Updated February 10, 2023
Definition of Java 11 var
Java 11 var is a keyword that was used while developing code in java language. We are using type inference in the var keyword which detects the variable datatype based on the surrounding context. We are using the var keyword in java for declaring the local variable. We can also use the var keyword with lambda expression for avoiding the variable name, otherwise, it will conflict with the variable.
Key Takeaways
- We are using the var keywords to declare the local variable without typing their type. We are using the var keyword with the lambda expression.
- We can declare the var keyword with data type. At the time of declaring the var keyword, then no need to define type.
What is Java 11 var?
Java 11 introduced the type of local variable as a var keyword. By using inference type compiler figures out the types of static that were not written. Var keyword reduces the boilerplate of the repeated code. Using var it is not necessary whether our team is referring var or not. By using var code sometimes we can reduce the code maintenance but sometimes it will also increase the readability of code because it will hide the parameter type.
We are declaring a local variable with lambda by using the var keyword. The Var keyword is supporting a new feature of a local variable, by using the var keyword compiler java will guess the variable type based on the context that is surrounded. Programmers are not declaring the explicit type context. We can use the java var keyword at the time of declaring local variables.
Syntax of Java 11 var
We can declare any type of variable with the var keyword.
1. With integer type value.
var variable_name = (int type value)2. With double type value.
var variable_name = (double type value)3. With char type value.
var variable_name = (char type value)4. With string type value.
var variable_name = (string type value)5. With Boolean type value.
var variable_name = (Boolean type value)In the above syntax, we are using the var keyword with any type value that we have defined. Also, we need to define the variable name at the time of declaring the var keyword in java. If we need to pass the default value of the variable then we also need to pass the variable value with the var keyword.
Java 11 var – New Language Keyword
Java 11 introduced the new language keyword var which replaces the information type when we have declared the local variable. At the time of declaring any value before 10, we need to define the type of the variable at the time of declaring value now from java version 10 we are using var as a new language keyword for declaring any variable value.
In the below example, we are declaring the int type value using the java 11 var – new language keyword as follows.
Code:
public class java_var {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
var stud_no = 101;
System.out.println (stud_no);
}
}Output:
In the below example, we are declaring the string type value using the java 11 var – new language keyword as follows.
Code:
public class java_var {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
var stud_name = "ABC";
System.out.println (stud_name);
}
}Output:
In the below example, we are declaring the Boolean type value using the new language keyword as follows.
Code:
public class java_var {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
var st = true;
System.out.println (st);
}
}Output:
In the below example, we are declaring the double type value using the java 11 var – new language keyword as follows.
Code:
public class java_var
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
var st = 2.5;
System.out.println (st);
}
}Output:
Java 11 var Lambda Parameters
Java 11 allows us to use the var keyword in lambda parameters and the same is used to apply modifiers to the local variables.
The below syntax shows lambda parameters as follows:
Syntax:
(@NonNull var val1, @Nullable var val2) -> val1 + val2At the time of using the lambda parameter, we need to define the NonNull value. We are defining the value as per parameters that we are using with lambda parameters.
The below example shows the java 11 lambda parameter as follows:
Code:
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.stream.Collectors;
@interface NonNull {}
public class java_var {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<String> st = Arrays.asList ("var", "keyword");
String stn1 = st.stream ()
.map((@NonNull var stn) -> stn.toUpperCase ())
.collect (Collectors.joining (", "));
System.out.println (stn1);
} }Output:
In the below example we are converting the string into lowercase letters as follows:
Code:
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.stream.Collectors;
@interface NonNull {}
public class java_var
{
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<String> st = Arrays.asList ("VAR", "KEYWORD");
String stn1 = st.stream ()
.map((@NonNull var stn) -> stn.toLowerCase ())
.collect (Collectors.joining (", "));
System.out.println (stn1);
}
}Output:
Java 11 Local Variables
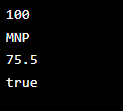
While using java 11 we can declare the local variable by using non-null initializers, we are using the var keyword which helps us to write our application code. Local variables are making the code readable for developers, it will also eliminate redundant information from the code. Local variables exist in the isolation. The below example shows java 11 local variables as follows. In the below example, we are declaring multiple variables in a single code. We are declaring multiple types of data.
Code:
public class java_var {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
var stud_no = 100;
var stud_name = "MNP";
var stud_mark = 75.5;
var stud_res = true;
System.out.println (stud_no);
System.out.println (stud_name);
System.out.println (stud_mark);
System.out.println (stud_res);
}
}Output:
Benefits
This keyword contains multiple benefits as follow:
- The var keyword is introduced in java 11 which was used to declare the local variables in our code.
- Using the keyword we are declaring the keyword without typing the name of the class explicitly.
- We can also declare the var keyword without typing the type information of the variable in our code.
- Using the keyword we can reduce the redundant code from our code. It will reduce the redundant code.
- By using keyword we can improve the code readability. We can easily read our code by using the var keyword.
- We can write our code implicitly, we do not need to write our code explicitly by using the var keyword.
- We can use the lambda expression and its parameter by using the var keyword in java 11.
- We are using java 11 code when we need to simplify our expression.
- Java 11 will encourage the user to use the more descriptive variable name like Scala or Kotlin.
- While using it we can avoid the trouble of forgetting long literals, instead of long literals we can use the var keyword.
Conclusion
Var keyword reduces the boilerplate of the repeated code. Using var it is not necessary whether our team is referring or not. We are using type inference in the var keyword which detects the variable datatype based on the surrounding context. We are using the var keyword in java for declaring the local variable.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Java 11 var. Here we discuss the definition, syntax, java 11 var lambda parameters, local variables and benefits respectively. You can also look at the following articles to learn more –