Updated December 16, 2023
Introduction to Java Collection Framework
Java collection framework, which is included in the Java platform and it is the representation of a group of objects such as the classic Vector class, Array List, Hash Map, Hash Set and even other collections frameworks, is a unifying architecture for describing and manipulating the collections that allowed for them to be modified with regardless of implementation details that provides an architecture for storing and manipulating a collection of objects it capable of doing any data operations such as searching, sorting, insertion, manipulation, and deletion even single unit of objects in Java is referred to as a collection.
What is Java Collection Framework?
Every programming language uses the collections, and they return the data items that can be combined with a number of different elements into a single entity. Mainly, it was difficult to understand and build with programmers to develop algorithms that worked for many types of collections before the Collections Framework was used. Sometimes, other frameworks will call and be used with certain conditions. Some Collection classes, which include Vector, Stack, Hash table, and Arrays, were included with Java, but it all had some drawbacks to achieving it.
Java Collections Framework components
With the support of key interfaces, the Collections framework is easier to grasp. These interfaces are implemented and the collections classes provide concrete functionality. The interface for collecting data is at the top of the hierarchy. The Collection interface provides all general-purpose methods that all collections classes must provide or throw an error like “UnsupportedOperationException”. It adds some functionality for iterating with over-collection elements by using the “for-each loop” statement to the Iterable interface. Classes extend to implement this interface except for the Map interface and all other collection interfaces. This collection is implemented by the List (indexed, ordered) and Set (sorted) interfaces, as well as Map(key, value) pairs.
Interfaces
It’s one collection component that can be abstracted with a data type to represent the collection. The framework’s root interface in java.util.Collection by using this imports the significant class of the framework, with some default methods like add(), remove(), size() etc. Mainly it has below default interfaces like Map, Set, and Deque all come under the util package.
Implementation classes
The framework libraries provide the Collection implementation classes. And the Java programs, which may utilize them to create many types of collections based on this parent and root class of the collection package. It includes some types like ArrayList, HashMap, TreeMap, LinkedList, Doubly-LinkedList, etc.
Algorithms:
In this section, they perform some crucial collections related to the tasks, such as sorting lists and other data structures, which include performing the data operations from the user end.
Java collection framework Interfaces
The Collections framework has contained a number of Interfaces and their features to define the basic nature of various collection types. Like Collection, Set, List, Map, Queue, Dequeue, SortedMap, etc. These interfaces will be used and implemented with some type of hierarchy provided by the collection framework. Mainly, the collection is the parent root of this hierarchy. If we use the List interface, it maintains the data sequence order of the elements. It does not need the Uniqueness. When uniqueness comes, it will move to the Set and not accept the duplicates. The Queue is another interface that holds the user data in a different sequence. Using the Deque interface, it performs the data operations. The map interface represents the object that is referred to as both keys and value pairs for storing and retrieving the elements.
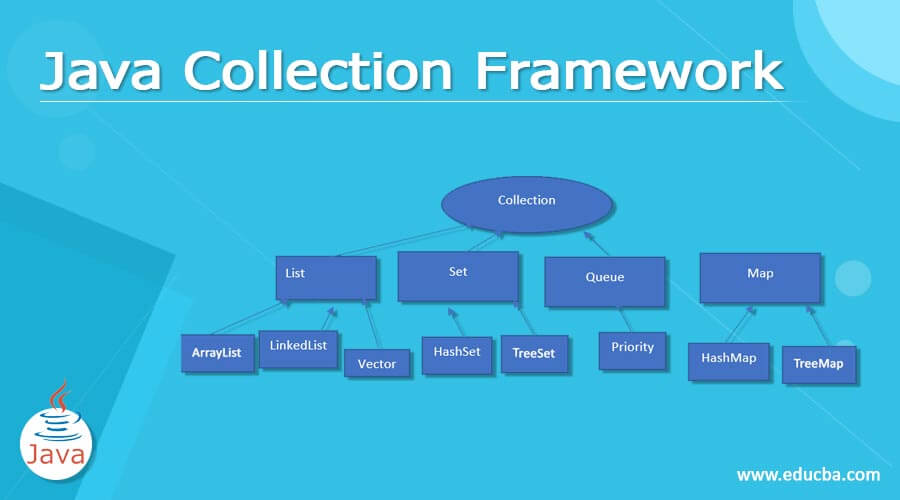
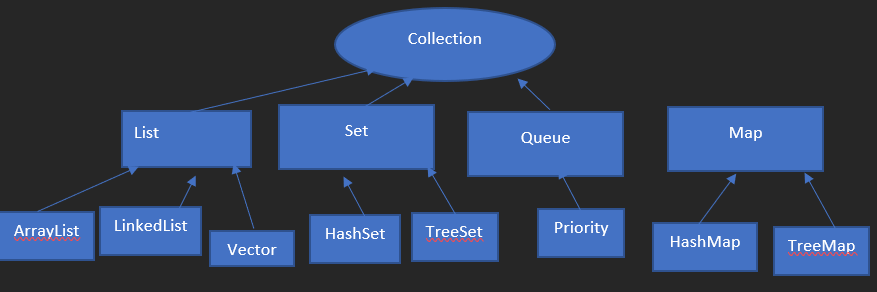
Java Collection Framework Architecture
The above diagram is the basic architecture and hierarchy flow of the Collection framework. Map Interface is separated, called, and used with its default classes. We know that the Collection interface is the root node of all other interfaces and classes. Even though the object is played the role here because it’s the base and parent of all other Interfaces and Classes. Some collection interfaces use fixed size, so it’s not increased dynamically during the run time; also, it calculates the memory management.
Use an Iterator
Generally, the ‘Iterator’ is one of the interfaces, and it is the main part of the collection framework for iterating the data using the loop conditions.
It is also used to navigate the collection for storing, retrieving, and deleting the data element if not required. The public interface calls and is imported from the util package, and the programmer accesses its default methods. Some of the methods like hasNext(), next(), and remove() are the three different methods with different data types hasNext() will return only the boolean condition, the next() method returns only the object value, and remove() return void this method. It has some type like ListIterator for traversing the data in both forward and backward directions.
Use a Comparator
The Instances of different classes can be compared using the Comparator Interface.
Generally, the class requires a natural ordering for its objects, so it implements using the Comparable Interface.
Use Comparator to design an externally configurable ordering behavior that overrides the default ordering behavior. A comparator interface is also used to sort the objects of a user-defined class.
The return value of the TreeSet interface, which compares using the comparator set and is used to sort the elements of the same set in a certain order, is returned by this method. If the set follows the default or natural ordering pattern, it will return a Null value.
Conclusion
The Java collections framework provides access to pre-packaged data structures and manipulation methods. A collection is a type of object that may keep track of other things by storing references to them. The operations that can be performed on each type of collection are defined by the collection interfaces.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to the Java Collection Framework. Here we discuss the Introduction, What Java Collection Framework is, components, and examples with code implementation for better understanding. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –