Updated December 12, 2023
Introduction to Java Vector Class
Java has a class called Vector, which dynamically implements an array of objects. This means the array can expand or shrink based on requirements. Vector is particularly useful when the array size is unknown in advance. Unlike arrays, Vector is synchronized and includes many legacy methods not found in collection frameworks. It inherits from the java.util package and implements the List interface. It is advisable to use this class for thread-safe implementation. Otherwise, it is preferable to use ArrayList.
Declaration:
Below is the declaration of vector class in Java:
public class Vector<E> extends Object<E> implements List<E>,Cloneable, Serializable
Table of Content
Constructors of Java Vector Class
Given below are the constructors of Java Vector Class:
- Vector(): An empty vector gets constructed with size of internal data array as ten and standard capacity increment as 0.
- Vector(Collection<? extends E> c): A vector gets constructed with elements in the mentioned collection and ordered based on the collection’s iterator.
- The Vector(int c) constructor constructs an empty vector with an initial capacity of c and a capacity increment of 0.
- The Vector(int c, int capacityIncrement) constructor constructs an empty vector with an initial capacity of c and a specified capacity increment.
Methods of Java Vector Class
Given below are the methods of Java Vector Class:
- add(E e): Element e appends to the vector end.
- add(int index, E element): Element e will be inserted to the position mentioned in the vector.
- addAll(Collection<? extends E> c): Appends all elements to the end of the vector in order based on the collection’s iterator.
- add(int index, E element): Inserts all elements from the mentioned collection to the specified position in the vector.
- addElement(E obj): Adds the specified component to the end of the vector, incrementing the size by one.
- capacity(): Returns the current capacity of the vector.
- clear(): Removes all elements from the vector.
- clone(): Returns a clone for the vector.
- contains(Object o): If the vector consists of the element mentioned, true will be returned.
- containsAll(Collection<?> c): If the vector consists of all the elements mentioned in the collection mentioned, true will be returned.
- copyInto(Object[] anArray): Copies the components of this vector into the specified array.
- elementAt(int index): Returns the components at the specified index.
- elements(): Returns an enumeration of the components for this vector.
- ensureCapacity(int minCapacity): Increases the vector’s capacity, ensuring that the vector can hold the number of components specified by the minimum argument capacity.
- equals(Object o): For equality, specified object will be compared with the vector.
- firstElement(): First item, at index 0 for the vector will be returned.
- get(int index): Returns the element at the specified position in this Vector.
- hashCode(): Returns the value of the hashcode for this Vector.
- indexOf(Object o): Returns the index for the first occurrence of an item in the Vector. If that item is not present, -1 will be returned.
- indexOf(Object o, int index): Index will be returned for the 1st occurrence of the mentioned item in the Vector. If that item is not present, -1 will be returned.
- insertElementAt(E obj, int index): Object mentioned will be inserted as a component in the vector to the index mentioned.
- isEmpty(): Checks whether the vector has components or not.
- iterator(): Returns an iterator over the items in the list in the correct sequence.
- lastElement(): Returns the last component for the vector.
- lastIndexOf(Object o): Returns the index for the final occurrence of an item in the Vector. If that item is not present, -1 will be returned.
- lastIndexOf(Object o, int index): Index will be returned for the final occurrence of mentioned item in the Vector. If that item is not present, -1 will be returned.
- listIterator(): A list iterator will be returned over the list items.
- listIterator(int index): A list iterator will be returned over the list items where starting is the mentioned position.
- remove(int index): Removes the element at the specified position from this Vector.
- remove(Object o): Removes the first occurrence of an item from the Vector. If the item is not present, it remains unchanged.
- removeAll(Collection<?> c): All elements that are available in the collection will be removed from the Vector.
- removeAllElements(): Removes all elements from the Vector, and the size becomes 0.
- retainAll(Collection<?> c): All elements that are available in the collection will be retained from the Vector.
- set(int index, E element): Element at the mentioned position will be replaced in this Vector with the element mentioned.
- setElementAt(E obj, int index): Sets the component at the specified index to the provided object.
- setSize(int newSize): Adjusts the size of the Vector.
- size(): Returns the count of components.
- subList(int fromIndex, int toIndex): Returns a view of the portion between fromIndex (inclusive) and toIndex (exclusive).
- toArray(): Gets an array that contains all elements in the vector in right order.
- toString(): String representation will be returned for the vector.
- trimToSize(): Vector capacity is trimmed to current size of vector.
Examples
Here are the different examples of Vector Class in Java:
Example #1
Code:
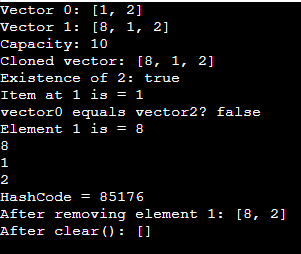
import java.util.Vector;
public class Main {
public static void main(String arg[]) {
Vector<String>vctr = new Vector<>(2);
vctr.add("1");
vctr.add(1,"2");
System.out.println("Vector 0: " + vctr);
Vector<String> vctr1 = new Vector<>();
vctr1.add("8");
vctr1.addAll(vctr);
System.out.println("Vector 1: " + vctr1);
System.out.println("Capacity: "+vctr1.capacity());
System.out.println("Cloned vector: "+vctr1.clone());
System.out.println("Existence of 2: "+vctr1.contains("2"));
System.out.println("Item at 1 is = "+vctr1.elementAt(1));
System.out.println("vector0 equals vector2? "+vctr.equals(vctr1));
System.out.println("Element 1 is = "+vctr1.firstElement());
vctr1.forEach(System.out::println);
System.out.println("HashCode = "+vctr1.hashCode());
vctr1.remove(1);
System.out.println("After removing element 1: " + vctr1);
vctr1.clear();
System.out.println("After clear(): " + vctr1);
}
}Output:
Example#2
Code:
import java.util.ListIterator;
import java.util.Vector;
public class Main {
public static void main(String arg[]) {
Vector<Integer>vctr = new Vector<>(2);
vctr.add(3);
vctr.add(1,2);
vctr.setElementAt(2, 1);
System.out.println("Vector 0: " + vctr);
vctr.setSize(6);
System.out.println("Components after new size: ");
for (Integer n :vctr) {
System.out.println("Numbers: " +n);
}
ListIterator<Integer> li = vctr.listIterator();
System.out.println("Elements are: ");
while(li.hasNext())
{
System.out.println(li.next());
}
}
}Output:

Example #3
Let us see a basic example of the vector class in java as given below.
Code:
import java.util.*;
public class VectorDemo{
public static void main(String args[]){
// Creating a vector instance which is not type safe and can contain any type of element
Vector vector= new Vector();
vector.add(1);
vector.add(5);
vector.add("Edubca");
vector.add("Java");
vector.add("Training");
vector.add(4);
System.out.println("Vector has the following elements " + vector);
// Creating a vector instance which is type safe
// This can contain only String elements. If any other type of element is added, it will result in compile //time error.
Vector<String> typeSafeVector= new Vector<String>();
typeSafeVector.add("Edubca");
typeSafeVector.add("Java");
typeSafeVector.add("Training");
System.out.println("Vector has the following elements " + typeSafeVector);
}
}Output:
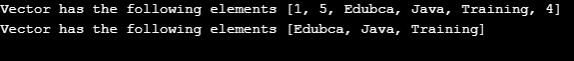
The above code shows the creation of a java vector class, and it adds a method. Also, we have seen how to create a type-safe vector. The following output will be produced:
Example #4
In this example, we will see some more methods of Vector class like add at the specified position and get the element at a specified index in vector.
Code:
import java.util.*;
public class VectorDemo{
public static void main(String args[]){
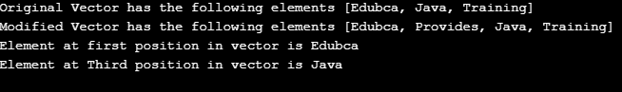
Vector<String> vector= new Vector<String>();
vector.add("Edubca");
vector.add("Java");
vector.add("Training");
System.out.println("Original Vector has the following elements " + vector);
vector.add(1, "Provides"); // adding element at specified position
System.out.println("Modified Vector has the following elements " + vector);
String elementAtFirst= vector.get(0); //get element at first position in vector
System.out.println("Element at first position in vector is " + elementAtFirst);
String elementAtThird = vector.get(2); //get element at third position in vector
System.out.println("Element at Third position in vector is " + elementAtThird );
}
}In the above example, we have seen how to create a Vector class and usage of its methods. The above code will display the following as output.
Output:
Example #5
In this example, we will see how to create a vector from an existing collection and contain the vector class method.
Code:
import java.util.*;
public class VectorDemo{
public static void main(String args[]){
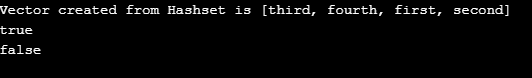
HashSet set =new HashSet();
set.add("first");
set.add("second");
set.add("third");
set.add("fourth");
Vector vector= new Vector(set);
System.out.println("Vector created from Hashset is " + vector);
System.out.println(vector.contains("third"));
System.out.println(vector.contains("fifth"));
}
}Output:
Example #6
In this example we will see the use of remove(), isEmpty() and clear() methods in Vector.
Code:
import java.util.*;
public class VectorDemo{
public static void main(String args[]){
HashSet set =new HashSet();
set.add("This");
set.add("is");
set.add("Vector");
set.add("Class");
set.add("Demo");
set.add("In");
set.add("Java");
Vector vector= new Vector(set);
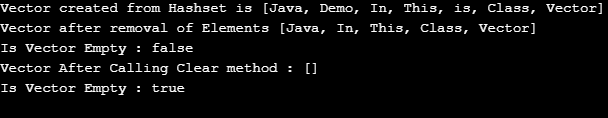
System.out.println("Vector created from Hashset is " + vector);
vector.remove(1);
vector.remove(3);
System.out.println("Vector after removal of Elements " + vector);
System.out.println("Is Vector Empty : " + vector.isEmpty());
vector.clear(); // Clear All Elements of Vector
System.out.println("Vector After Calling Clear method : " + vector);
System.out.println("Is Vector Empty : " + vector.isEmpty());
}
}The above code produces this output.
Output:
Example #7
In this example, we will see how to iterate elements of a vector using an iterator.
Code:
import java.util.*;
public class VectorDemo{
public static void main(String args[]){
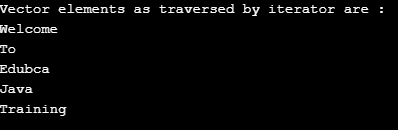
Vector<String> vector= new Vector<String>();
vector.add("Welcome");
vector.add("To");
vector.add("Edubca");
vector.add("Java");
vector.add("Training");
Iterator it=vector.iterator();
System.out.println("Vector elements as traversed by iterator are : ");
while(it.hasNext()){
System.out.println(it.next());
}
}
}The above code will produce the following output.
Output:
Best Practices and Tips for Using Vector
- Thread Safety: When thread safety is required, use Vector. Because it guarantees synchronized access, multi-threaded environments can benefit from its use.
- Consider Alternatives: For better performance in single-threaded scenarios, think about using more contemporary alternatives like ArrayList if thread safety is not absolutely necessary
- Capacity Planning: Depending on your anticipated usage, specify an initial capacity and capacity increment to maximize performance and prevent frequent resizing
- Generics Usage: For type safety and to keep casting problems with raw types to a minimum, always use generics (Vector<Type>).
- Enhanced For Loop: For improved code readability, use the enhanced for loop when iterating over elements.
- Avoid Enumeration: For traversing elements, use more contemporary iterators rather than Enumeration.
- Consider Synchronized Collections: Use Collections to increase synchronization flexibility.other synchronized collections, such as synchronizedList(new ArrayList<>()).
FAQ’s
Q1. When should I use Vector instead of ArrayList?
Answer: When thread safety is required, use Vector. Vector may be a good option if you require synchronization in a multi-threaded environment. If not, use ArrayList since it performs better.
Q2. Why is the Vector class regarded as legacy?
Answer: Contemporary Java programming typically avoids using the Vector class primarily due to its synchronization overhead. Instead, developers commonly opt for non-synchronized collections such as ArrayLists.
Q3. Can Vector have its size changed dynamically?
Answer: Vector can indeed be dynamically resized. The vector’s capacity is increased by the capacity increment (if supplied) or doubled by default when the number of components exceeds the current capacity.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “Java Vector Class” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.


