Introduction on Java Booleans
In day to today life, we often make decisions about each of our activities, situations, visions, results, happenings, etc. The value of our decision is either of the twofold: yes or no; true or false; on or off; go or no-go etc. Programming does not fall under any exception. In programming, based on our core logic and use cases, we need to make decisions and based on those decisions; we need to write code accordingly. As a programming language, Java is not an exception and allows us to provide a special data type called “Boolean” to use them in our code for decision-making purposes. A Java Boolean variable or A Boolean expression can take either of the two values: true or false.
Let us discuss about Booleans from a java programming perspective.
Types of Java Boolean Value
Following are the different types of Java Boolean Value:
1. Keyword Boolean with Variable Names
You only have two options with you regarding the values of a Boolean type variable in java. Value to a Boolean type is either true or false. There is no other option available. Don’t rush to ask for help with Java homework or tasks; continue reading to understand the Java Booleans. You need to use keyword Boolean along with variable names and assign the value (true or false) to it.
Syntax:
Boolean <variable_name> = <value>, where value is either true or falseFor example:
boolean bool = true, where bool is the variable name and associated with value as true
boolean bool2 = false, where bool is the variable name and associated with value as false
Code Example 1:
public class BooleanInJava {
public static void main(String[] args){
boolean bool = true ;
boolean bool2 = false;
System.out.println(bool);
System.out.println(bool2);
}
}Output:

2. Boolean Type Variable
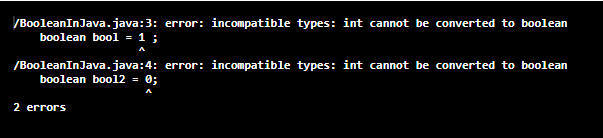
What if you provide values other than true or false to a Boolean type variable?
For example:
boolean bool = 1 ;
boolean bool2 = 0;
You will get an error for this.
Code Example 2:
public class BooleanInJava {
public static void main(String[] args) {
boolean bool = 1 ;
boolean bool2 = 0;
System.out.println(bool);
System.out.println(bool2);
}
}Output:
3. Feature of Boolean
Now, how to use this feature of Boolean effectively?
We can use it to make decisions in our program. I mean to say that you can use to test some deciding factors in your program by using conditional operators to get or print a Boolean value. This is testing of condition of a Boolean Expression. The program will evaluate this expression, and a decision will be given accordingly.
Let us have some examples:
Code Example 3:
public class BooleanInJava {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int num1 = 10;
int num2 =11;
System.out.println(num1 > num2); // returns false, because 11 is higher than 10
System.out.println(num2 > num1); // returns true, because 11 is higher than 10
System.out.println(num1 < num2); // returns true, because 10 is lesser than 11
System.out.println(num2 <num1); // returns false, because 10 is lesser than 11
}
}Output:

How Boolean Value Works?
In this article, we will point out how Boolean works, which means how we can use the feature of Booleans in our program or use cases. As Boolean is helping us to make decisions, we can put this decision logic inside our conditional expressions such as: in while loop evaluation or if-else decision making. First, let us look at the Boolean operators, which will be used to generate a Boolean value from a Boolean expression and eventually use that value in making decisions. We will use here the logical operators for Boolean, which are: | , & , ^ , ! , || , && , == , != . Let us take two Boolean variables, num1 and num2, for use.
| Symbol of Boolean operators | Name of the corresponding Symbol |
| | | OR |
| & | AND |
| ^ | XOR |
| ! | NOT |
| != | NOT EQUAL |
| && | Short circuit AND |
| || | Short circuit OR |
| == | EQUAL |
Please check the table for your understanding of how evaluation is happening in Boolean expressions. This understanding is very important to clear your concepts:
| Variables/Boolean Expressions | num1 | num2 | num1|num2 | num1&num2 | num1^num2 | !num1 | !num2 |
|
Values/Result of evaluations |
true | true | true | true | false | false | false |
| true | false | true | false | true | false | true | |
| false | true | true | false | true | true | false | |
| false | false | false | false | false | true |
true |
4. Public Class
Code Example 4:
public class BooleanInJava {
public static void main(String[] args) {
boolean num1 = true;
boolean num2 = false;
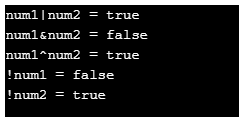
System.out.println("num1|num2 = "+(num1|num2));
System.out.println("num1&num2 = "+(num1&num2));
System.out.println("num1^num2 = "+(num1^num2));
System.out.println("!num1 = "+(!num1));
System.out.println("!num2 = "+(!num2));
}
}Output:
Let us see some more code examples.
5. Boolean Operators
Code Example 5:
Here we will compare two Boolean variables and assign values to them and then create Boolean expression for those using Boolean operators and then print them to see the final output.
public class BooleanInJava {
public static void main(String[] args) {
boolean num1 = true;
boolean num2 = false;
boolean num3=(num1==num2); // Boolean expression evaluating whether values of num1 and num2 are equal or not
System.out.println(num1);
System.out.println(num2);
System.out.println(num3); //will return false as num1 and num2 have different values
}
}Output:
6. Boolean Objects.
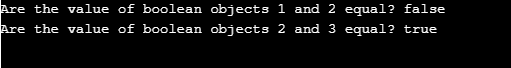
Code Example 6:
Here we will compare two Boolean objects.
public class BooleanInJava {
public static void main(String[] args) {
boolean boolObj1=new Boolean("TRUE");
boolean boolObj2=new Boolean("FALSE");
boolean boolObj3=new Boolean("FALSE");
boolean decision=(boolObj1==boolObj2); // evaluating values of boolObj1 and boolObj2
System.out.println("Are the value of boolean objects 1 and 2 equal? "+decision);
boolean decision2=(boolObj3==boolObj2); // evaluating values of boolObj2 and boolObj3
System.out.println("Are the value of boolean objects 2 and 3 equal? "+decision2);
}
}Output:
Conclusion – Java Boolean
All of the comparisons and conditions in Java are primarily based on Boolean expressions; hence you need to use them in an effective manner. In this topic, you have learned about many aspects of Boolean values but, you need to use them effectively based on your business/ client requirements and use cases.
Recommended Articles
This has been a guide to Java Boolean. Here we have discussed what is Java Boolean, how it works? Explaining the logical operations with Codes and Output. You can also go through our other suggested articles to learn more–



