Updated June 14, 2023

Introduction to Java LocalDateTime
LocalDateTime in java displays the local date and time on the output screen. The default format for displaying the time is YYYY-MM-DD-hh-mm-ss-zzz. The different factors in showing the date and time are the year, month, day, hours, minutes, seconds, and nanoseconds. The date and time can be added to a particular number of days, subtracted by a number of days, and finally, the output can be produced very smoothly. The LocalDateTime class is a final class; hence, no extension of the class is allowed. LocalDateTime class is a value-based class used to check whether two dates and times are equal to each other or not with equals().
Syntax of Java LocalDateTime
The Java LocalDateTime class is a part of java.time package. We can create the java instance of the class in the following manner.
The following is the syntax.
import java.time.LocalDateTime;We can also pass values to the of() in the LocalDateTime class.
The syntax of the following is given below:
LocalDateTime Idt= LocalDateTime.of(2011,15,6,6,30,50,100000);We can also use the parse() and pass the values of the time in String representation.
LocalDateTime Idt= LocalDateTime.parse("2011-11-10T22:11:03.46045");Also, we can use ofInstant() by passing ID and Zone ID information.
LocalDateTime Idt= LocalDateTime.ofInstant(Instant.now(), ZoneId.SystemDefault());Methods of LocalDateTime in Java
There are different methods in the Java LocalDateTime class.
- String format(DateTimeFormatter formatter): Used to format the date and time using the specified formatter.
- LocalDateTime minusDays(long days): Used to format the date and time using specific days, which are to be subtracted from the respective date.
- LocalDateTime plusDays(long days): Used to add a certain number of days to the current date and then print the output respectively.
- int get(TemporalField field): Used to get the date and time values as an integer format that is int.
- static LocalDateTime now(): We use this method to retrieve the default date and time from the current time zone, which serves as the default time zone.
Examples of Java LocalDateTime
Given below are the examples mentioned:
Example #1
In the first coding example, we will witness the format() used in java to format a specific amount of code.
Code:
import java.time.LocalDateTime;
import java.time.format.DateTimeFormatter;
public class LocalDateTimeExample
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
LocalDateTime now = LocalDateTime.now();
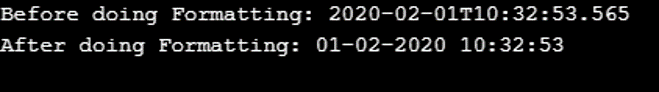
System.out.println("Before doing Formatting: " + now);
DateTimeFormatter format = DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern("dd-MM-yyyy HH:mm:ss");
String fDTime = now.format(format);
System.out.println("After doing Formatting: " + fDTime);
}
}Output:
As shown in the sample output, we can see that the date and time before and after formatting have been shown.
Example #2
In the second program, we will see the working of the minusDays() when a certain date subtracts up certain values of days from the date and then finally prints the specific output.
Code:
import java.time.LocalDateTime;
import java.time.format.DateTimeFormatter;
public class LocalDateTimeExample2
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
LocalDateTime dt1 = LocalDateTime.of(2018, 2, 14, 15, 22);
LocalDateTime dt2 = dt1.minusDays(100);
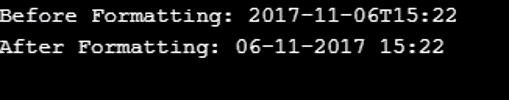
System.out.println("Before Formatting: " + dt2);
DateTimeFormatter format = DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern("dd-MM-yyyy HH:mm");
String fDTime = dt2.format(format);
System.out.println("After Formatting: " + fDTime );
}
}In the above code, we subtract a certain number of days; in this case, it is 100 from the date 14th February 2018, as given in the code. We get the answer before formatting as well as after formatting, which is shown below.
Output:
Example #3
The plusDays() function is highly similar to the minusDays() function, with the only distinction being that it adds days to the current date instead of subtracting a specific number of days. So in this coding example, we will add a certain number of days to the existing date and time.
Code:
import java.time.LocalDateTime;
import java.time.format.DateTimeFormatter;
public class LocalDateTimeExample3
{
public static void main(String[] args) {
LocalDateTime dt1 = LocalDateTime.of(2018, 1, 8, 12, 34);
LocalDateTime dt2 = dt1.plusDays(60);
System.out.println("Before Formatting: " + dt2);
DateTimeFormatter format = DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern("dd-MM-yyyy HH:mm");
String fDTime = dt2.format(format);
System.out.println("After Formatting: " + fDTime );
}
}In this sample code, we give the date as 8th January 2018 in the default date provided. And we see the added days, that is, 60 days. When we add 60 days to the code, we see that the date has changed, and it has been 9th March 2018. Time has remained the same. Only the number of days has changed, moving the date from 8th January to 9th March.
Output:
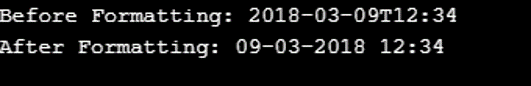
Example #4
In this coding example, we will see the features of the get(), where we will get the integer values of the date and time, respectively. We will also see a coding example to illustrate the program properly.
Code:
import java.time.LocalDateTime;
import java.time.temporal.ChronoField;
public class LocalDateTimeExample4
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
LocalDateTime b = LocalDateTime.of(2018, 3, 10, 14, 36);
System.out.println(b.get(ChronoField.DAY_OF_WEEK));
System.out.println(b.get(ChronoField.DAY_OF_YEAR));
System.out.println(b.get(ChronoField.DAY_OF_MONTH));
System.out.println(b.get(ChronoField.HOUR_OF_DAY));
System.out.println(b.get(ChronoField.MINUTE_OF_DAY));
}
}The sample code gives the Day of the Week, Day of the Year, Day of the Month, Hour of the day, and Minute of the day in chronological order. The program calls the ChronoField package to ensure that it runs correctly and produces the specific output as required.
Output:

Example #5
In this coding example, we will see the now() in the LocalDateTime class in Java programming language. This program will return the current date and time along with the seconds in the program.
Code:
import java.time.LocalDateTime;
import java.time.format.DateTimeFormatter;
public class LocalDateTimeExample5
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
LocalDateTime dt1 = LocalDateTime.now();
DateTimeFormatter format = DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern("dd-MM-yyyy HH:mm:ss");
String fDTime = dt1.format(format);
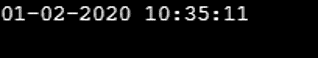
System.out.println(fDTime);
}
}Output:
The output clearly displays the date and time of the current time zone in the format of hh-mm-ss, providing a clear representation.
Conclusion
This article has seen several programs illustrating all the methods and functions inside the LocalDateTime class. Also, we know the syntax of the LocalDateTime class that is present. Beyond this, we also notice the output of several programs. In aeronautical engineering, professionals frequently utilize the LocalDateTime class to maintain and monitor an aircraft’s current date and time, observing any changes in time zones and their impact on the watch time.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Java LocalDateTime. Here we discuss the introduction, the LocalDateTime methods, and different examples and their code implementation. You may also look at the following articles to learn more –


