Updated February 10, 2023
Introduction to Java 8 Predicate
Java 8 predicate is defined in the package of java.util. In Java, a functional interface is an interface that allows the abstract method to be called from within the scope interface. There are multiple types of functional interfaces defined in java, like predicate, supplier, and consumer. The return type of java lambda function is a functional interface. The predicate interface is defined in Java, which improves the application’s code manageability.
Key Takeaways
- At the time of working with predicate, we are using five methods of predicate i.e. test, or, and, isEqual, and negate.
- We are defining the functional interface of java 8 predicate method by using the package name as java.util. While using the predicate method, we can improve code manageability.
What is Java 8 Predicate?
The java 8 predicate is nothing but a user interface that represents the predicate of a single argument. It contains the test functional method. It is a single argument that returns the true and false values. It will take a single argument and return results in true and false conditions. We are using it in an assignment target for method reference and lambda expression.
In our day-to-day programming, we use predicate. Predicate can be used to define whether a condition is true or false. We can use interfaces to implement java 8 predicate. Predicate is a function that takes a single argument and returns a Boolean value. In java, we don’t have standalone functions, so we define the interfaces for creating the object for specified functions. To interact with the predicate, we use lambda in Java.
Java 8 Predicate Interface Functional
Java 8 predicate is defining the functional interface. The below example shows the java 8 predicate interface as follows. In the below example, we are creating the class name as PredInt and creating the predicate; after creating the predicate, we are calling the method of the predicate. We are calling the test method of predicate as follows.
Code:
import java.util.function.Predicate;
public class PredInt {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Predicate<Integer> pr = p -> (p > 13);
System.out.println (pr.test (10));
}
}Output:
Below is an example of java 8 predicate functional interface. We are creating the class name as PredInt, checking the age of the student. We are defining the student’s age; if the age is greater than 15, it will return true; if the age is less than 15, it will return a false value. We are using and calling the predicate interface as follows.
Code:
import java.util.function.Predicate;
public class PredInt {
static Boolean checkAge (int stud_age){
if(stud_age > 15)
return true;
else return false;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Predicate<Integer> pred = PredInt::checkAge;
boolean res = pred.test (20);
System.out.println (res);
}
}Output:
Java 8 Predicate Methods Examples
To create and call the predicate in java we use multiple methods.
1. isEqual (object targetref)
This method returns the predicate value that was used to determine whether two arguments are equal according to the objects. In this method, T is the type of argument for the specified predicate. The below example shows isEqual predicate method.
Code:
import java.util.function.Predicate;
public class PredMethod {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Predicate<String> pred = Predicate.isEqual ("ABC");
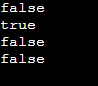
System.out.println (pred.test("PQR"));
System.out.println (pred.test("ABC"));
System.out.println(pred.test("CBC"));
System.out.println(pred.test("ABD"));
}
}Output:
2. and (predicate other)
This method returns the composed predicate for the specified predicate that represents the logical AND. The below example shows the predicate method.
Code:
import java.util.function.Predicate;
public class PredMethod
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Predicate<Integer> pred1 = i -> i > 150;
Predicate<Integer> pred2 = i -> i < 250;
Predicate<Integer> pred = pred1.and (pred2);
boolean rcheck = pred.test(300);
System.out.println ("300 between 150 and 250: "+ rcheck);
}
}Output:
3. negate()
This method returns the predicate that represents the logical negation for the specified predicate. The below example, shows negate predicate method as follows:
Code:
import java.util.function.Predicate;
public class PredMethod {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Predicate<Integer> pred = i -> i > 50;
Predicate<Integer> NegatePredicate = pred.negate ();
boolean rcheck = NegatePredicate.test (75);
System.out.println ("50 is greater than 75: "+ rcheck);
}
}Output:
This method returns a predicate that was composed by representing the logical OR and predicate. The below example shows or predicate method as follows.
Code:
import java.util.function.Predicate;
public class PredMethod {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Predicate<Integer> pred1 = i -> i > 70;
Predicate<Integer> pred2 = i -> i < 40;
Predicate<Integer> pred = pred1.or (pred2);
boolean rcheck = pred.test(25);
System.out.println ("(25 > 70) or (25 < 40) returns: "+ rcheck);
}
}Output:
5. test ()
This is the abstract method for the predicate interface. It will evaluate the true condition if the predicate will match the input argument. Below is an example of a test predicate method in java as follows. In the test method, T parameter is defined as the input argument.
Code:
import java.util.function.Predicate;
public class PredMethod
{
public static void main(String[] args) {
Predicate<Integer> pred = i -> i > 40;
boolean gcheck = pred.test(80);
System.out.println ("80 greater than 40: "+gcheck);
}
}Output:
FAQs
Given below are the FAQs mentioned:
Q1. What is the use of predicate method in java?
Answer: Predicate method is a functional interface that represents a single argument’s predicate. This method returns the true and false conditions.
Q2. Which method of predicate we are using in java?
Answer: We are using five methods of predicate in java i.e. test, or, and, isEqual, and negate. All the method is used to define the true and false conditions.
Q3. What is the use of and predicate method in java?
Answer: And predicate method is used to return the composed predicate, which represents the logical and for the specified predicate.
Conclusion
Java 8 predicate is defined in the package of java.util. The functional interface in Java is an interface that allows the abstract method within the scope interface. It is nothing but a user interface which was representing the predicate of a single argument. It contains the test functional method.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Java 8 Predicate. Here we discuss the introduction, interface functional, and java 8 predicate methods examples. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –