Updated April 6, 2023

Introduction to Java Locale
Java locale class is a final class in java.util package that helps to present the information according to the geographical region of the user. The information that needs to be displayed is altered according to a specific geographical, political or cultural region, and the operation that requires locate task to be performed is known to be locale-sensitive.
An object of this class uses below five variants as its fields:
- Language
- Script
- Country
- Variant
- Extensions
This does not represent a container of objects; instead is a mechanism for identifying objects. Here Unicode locale contains attributes and keywords that are used to override the default behavior of the locale.
Syntax:
public final class Locale
extends Object
implements Cloneable, SerializableThe above syntax signifies that the Locale class is a final class that means no other class can extend this class.
Locale class implements behavior of two below interfaces:
- Cloneable: Implementing this interface allows this class’s object to generate a field for a field copy of its objects using the object.clone () method.
- Serializable: Implementing this interface allows the object that needs to be transferred over a network to retain its state so that it can be easily restored using readObject.
How does Java Locale Class work?
Java locale class implements identifier with BCP 47 with support for the LDML BCP 47-compatible extensions for locale data exchange.
Java locale class consist of the below fields:
- Language: It is a case -insensitive field that contains the values of the form [a-zA-Z]{2,8}, ISO 639 alpha-2 or alpha-3 language code, or registered language subtags up to 8 alpha letters. Example: “es” used for Spanish, “ja” for japenese.
- Script: It is also a case-insensitive field that contains script in the form –[a-zA-Z]{4}, ISO 15924 alpha-4 script code. Example: Latin, Cyril.
- Country (region): This is a case insensitive field that is used to represent the country or region of locale object of the form –[a-zA-Z]{2} | [0-9]{3}. Example: “IN” (India), “FR” (France).
- Variant: This is a case sensitive field that is used to represent a variant of Locale having their own semantics using values of the form – ( (‘_’|’-‘) SUBTAG)* where SUBTAG = [0-9][0-9a-zA-Z]{3} | [0-9a-zA-Z]{5,8}. Example: “polyton” (Polytonic Greek), “POSIX”.
- Extensions: It is a map that indicates extensions apart from language identification in key-value pair form.
Class has 3 constructors:
- Locale (String language)
- Locale (String language, String country)
- Locale (String language, String country, String variant)
One cannot specify script or extensions. Using any one of the above constructors, one can create a locale object and specify its fields, and this information is used to alter the information to be displayed according to the country or region of the user.
Java Locale Methods
Given below are the java locale methods:
1. getDefault ()
This method returns the default object of the locale according to the calling JVM instance.
Example: If one runs this on France JVM, the Locale object with language French is returned.
Syntax 1:
public static Locale getDefault ()Syntax 2:
public static Locale getDefault (Locale.Category category)2. setDefault (Locale locale1)
This method is used to set the given locale as the default locale for a JVM instance.
3. hashCode ()
This method is an overriding method for the hashCode method in Object Class, where the hashCode value for that object is returned.
Syntax:
public int hashCode ()4. getISOCountries ()
This method returns the list of 2-letter country codes that has been mentioned in ISO 639.
Syntax:
public static String[] getISOCountries ()5. getISOLanguages ()
This method returns 2-letter language codes that are present in ISO 639.
Syntax:
public static String[] getISOLanguages ()6. getLanguage ()
This method is used to display the language code of the calling locale object.
Syntax:
public String getLanguage ()7. getDisplayScript ()
This method is used to get the string representation of the script of the given locale. This method is available from JDK 1.7.
Syntax:
public String getDisplayScript ()8. getDisplayCountry ()
This method is used to display the name of the country to which the locale object belongs to.
Syntax 1:
public final String getDisplayCountry ()Syntax 2:
public String getDisplayCountry (Locale locale1)9. getCountry ()
This method is used to get the ISO 3166 2-letter code for the country that the given locale belongs to.
Syntax:
public String getCountry ()10. equals (Object locale2)
This is an inherited method from the Object class in this class that helps to check whether 2 locale objects are equal or not. It requires an object to a second locale object to be passed as an argument.
Syntax:
public Boolean equals (Object Locale2)11. getDisplayVariant ()
This method is used to display the value stored in a given locale object’s variant field according to the given user.
Syntax 1:
public final String getDisplayVariant ()Syntax 2:
public final String getDisplayVariant (Locale locale1)12. getDisplayName ()
This method is used to display the given locale object’s name according to the user’s perspective.
Syntax 1:
public final String getDisplayName ()Syntax 2:
public String getDisplayName (Locale locale1)13. clone ()
This method is used to copy one object’s field-to-field value to other objects of the same class. This method is an inherited method from Cloneable Interface and helps to create a clone object of a given locale object.
14. getAvailableLocales ()
This method is used to get the array of all installed locales.
Syntax :
public static Locale[] getAvailableLocales15. getDisplayLanguage ()
This method returns the language associated with a given locale.
Syntax 1:
public final String getDisplayLanguage ()Syntax 2:
public final String getDisplayLanguage (Locale locale1)16. getISO3Country ()
This method is used to get a 3-letter abbreviation of locale country.
Syntax:
public String getISO3Country ()17. getISO3Language ()
This method is used to get a 3-letter abbreviation of ones locale language object.
Syntax:
public String getISO3Language ()18. toString ()
This method returns the String representation of the locale object.
Syntax:
public final String toString ()19. forLanguageTag (StringlanguageTag)
This method is used to get the locale object for the given language tag string according to IETF BCP 47.
Syntax:
public static Locale forLanguageTag (String langTag)Examples of Java Locale
Given below are the examples:
Example #1
Example to use Locale Class calling Locale constructor.
Code:
import java.util.Locale;
public class demo1 {
public static void main (String[] args)
{
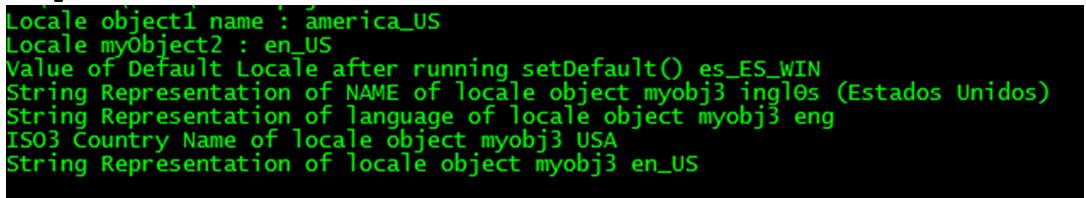
Locale object1 = new Locale ("America", "US");
Locale myObject2 = Locale.getDefault ();
System.out.println ("Locale object1 name : " + object1);
System.out.println ("Locale myObject2 : " + myObject2);
Locale.setDefault (new Locale ("es", "ES", "WIN"));
System.out.println ("Value of Default Locale after running setDefault () "+Locale.getDefault ());
System.out.println ("String Representation of NAME of locale object myobj3 " + myObject2.getDisplayName ());
System.out.println ("String Representation of language of locale object myobj3 " + myObject2.getISO3Language ());
System.out.println ("ISO3 Country Name of locale object myobj3 " + myObject2.getISO3Country ());
System.out.println ("String Representation of locale object
myobj3 " + myObject2.toString ());
}
}Output:
Example #2
Code:
import java.util.Locale;
public class demo1 {
public static void main (String[] args)
{
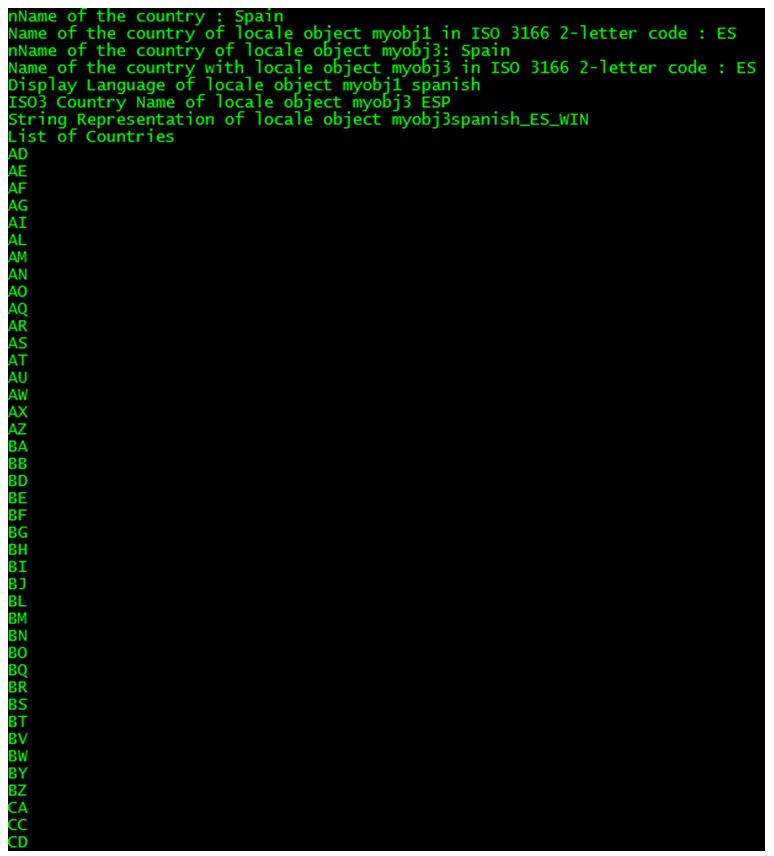
Locale myobj1= new Locale ("SPANISH", "ES", "WIN");
Locale myobj3= (Locale) myobj1.clone ();
System.out.println ("nName of the country : " + myobj1.getDisplayCountry ());
System.out.println ("Name of the country of locale object myobj1 in ISO 3166 2-letter code : " + myobj1.getCountry ());
System.out.println ("nName of the country of locale object myobj3: " + myobj3.getDisplayCountry ());
System.out.println ("Name of the country with locale object myobj3 in ISO 3166 2-letter code : " + myobj3.getCountry ());
System.out.println ("Display Language of locale object myobj1 " + myobj1 .getDisplayLanguage ());
System.out.println ("ISO3 Country Name of locale object myobj3 " + myobj3.getISO3Country ());
System.out.println ("String Representation of locale object myobj3" + myobj3.toString ());
System.out.println ("List of Countries ");
String[] listCountries = myobj3.getISOCountries ();
for (String s:listCountries){
System.out.println (s);
}
}
}Output:
Example #3
Code:
import java.util.Locale;
public class demo1 {
public static void main (String[] args)
{
Locale myobject1 = new Locale ("FRENCH", "FR",
"WIN");
Locale myobject2 = new Locale ("FRENCH", "FR", "WIN"); System.out.println ("Variant of object 1:" + myobject1.getDisplayVariant ());
System.out.println ("Whether the two locale objects are equal:" + myobject1.equals (myobject2));
Locale[] arrLocales = Locale.getAvailableLocales ();
System.out.println ("\nName of Locales are : ");
for (int i = 1; i<arrLocales.length/10; i++)
System.out.println (i + ":" + arrLocales[i]);
}
}Output:

Conclusion
Locale class is a part of the java.util package that helps to alter the information according to the specific geographical or political region. A locale-sensitive operation use this class to store information related to each variant of the locale object. Many methods are provided in this class to get the information related to the locale object.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Java Locale. Here we discuss the introduction to java locale, how does the local class work with 19 methods and respective examples. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –


