Updated March 13, 2023

Introduction to ISNULL SQL Server
ISNULL () function is used when you want a specific value that needs to be returned if the expression value is NULL. If the expression value will be returned then the expression value is not null. In this topic, we are going to learn about ISNULL SQL Server.
We get two arguments in the ISNULL () function. One is the expression and the other is value. Based on the expression it decides whether to return the expression value (if expression value is not null) or defined value (if expression value is null).
Now in this session let us see the usage of ISNULL () function and find the example of the ISNULL () function.
Syntax: –
Below is the syntax for the ISNULL () function: –
isnull(<expression>,<value>); /* - - - - ISNULL () SYNTAX - - - */Based on the expression it decides whether to return the expression value (if expression value is not null) or defined value (if expression value is null).
How ISNULL in SQL Server Works?
Now let us see the usage of ISNULL () function in the SQL server.
select isnull('Hello','replace value of the NULL')AS "IS NULL";Output:
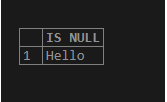
Here the expression value is not NULL because of which the actual values is returned.
select isnull(NULL,'replace value of the NULL')AS "IS NULL";Output:
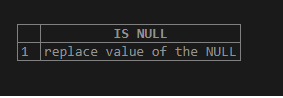
Here the expression value is NULL because of which the replacement values is returned.
Now let us apply the ISNULL () function in a table.
Table creation: –
CREATE TABLE test_NULL
(
SERIAL_NO INT
,NAME VARCHAR(20)
,LOCATION VARCHAR(20)
, AGE INT
, OCCUPATION VARCHAR(20)
)Now let us insert data into the table: –
INSERT INTO TEST_NULL VALUES (1,'Rose','USA', 24,'Software Engineer');
INSERT INTO TEST_NULL VALUES (2,'Rahul','India',NULL,'Artist');
INSERT INTO TEST_NULL VALUES (3,'Will','Denmark', 24,'Software Engineer');
INSERT INTO TEST_NULL VALUES (4,'Ben','Polland',NULL,'Actress');
INSERT INTO TEST_NULL VALUES (5,'Sian','FIA', 24,'Writer');
INSERT INTO TEST_NULL VALUES (6,'Rodger','Norway', 24,'Software Engineer');
INSERT INTO TEST_NULL VALUES (7,'Harry','USA',NULL,'Artist');
INSERT INTO TEST_NULL VALUES (8,'Kiyana','USA', 24,'Software Engineer');
INSERT INTO TEST_NULL VALUES (9,'Pradhush','USA', 24,'Writer');
INSERT INTO TEST_NULL VALUES (10,'Dawson','USA',NULL,'Painter');Let us select the table and below output rows are display: –
select * from TEST_NULL;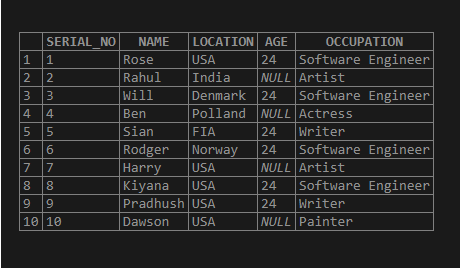
Here in the above output, you could see that the age of the people is NULL for a few rows. Instead of entering the value of NULL, we can insert a default value as 99 if the age is not mentioned with the below statement.
SELECT *,ISNULL(AGE, 99)AS "FORMATTED_AGE" FROM TEST_NULL;Output:
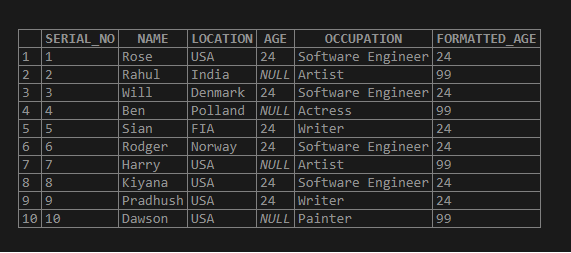
The value of NULL is replaced with the default value 99.
If you want to update the existing table with the same values uses the below statement: –
UPDATE TEST_NULL
SET AGE =ISNULL(AGE, 99);
SELECT*FROM TEST_NULL;Output:

We can use the function in the insert statement as well as below: –
INSERT INTO TEST_NULL VALUES (11,'Sony','Korea',ISNULL(NULL, 99),'Painter');Quickly let us select the mentioned row. 99 value will be saved instead of NULL.
SELECT * FROM TEST_NULL WHERE SERIAL_NO = 11;The screenshot is for the same: –

Examples of ISNULL SQL Server
Below are the examples mentioned:
Example #1
Now let us see the usage of ISNULL () function in the SQL server.
Code:
select isnull('234567','replace value of the NULL')AS "IS NULL";Output:
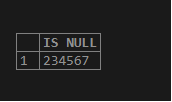
Example #2
Here in the above expression value is not NULL because of which the actual values is returned.
Code:
select isnull(NULL,'replace value of the NULL')AS "IS NULL";Output:
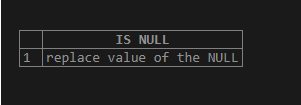
Example #3
Here in the above expression value is NULL because of which the replacement values is returned.
Code:
select isnull('ROSE','Dawson')AS "IS NULL";Output:
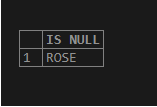
Example #4
Here in the above expression value is not NULL because of which the actual values is returned.
Code:
select isnull(NULL,'Rose')AS "IS NULL";Output:
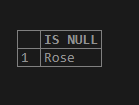
Here in the above expression value is NULL because of which the replacement values is returned.
Conclusion
ISNULL () function is used when you want a specific value that needs to be returned if the expression value is NULL. If the expression value is not null, then the expression value will be returned.
We get two arguments in the ISNULL () function. One is the expression and the other is value. Based on the expression it decides whether to return the expression value (if expression value is not null) or defined value (if expression value is null).
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “ISNULL SQL Server” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.

