Updated April 13, 2023

Introduction to Java ThreadLocal
The variables which can be read and written by the same thread can be created using a class called ThreadLocal class in Java, and hence if the same code is executed by the two threads and the code is referencing to the variables of the same ThreadLocal, the two threads cannot see these variables of the ThreadLocal and therefore a code can be made thread-safe by the use of ThreadLocal class and the code would not be thread-safe without the use of ThreadLocal class and an instance of the ThreadLocal class can be created like creating the instance of any other class in java using the new operator.
How does ThreadLocal class work in Java?
The thread-local variable is provided by java.lang.ThreadLocal class in Java. These variables are different from the normal variables so that they can be accessed by using the get or set method by each thread that is independent, own, and has a copy of the variable, which is initialized. This is basically one of the other ways to achieve the safety of the thread apart from the writing of immutable classes.
There is no more sharing of the object, and hence there is no necessity for synchronization through which the performance and scalability of the application are improved. The ThreadLocal class in Java extends the class object. The extension of the local variable, which is a restriction of the thread, is provided by the ThreadLocal class in Java. Only a single thread can view the ThreadLocal. Each other’s threads cannot see the ThreadLocal variables of two threads. The ThreadLocal variables belong to the private field, which is static in classes, and the state is maintained inside the thread.
Creation of ThreadLocal in Java
The instance of ThreadLocal is created like how an instance of any other java object is created using a new operator. Consider the below syntax to create a ThreadLocal in Java:
private ThreadLocal variable_name = new ThreadLocal();The creation of ThreadLocal must be done only once for one thread. The values can be set and then get by multiple threads inside this ThreadLocal, and only those values set by the thread can be seen by themselves.
Get ThreadLocal value in Java
The value stored in the ThreadLocal can be read using its get() method. Consider the below syntax to get a ThreadLocal value in Java:
String variable_name = (String) threadLocal.get();Set ThreadLocal value in Java
The value to be stored in the ThreadLocal after its creation can be set usingset() method. Consider the below syntax to set a ThreadLocal value in Java:
threadLocal.set("value_that_needs_to_be_set");Remove ThreadLocal value in Java.
The value set in the ThreadLocal after the creation of it can be removed. The ThreadLocal value can be removed by using ThreadLocal remove() method. Consider the below syntax to remove a ThreadLocal value that is set in Java:
threadLocal.remove();Examples to Implement Java ThreadLocal
Below are examples mentioned:
Example #1
Program to demonstrate get() method and set() method of ThreadLocal class:
Code:
//a class called demo is defined
public class Demo
{
//main method is called
public static void main(String[] args)
{
//an instance of the ThreadLocal is created for a number
ThreadLocal<Number> local = new ThreadLocal<Number>();
//an instance of the ThreadLocal is created for a string
ThreadLocal<String> val = new ThreadLocal<String>();
//setting the first number value using set() method
local.set(100);
//obtaining the current thread's value which returns a number using get() method
System.out.println("The number value that was set is = " + local.get());
//setting the second number value using set() method
local.set(90);
//obtaining the current thread's value which returns a numberusing get() method
System.out.println("The number value that was set is = " + local.get());
//setting the first string value using set() method
val.set("Welcome to ThreadLocal");
//obtaining the current thread's value which returns a stringusing get() method
System.out.println("The string value that was set is = " + val.get());
//setting the second string value using set() method
val.set("Learning is fun");
//obtaining the current thread's value which returns a stringusing get() method
System.out.println("The string value that was set is = " + val.get());
}
}Output:
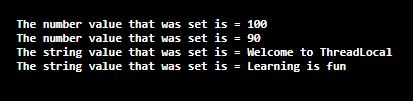
Explanation: In the above program, a class called demo is defined. Then the main method is defined. Then an instance of the ThreadLocal is created for a number. Then an instance of the ThreadLocal is created for a string. Then the first number value is set using the set() method. Then the current thread’s value which returns a number is obtained using the get() method. Then the second numerical value is set using the set() method. Then the current thread’s value which returns a number is obtained using the get() method. Then the first string value is set using the set() method. Then the current thread’s value which returns a string is obtained using the get() method. Then the second string value is set using the set() method. Then the current thread’s value which returns a string is obtained using the get() method. The output of the program is shown in the snapshot above.
Example #2
Java program to demonstrate remove() method of ThreadLocal class:
Code:
//a class called demo is defined
public class Demo
{
//main method is called
public static void main(String[] args)
{
//an instance of the ThreadLocal is created for a number
ThreadLocal<Number> local = new ThreadLocal<Number>();
//an instance of the ThreadLocal is created for a string
ThreadLocal<String> val = new ThreadLocal<String>();
//setting the first number value using set() method
local.set(100);
//obtaining the current thread's value which returns a number using get() method
System.out.println("The first number value that was set is = " + local.get());
//setting the second number value using set() method
local.set(90);
//obtaining the current thread's value which returns a number using get() method
System.out.println("The second number value that was set is = " + local.get());
//setting the first string value using set() method
val.set("Welcome to ThreadLocal");
//obtaining the current thread's value which returns a string using get() method
System.out.println("The first string value that was set is = " + val.get());
//Using remove() method to remove the first string value that was set using set() method
val.remove();
//obtaining the current thread's value which returns a string using get() method
System.out.println("The first string value after using remove() method is = " + val.get());
//Using remove() method to remove the first number value and second number value that was set using set() method
local.remove();
//obtaining the current thread's value using get() method
System.out.println("The first number value and second number value after using remove() method is = " + local.get());
}
}Output:
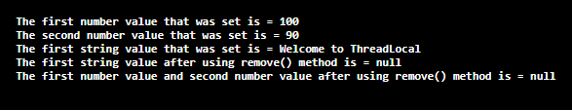
Explanation: In the above program, a class called demo is defined. Then the main method is defined. Then an instance of the ThreadLocal is created for a number. Then an instance of the ThreadLocal is created for a string. Then the first number value is set using the set() method. Then the current thread’s value which returns a number is obtained using the get() method. Then the second numerical value is set using the set() method. Then the current thread’s value which returns a number is obtained using the get() method. Then the first string value is set using the set() method.
Then remove() method is used to remove the first string value that was set using the set() method. Then the current thread’s value is obtained using the get() method, and it returns null because we removed the value that was set using the remove() method. Then remove() method is used to remove the first number value and second number value that was set using the set() method. Then the current thread’s value is obtained using the get() method, and it returns null because we removed the values that were set using the remove() method. The output of the program is shown in the snapshot above.
Advantages of ThreadLocal class in Java
- ThreadLocal class makes the task of multi-threading easier because the state of the object is not shared across the threads.
- There is no need for synchronization since the state of the object is not shared across the threads.
- ThreadLocal avoids the exposure of an object to multiple threads.
Conclusion
In this tutorial, we understand ThreadLocal class’s concept through definition, working of ThreadLocal class, and their methods through programming examples and their outputs.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Java ThreadLocal. Here we discuss an introduction to Java ThreadLocal, how does it work, create, advantages and respective examples. You can also go through our other related articles to learn more –


