Updated December 30, 2023
Table of Content
- Introduction
- Types of Java Base64 Encoding
- Methods of the Java Base64 class
- Examples of Java Base64 Encoding
- Use Case of Base64 Encoding
- Performance of Base64 Encoding
Introduction to Java Base64 Encoding
The Base64 java class used to perform the encryption. Java 8 introduced the Base64 class, which is available in the java.util.Base64. The Base 64 is a strategy or scheme to encode the binary data into encoded text format, which can be easily sent over the internet without corrupted and data loss with securely. The Base 64 technique is to map the binary data to the [A-za-z0-9+/] set of characters. This class provides the methods to use to perform the encode and decode java provided the build-in class Base64. This class also provides three different encodings and decoding technique that can be used at different levels. The static Base64.The encoder class is the nested class of Base64.
Types of Java Base64 Encoding
There are three types are
Simple Encoding
Here, encode the data by mapping to the character set in “A-Za-z0-9+/” and does not add any line separator character in the output. If outside any character contain other than base64, then the decoder rejects it.
For encoding and decoding operations in this type, use the Base64 alphabets specified by Java in RFC 4648 and RFC 2045. The encoder does not add any character that separates the line, and the decoder does not allow characters outside the Base64 alphabet.
URL and filename Encoding
Here encode the data by mapping to the character set in “A-Za-z0-9+ _” and does not add any line separator character in the output. If outside any character contain other than base64, then the decoder rejects it. An encoded output is a URL and filename safe.
In this type, to perform the encoding and decoding operation, the Base64 alphabets are being used that are specified by java in RFC 4648. This type’s working is the same as basic encoding, but the output of this is URL.
MIME Encoding
Here encode the data by mapping to MIME friendly format. The encoded output specifies lines of 76 characters each, not exceeding this limit. Carriage returns (‘\r’) are used for line breaks, followed by ‘\n’ as the line separator. No line separator is added at the end of the output. In the decoding operation, all line separators and characters not present in the base64 are ignored.
To perform encoding and decoding operations, it uses the Base64 alphabet specified in RFC 2045. The encrypted result must be in lines of no more than 76 characters. The encoded output doesn’t include a line separator at its conclusion. During decryption, any characters or line separators absent from the Base64 alphabet table are disregarded.
Methods of the Java Base64 class
Following are the methods:
1. getEncoder() – This is a method of Base64 class that gives the Base64.Encoder object, which is encoded by Basic type base64 encoding.
Syntax:
public static Base64.Encoder getEncoder()2. getUrlEncoder() – This is a method of the Base64 class that gives the Base64.Encoder object, which is encoded by URL and Filename base64 encoding.
Syntax:
public static Base64.Encoder getUrlEncoder()3. getMimeEncoder() – This is a method of the Base64 class that gives the Base64.Encoder object, which is encoded by MIME type base64 encoding.
Syntax:
public static Base64.Encoder getMimeEncoder()4. getMimeEncoder(int lineLength, byte[] lineSeparator) – This is a method of Base64 class that gives the Encoder object which is encoded with given line length and line separators by MIME type base64 encoding.
Syntax:
public static Base64.Encoder getMimeEncoder(int lineLength, byte[] lineSeparator)5. encode(byte[] src) – This method returns an encoded byte array of given all bytes array by using the Base64 encoding.
Syntax:
public byte[] encode(byte[] src)6. encode(byte[] src, byte[] dst) – This method writes an encoded byte array of given all bytes array to the given output byte array, starting at offset 0 by using the Base64 encoding.
Syntax:
public int encode(byte[] src, byte[] dst)7. encodeToString(byte[] src) – This method returns an encoded byte array into a string by using the Base64 encoding.
Syntax:
public String encodeToString(byte[] src)8. encode(ByteBuffer buffer) – This method returns buffer whose position will be zero and length of the number of resulting encoded bytes of all remaining bytes from the given buffer byte into a newly-allocated ByteBuffer by using the Base64 encoding.
Syntax:
public ByteBuffer encode(ByteBuffer buffer)9. wrap(OutputStream os) – This method returns the output stream of encoding byte data by using Base64 encoding.
Syntax:
public OutputStream wrap(OutputStream os)10. withoutPadding() – This method returns the encoder’s object, which is encoded but without adding any character at the end for padding.
Syntax:
public Base64.Encoder withoutPadding()Examples of Java Base64 Encoding
Here are the following examples mention below
Example #1
Examples for the Base64 different types of Encoding in java:
Next, we write the java code to understand the Base64 Encoder class more clearly with the following example where we encode the string message by using all three different type of encoding, as below –
Code:
package p1;
import java.util.Base64;
import java.util.UUID;
public class Demo {
public static void main( String[] arg) {
try {
// Simple string message to encode
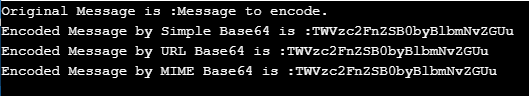
String message = "Message to encode.";
// display original message
System.out.println("Original Message is :"+message);
// Encode message to basic Base64 format
String EncodeBasicBase64 = Base64.getEncoder().encodeToString(message.getBytes());
// display Basic or simple encoded message
System.out.println("Encoded Message by Simple Base64 is :"+EncodeBasicBase64);
// Encode message to URL Base64 format
String EncodeUrlBase64 = Base64.getUrlEncoder().encodeToString(message.getBytes("utf-8"));
System.out.println("Encoded Message by URL Base64 is :" +EncodeUrlBase64);
// Encode message to MIME Base64 format
String EncodeMimeBase64 = Base64.getMimeEncoder().encodeToString(message.getBytes("utf-8"));
System.out.println("Encoded Message by MIME Base64 is :" +EncodeMimeBase64);
}catch(Exception e)
{
}
}
}Output:
Example #2
Next, we write the java code to understand all the methods of the Base64 Encoder class more clearly with the following example, as below –
Code:
package p1;
import java.util.Base64;
public class Demo {
public static void main( String[] arg) {
// Simple string message to encode
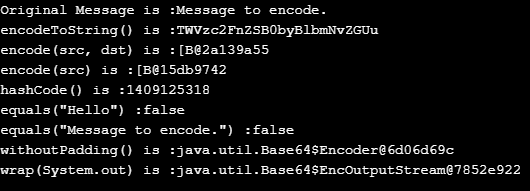
String message = "Message to encode.";
// display original message
System.out.println("Original Message is :"+message);
// Encode message to basic Base64 format
String EncodeBasicBase64 = Base64.getEncoder().encodeToString(message.getBytes());
// Encode message to basic Base64 format
System.out.println("encodeToString() is :" +EncodeBasicBase64);
byte src[]= {10,20};
byte dst[]= new byte[4];
Base64.getEncoder().encode(src, dst);
System.out.println("encode(src, dst) is :" +dst);
System.out.println("encode(src) is :" +Base64.getEncoder().encode(src));
System.out.println("hashCode() is :" +EncodeBasicBase64.hashCode());
System.out.println("equals(\"Hello\") :" +EncodeBasicBase64.equals("Hello"));
System.out.println("equals(\"Message to encode.\") :" +EncodeBasicBase64.equals("Message to encode."));
System.out.println("withoutPadding() is :" +Base64.getEncoder().withoutPadding());
System.out.println("wrap(System.out) is :" +Base64.getEncoder().wrap(System.out));
}
}Output:
Use Case of Base64 Encoding
Here are some use cases with scenarios are as follows :
1. Data URLs in Web Development
In Data URLs, When you want to embed small binary files, such as images, within a web page without making addititonal HTTP requests.
- Solution: Embedding images directly in HTML, CSS, or JavaScript using data URLs. This reduces the number of server requests and improves page load times.
2. Transmitting Binary Data in JSON
In Transmitting Binary Data, When you need to include binary data, like images or files, in JSON data structures.
- Solution: Sending Binary data with JSON payloads, especially in environments where transmitting raw binary is not feasible.
3. Authentication
In Authentication, When handling credentials or tokens that may contain binary data.
- Solution: Encoding binary data, such as cryptographic digests or signatures, in authentication tokens or headers.
4. XML and Email Attachments:
When including binary data, such as images or files, in XML documents or email attachments.
- Solution: Encoding binary data within XML elements or email bodies, allowing for the inclusion of non-textual information.
5.Database Storage
Storing binary data in database that may not supported raw binary formats.
- Solution: Encoding binary data before storage in database, making it easy to store and retrieve data in text-friendly format.
Performance of Base64 Encoding
Base64 encoding, while versatile, introduces an overhead due to the expansion of data size. Since every three bytes of binary data result in four Base64-encoded characters, the encoded output is approximately 33% larger than the original binary data. While this expansion may lead to increased data transmission and storage requirements, the performance impact is generally negligible for smaller pieces of data.
However, when dealing with large datasets, the increased size may contribute to higher bandwidth usage and longer processing times. Developers should be mindful of this trade-off and evaluate the specific requirements of their applications, considering factors such as network efficiency and storage constraints, when deciding whether to use Base64 encoding.
Conclusion
The Base64 class is introduced in java 8, which contains two nested class, Encoder and Decoder. This Base64 encoder class can be used to perform the encryption to the byte data, which is available in the java.util.Base64 package of the Java API.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “Java Base64 Encoding” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.