Updated June 29, 2023
Definition of Java NIO Path
Java nio path contains the path of the directory or file. Path name will suggest the path of a particular location or an entity like a file or directory. In java, the path is nothing but the interface that introduced the nio file package of java; this was introduced in java version 7. It is helpful to search the specified file or directory.
Introduction to Java NIO Path
The java nio path is a representation of a particular file location. It is an entity that contains two types, i.e., relative path and absolute path. Both path names suggest that the absolute path is the address location relative to the other path.
To use the java nio path, we need to use delimiter as its definition; for Windows, we need to use “\,” and for Linux, we need to use the “/.” The get method converts the string path or a string sequence when we have joined from the path instance or string of path. This method throws an exception for an invalid path if the arguments contain illegal characters.
Key Takeaways
- To retrieve the absolute path, we must pass the complete directory and element list required for the file location.
- To retrieve the relative path, we need to combine both the nio file path together. We can retrieve relative and absolute paths in a single code.
How to Create Java NIO Path Class?
The path instance of java represents the file system path. The java nio path point to either file or a specified directory. In the java nio path, the absolute path contains the full path, whereas the relative file path contains the path to the specified file or directory. The interface of the java nio file path is similar to the class of the java IO file with the interface of the path.
1. Create a Path Instance
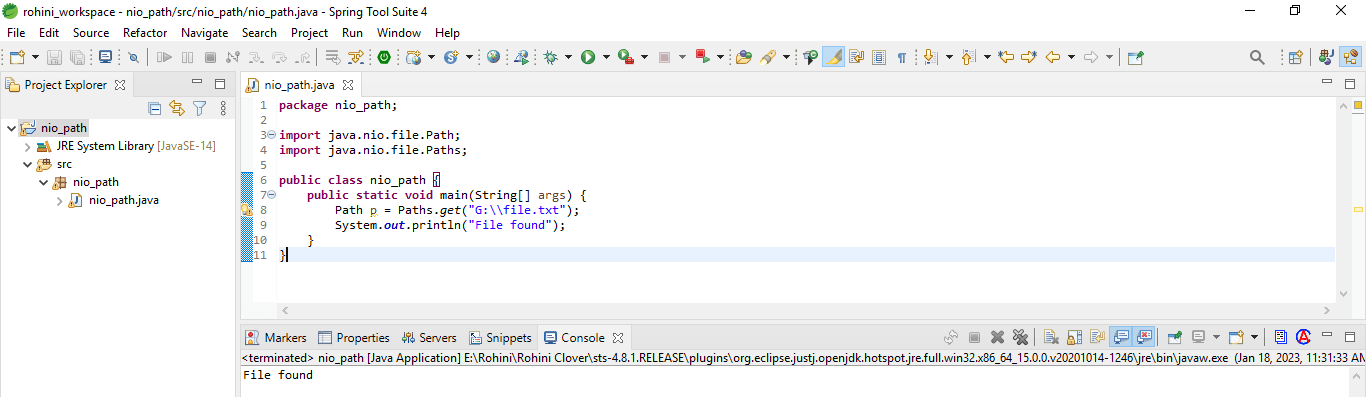
To use the file path of java.nio.file.Path we need to create an instance of the path. We can make the instance of the path to use the static method. The below example shows the creation file path as follows.
Code:
import java.nio.file.Path;
import java.nio.file.Paths;
public class nio_path {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Path p = Paths.get ("G:\\file.txt");
System.out.println ("File found");
}
}In the above example, we use two import statements, first for the path interface and another for the class. We use the Paths method to call the get method that creates the path instance.
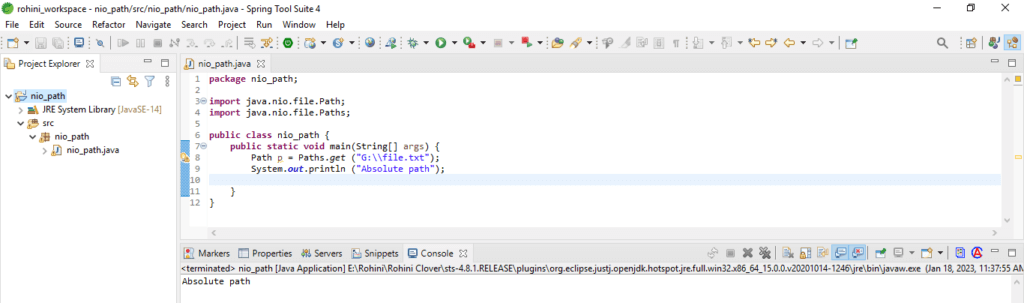
2. Create an Absolute Path
We can create the absolute path in the get method; we need to use the absolute file parameter. Below example shows to create an absolute path in Windows OS as follows.
Code:
import java.nio.file.Path;
import java.nio.file.Paths;
public class nio_path {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Path p = Paths.get ("G:\\file.txt");
System.out.println ("Absolute path");
}
}The “\\” contains the java string, which includes the escape (\ character) that shows that character is located in the string. The above example’s absolute path is “G:\\file.txt”.
The above file path is for the Windows system. We can define the path in the UNIX system. The below example shows the absolute path in the UNIX system.
Example:
Code:
Path p = Paths. get("https://cdn.educba.com/home/file.txt")3. Create a Relative Path
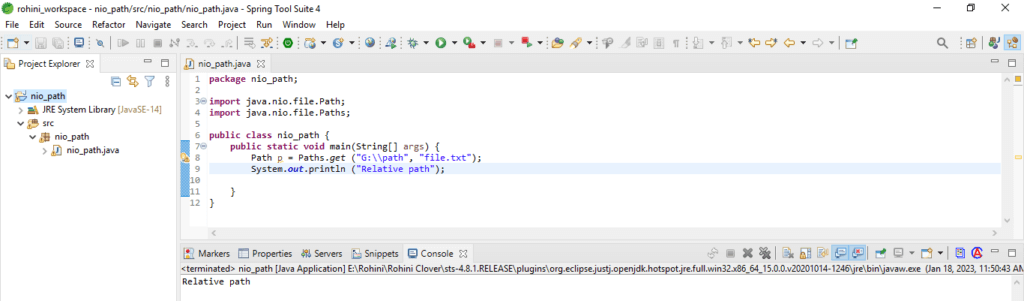
The relative path defines the path that points from one path to the file or directory. The full path is derived from the relative or base path. The below example shows the relative path as follows.
Code:
import java.nio.file.Path;
import java.nio.file.Paths;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Path p = Paths.get ("G:\\path", "file.txt");
System.out.println ("Relative path");
}
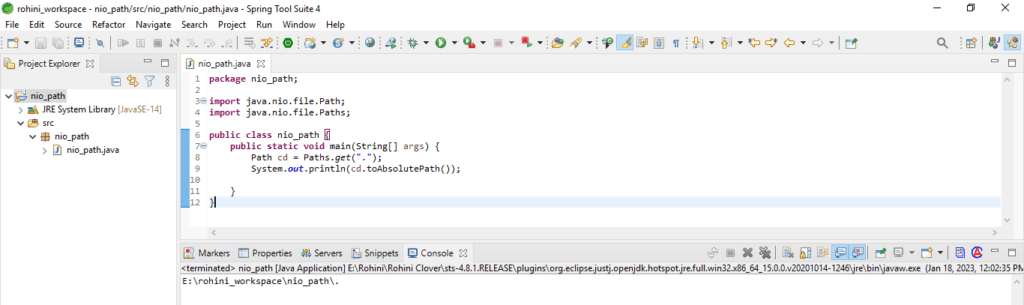
}To work with the relative path, we can use the below code inside the path string. The below code shows the current directory as follows.
Code:
import java.nio.file.Path;
import java.nio.file.Paths;
public class nio_path {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Path cd = Paths.get(".");
System.out.println (cd.toAbsolutePath ());
}
}4. Relativize Method
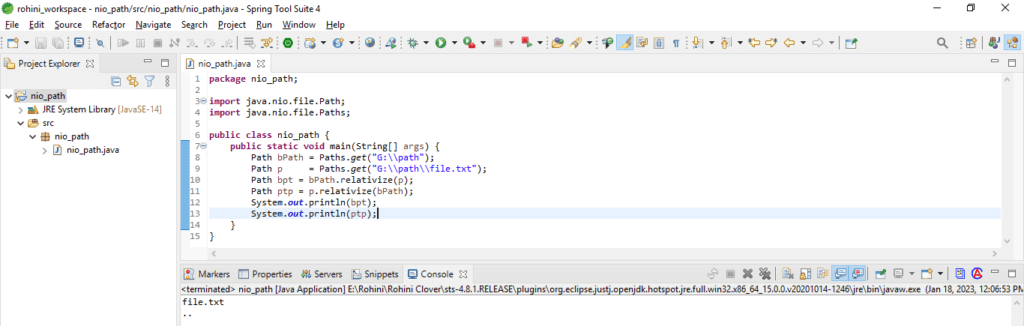
This method creates a new path that represents the second path. Below example shows relativize method as follows.
Code:
import java.nio.file.Path;
import java.nio.file.Paths;
public class nio_path {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Path bPath = Paths.get ("G:\\path");
Path p = Paths.get ("G:\\path\\file.txt");
Path bpt = bPath.relativize (p);
Path ptp = p.relativize (bPath);
System.out.println (bpt);
System.out.println (ptp);
}
}To add the relative path to the “G:\\path,” we get the full path. It will add the relative path to the “G:\\path,” and then we get the relative path.
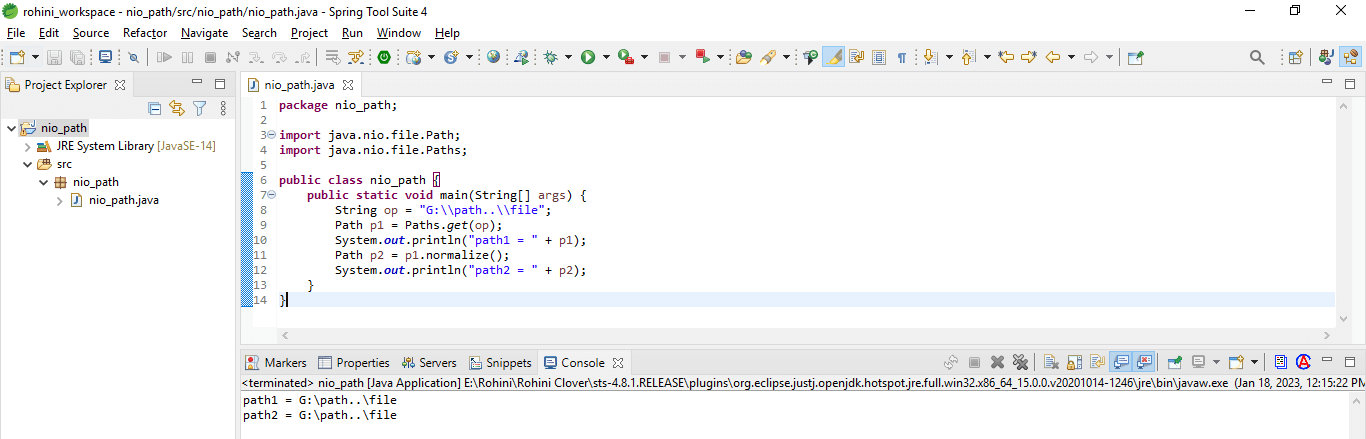
5. Normalize method
This method is part of the path interface and is used for path normalization. Normalization involves removing the (.) code from the path string. The below example shows the normalized method as follows.
Code:
import java.nio.file.Path;
import java.nio.file.Paths;
public class nio_path
{
public static void main(String[] args) {
String op = "G:\\path..\\file";
Path p1 = Paths.get(op);
System.out.println("path1 = " + p1);
Path p2 = p1.normalize();
System.out.println("path2 = " + p2);
}
}The above example first creates the path string with (..) code in the middle. Then it will create the instance of the path and print the instance of the path. Then we need to call the normalize method.
Java NIO Path Methods
The java nio path contains the multiple methods as follows:
- getFileName() – This method returns the object of the file system.
- getName() – This method returns the element name of the file path or path object.
- getNameCount() – This method returns the elements of a path name.
- Subpath() – The purpose of this method is to return a relative path that includes a subsequence element path.
- getParent() – This method is used to return the parent path.
- getRoot() – This method is used to return the path component.
- toAbsolutePath() – This method returns the object representing the absolute path.
- toRealPaht – This method is used to return the real path of the specified file.
- toFile – This method returns the file object that represents the path.
- normalize() – This method is used to return the path that contains the redundant element.
- compareTo() – This method compares two different abstract paths.
- endsWith() – This method tests the path that ends with the given path string.
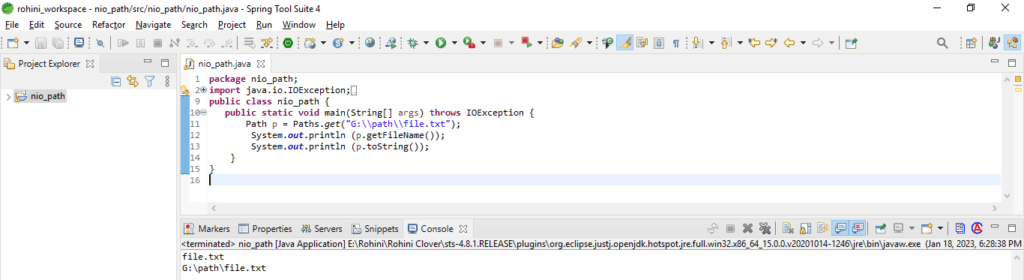
The below example shows java nio path methods as follows. In the below example, we have defined the getFileName and toString methods.
Code:
public class nio_path {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
Path p = Paths.get("G:\\path\\file.txt");
System.out.println (p.getFileName ());
System.out.println (p.toString ());
}
}Examples of Java NIO Path
Below are the mentioned examples:
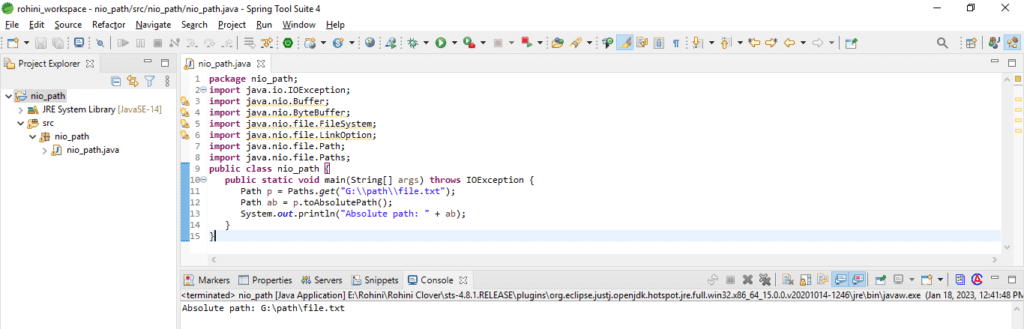
Example #1
In the below example, we have defined the absolute path as follows.
Code:
import java.io.IOException;
import java.nio.Buffer;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import java.nio.file.FileSystem;
import java.nio.file.LinkOption;
import java.nio.file.Path;
import java.nio.file.Paths;
public class nio_path {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
Path p = Paths.get("G:\\path\\file.txt");
Path ab = p.toAbsolutePath ();
System.out.println ("Absolute path: " + ab);
}
}Example #2
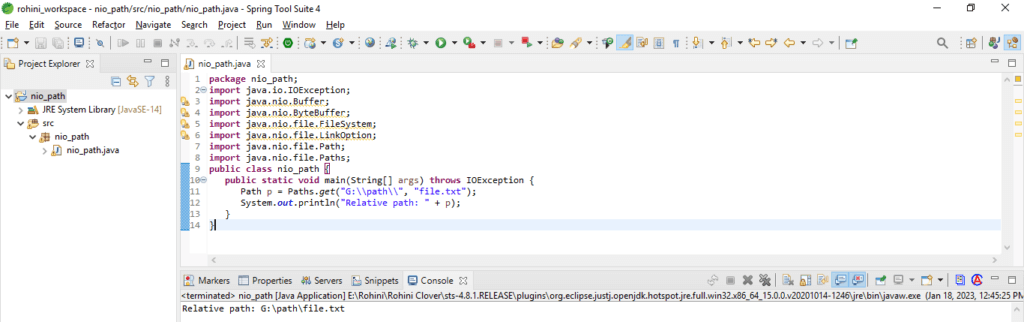
In the below example, we have defined the relative path as follows.
Code:
import java.io.IOException;
import java.nio.Buffer;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import java.nio.file.FileSystem;
import java.nio.file.LinkOption;
import java.nio.file.Path;
import java.nio.file.Paths;
public class nio_path {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
Path p = Paths.get ("G:\\path\\", "file.txt");
System.out.println ("Relative path: " + p);
}
}Conclusion
It is a representation of a particular file location. In java, the Path interface is part of the java.nio.file package. Java version 7 introduced this interface. The get method converts the string path or a string sequence by joining it with the path instance or string of path.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “Java NIO Path” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information,