Updated November 7, 2023
Introduction to Data Types in Java
In Java, programmers utilize data types to classify and define the data type a variable can hold. Data types determine the size and format of the data stored in a variable. Java has two main categories of data types: primitive data types (such as int, char, and boolean) that represent basic values and reference data types (such as objects and arrays) that refer to more complex data structures. The use of data types is crucial for ensuring data integrity and efficient memory usage in Java programs.
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- How do Data Types come into the Picture?
- Classification of Java Data Types
- Examples of Data Types in Java
How do Data Types come into the Picture?
Data types are essential in programming to define the data type that can be stored or used in a program. They come into the picture in several ways:
- Variable Declaration: When programming, declaring a variable involves specifying its data type. This lets the compiler or interpreter know how much memory to allocate and what operations are valid for that variable.
- Memory Allocation: Data types determine the amount of memory allocated for a variable. For example, an int typically uses 4 bytes of memory, while a double might use 8 bytes.
- Data Integrity: Data types limit the data stored in a variable to ensure integrity. For instance, a variable declared as an int can hold only integer values.
- Operations: Different data types allow for different operations. For instance, arithmetic operations can be performed on numeric data types but not on text data types.
- Performance: Data types can impact program performance. Using an appropriate data type can lead to more efficient code execution and reduced memory usage.
Data types are fundamental for ensuring that data is used correctly and efficiently in a program. They help catch errors, optimize memory usage, and define the behavior of operations on that data.
Classification of Java Data Types
Java has two main data type categories: primitive and reference. Here’s an overview of these two classifications:
1. Primitive Data Types
Primitive data types are the most basic data types in Java. They are used to represent simple values like numbers and characters. Java provides eight primitive data types:
- byte: Represents 8-bit signed integers. It has a range of -128 to 127.
- short: Represents 16-bit signed integers. It has a range of -32,768 to 32,767.
- int: Represents 32-bit signed integers. It has a range of -2^31 to 2^31-1.
- long: Represents 64-bit signed integers. It has a range of -2^63 to 2^63-1.
- float: Represents single-precision 32-bit floating-point numbers. Useful for representing real numbers with a fractional part.
- double: Represents double-precision 64-bit floating-point numbers. Used for more precise floating-point calculations.
- char: Represents a single 16-bit Unicode character.
- boolean: Represents a true or false value, typically used in conditional expressions.
Primitive data types are more memory-efficient and have better performance compared to reference data types, as they store the actual value directly. People typically use these devices to store data and perform straightforward calculations.
2. Reference Data Types
Reference data types are used to store references (memory addresses) to objects and are more complex than primitive data types. They include:
- Classes: Reference data types can represent objects created from classes. Objects in programming are defined by classes, which determine their structure and behavior.
- Interfaces: Interfaces are reference data types that define a contract for classes to implement. They allow for multiple inheritance in Java.
- Arrays: Arrays are reference data types that can hold a collection of elements of the same data type.
Reference data types do not store the actual data but reference the memory location where the data is stored. This allows for more complex data structures and dynamic memory allocation. Objects created from reference data types have methods and attributes associated with them.
In addition to these two primary classifications, it’s also worth noting:
3. User-Defined Data Types
Developers can create their custom data types in Java using classes and interfaces. These user-defined data types allow for creating objects with specific attributes and behaviors, making Java a versatile and object-oriented programming language.
Two major User defined data types are:
1. Class
Java, a true object-oriented language, is full of classes that encapsulate everything from data elements that act as instance variables and functions to process the data. It also provides templates to create Objects that are instances of Class that contain a method for performing the defined functions and interact with other parts of the program.
How Objects are created?
Objects are created or instantiated from the class and used as individual instances of the class. Instance variables are created for each of the objects to interact with other components of the program, and there could be as many objects created, and each object will have
- Clear identity with a unique name
- Different sets of instance variables to reflect its state.
- All the functionalities that define its behavior
Each class is a user-defined data type with the combined effect of all the data types of its data elements, and each object is a variable data.
Example
public class OrderValueCompute // Public class
{
public static void main(String[] args) // Execution starts here
{
int value1; // variable definition
int value2;
ValueStore VS1; // Object VS1 definition
VS1 = new ValueStore(); // Object VS1 instantiated
ValueStore VS2; // Object VS2 definition
VS2 = new ValueStore(); // Object VS2 instantiated
VS1.AssignData (200,10); // Assigndata method in Object VS1 invoked
//with values
value1 = VS1.ComputeValue(); // Computedata method in object VS1
// invoked
VS2.AssignData (500,20); // Assigndata method in Object VS2
// invoked with values
value2 = VS2.ComputeValue(); // Computedata method in object VS2
//invoked
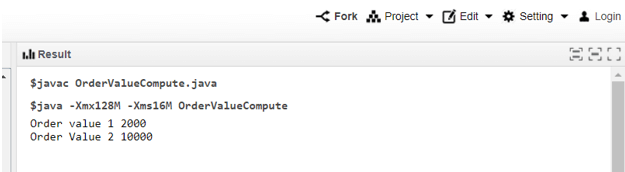
System.out.println("Order value 1 " +value1); // Output 1 displayed
System.out.println("Order Value 2 " +value2); // Output 2 displayed
}
}In the execution class, the objects in the other class are defined, and instantiated. Methods are invoked. Results obtained and displayed. Class is a user-defined data type, and each object is a variable.
Output:
2. Interface
The interface is similar to Class in architecture. It has data variables and methods. It broadly suggests what the classes calling it should do, but it does not suggest how it should be carried out.
The method in an interface differs from a normal method in a class by
- It is not full-fledged
- It is only an abstract, and it has only a definition, and the body is empty.
- It will not perform any functionalities.
Interfaces cannot instantiate any objects like class. But it facilitates abstraction, Multiple inheritances, and loose coupling of classes.
The class extends to another superclass by a level. The interface extends to another super interface by a level. Class implements interface, and multiple inheritance is achieved indirectly, which is otherwise not possible in a class.
Each interface created by a user has a unique data type with a combined effect of its data elements. Objects created in these classes use interfaces, and each of these objects are the variables for interface data types.
Example
The following example demonstrates how classes implement interfaces, how developers create objects of these classes that link to the interfaces, and how they execute them.
Code:
// Sample program to demonstrate Interfaces
interface Intface //Interface is defined
{ // It has its own data type
public void dayname(); //Abstract method within the interface
}
class day1 implements Intface { // Class interacts through
public void dayname() // interface implementation
{ // (each class is a variable for interface)
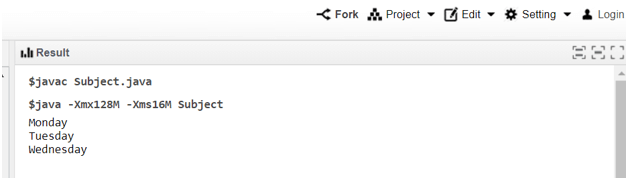
System.out.println("Monday");
}
}
class day2 implements Intface { // Another class
public void dayname()
{
System.out.println("Tuesday");
}
}
class day3 implements Intface { // Another class
public void dayname()
{
System.out.println("Wednesday");
}
}
public class Subject { // Execution starts here
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Intface t = new day1(); // Object of day1 class thru interface
t.dayname(); // method invoked
Intface tx = new day2(); // Object of day2 class thru interface
tx.dayname();
Intface tx2 = new day3(); // Object of day3 class thru interface
tx2.dayname(); }
} // objects t, tx1, tx2 are the variables of
// the interface data typeOutput:
Examples of Data Types in Java
Below are the different examples are as follows:
Example #1: Character values
Code:
public class Characters
{
//char global declaration
static char global;
public static void main(String[] args) {
//char local decalration
char a='a';
char b='b';
char c='c';
char d='d';
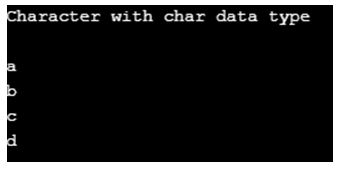
System.out.println("Character with char data type");
System.out.println(global);//gives you default value with empty means '\u0000'
System.out.println(a);
System.out.println(b);
System.out.println(c);
System.out.println(d);
}
}Output:
Example #2: String
Code:
public class StringDemo {
static String globalString;
public static void main(String[] args) {
String name1="Amardeep";
String specialChars="@#$%^";
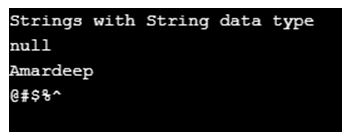
System.out.println("Strings with String data type");
System.out.println(globalString);
System.out.println(name1);
System.out.println(specialChars);
}
}Output:
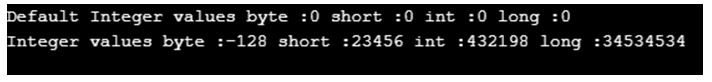
Example #3: Integer data type
Code:
public class IntegerDataTypes {
static byte globalByte;
static short globalShort;
static int globalInt;
static long globalLong;
public static void main(String[] args) {
byte b=-128;
short s=23456;
int i=432198;
long l=34534534L;//we can specify long value by suffix L
System.out.println("Default Integer values byte :"+globalByte+" short :"+globalShort+" int :"+globalInt+" long :"+globalLong);
System.out.println("Integer values byte :"+b+" short :"+s+" int :"+i+" long :"+l);
}
}Output:
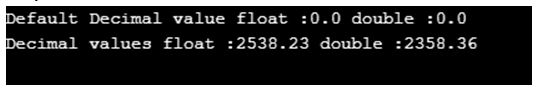
Example #4: Decimal data type
Code:
public class DecimalDataType {
static float globalFloat;
static double globalDouble;
public static void main(String[] args) {
float f=2538.23f;//we can specify float value by suffix f
double d=2358.36d;//we can specify double value by suffix d
System.out.println("Default Decimal value float :"+globalFloat+" double :"+globalDouble);
System.out.println("Decimal values float :"+f+" double :"+d);
}
}Output:
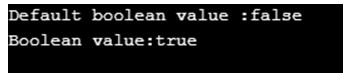
Example #5: Boolean data type
Code:
public class BooleanDataType {
static booleanglobalBoolean;
public static void main(String[] args) {
boolean b=true;
System.out.println("Default booleanvalue :"+globalBoolean);
System.out.println("Boolean value:"+b);
}
}Output:
Conclusion
Data Types in Java are primitive and reference types char, byte, short, int, long, float, double, boolean, and String, respectively. Data types decide the behavior of data.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “Data Types in Java” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.