output 2:
Example 5: Defining the function outside of the setTimeout() method
Code:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Delayed Alert Example</title>
</head>
<style>
body {
font-family: 'Arial', sans-serif;
text-align: center;
margin: 20px;
}
button {
padding: 10px;
font-size: 16px;
cursor: pointer;
}
</style>
<body>
<button id="clickMeButton">Click me</button>
<script src="script.js" defer></script>
<p id="instruction">Please click the button above and see what happens after 3 seconds.</p>
<script>
document.addEventListener("DOMContentLoaded", function () {
var clickMeButton = document.getElementById("clickMeButton");
function displayMessage() {
alert("Message displayed after 3 seconds!");
}
clickMeButton.addEventListener("click", function () {
setTimeout(displayMessage, 3000);
});
});
</script>
</body>
</html>Output 1:
Output 2:
Example 6: Asynchronous Function
Code:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Asynchronous Function Example</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Asynchronous Function Example</h1>
<div id="outputContainer">
</div>
<script>
function displayOutput(output) {
const outputContainer = document.getElementById("outputContainer");
const outputParagraph = document.createElement("p");
outputParagraph.textContent = output;
outputContainer.appendChild(outputParagraph);
}
setTimeout(function() {
displayOutput("Task 1 completed!");
}, 3000);
setTimeout(function() {
displayOutput("Task 2 completed!");
}, 2000);
setTimeout(function() {
displayOutput("Task 3 completed!");
}, 1000);
</script>
</body>
</html>Output:
Explanation: Asynchronous functions do not occur simultaneously, meaning they don’t block the execution of the rest of the code. Instead, they allow other tasks to continue while completing their operations in the background.
The tasks have different delays scheduled:
- Task 1: set to complete after 3000 milliseconds (3 seconds).
- Task 2: set to complete after 2000 milliseconds (2 seconds).
- Task 3: Set to be completed after 1000 milliseconds (1 second).
We were supposed to achieve the above output, but instead, we got the output as Task 3, followed by Task 2, followed by Task 1. This is because of JavaScript’s asynchronous nature. Instead of completing Task 1 and then waiting 2 seconds for Task 2, JavaScript completes Task 3 first due to the minimum waiting time (1000 milliseconds).
Example:
setTimeout(function() {
console.log("This will be executed after the timeout");
}, "2000");Explanation: In this case, the string “2000” is a non-number value, but it will be silently coerced into the number 2000 by the JavaScript engine, and the timeout is automatically set to 2000 milliseconds.
This behavior may produce unexpected results if the provided value is not converted to a number.
Example 2:
setTimeout(function() {
console.log("This will be executed immediately");
}, "not_a_number");Explanation: Here, “not_a_number” is an invalid numeric representation, and the conversion will result in NaN (Not a Number). In such cases, the timeout effectively gets set to 0, and the function executes almost immediately.
Best Practices for Using Delays
- Use Timers logically: Use timers, such as setTimeout() and setInterval(), only when necessary and avoid excessive use. Evaluate whether the intended functionality truly requires delays and consider alternative approaches if possible.
- Avoid Short Delays: Reduce the frequency of employing very brief delays, such as those shorter than 10 milliseconds, as they can strain resources and potentially cause performance drawbacks, particularly with frequent usage.
- Clear Timers Appropriately: Always clear or cancel timers when they are no longer needed to prevent memory leaks and unexpected behavior. Use clearTimeout() and clearInterval() to cancel timers as required.
- Optimize Delay Durations: Choose appropriate delay durations based on the specific requirements of your application. Avoid unnecessarily long delays that may lead to sluggish user experience, but also ensure that delays are sufficient to achieve the desired functionality without causing undue delays.
- Test and Monitor Performance: Test the performance of your application, especially when delays are involved, to identify potential bottlenecks or performance issues. Monitor CPU usage, memory consumption, and other relevant metrics to ensure optimal performance.
Conclusion – JavaScript Delay
The setTimeout() function in JavaScript is a valuable tool for introducing delays in code execution. It is beneficial when timing is crucial, such as creating animations, handling asynchronous operations, or managing user interactions. Inversely, The clearTimeout() function actively cancels a timeout that was previously set using the setTimeout() function.
FAQ’s
Q1. How does setTimeout() work?
Answer: When you call setTimeout(), it actively sets a timer to execute the specified function after the specified delay. Meanwhile, the rest of the code continues to execute. Once the delay is over, the function is moved to the JavaScript event queue and executed when the main thread is free.
Q2. How can I use setTimeout() for animations or timed updates?
Answer: setTimeout() is frequently used for animations or timed updates by calling it repeatedly with different delays. This allows you to create a sequence of events or changes over time.
Q3. How does setInterval() differ from setTimeout()?
Answer: setInterval() and setTimeout() are both JavaScript functions used for scheduling code execution after a specified delay. setTimeout() actively executes a function or code block after a specified delay, while setInterval() actively repeats the execution of a code block or function at specified intervals.
Q4. What are some real-life uses of the setTimeout() function?
Answer: Some of the real-life usage of setTimeout() functions are User Interface Delays, Autosave Functionality, Animations, Modal Dialogs or Alerts, Slideshow or Carousel Transitions, and many more.
Recommended Articles
We hope this EDUCBA information on “JavaScript Delay” benefited you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information: