What is Insurtech?
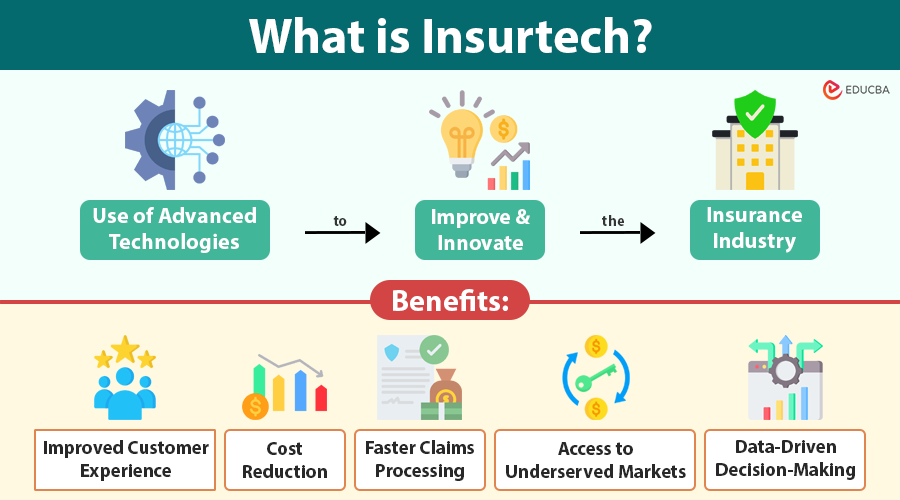
Insurtech (short for insurance technology) refers to the use of advanced technologies to improve and innovate the insurance industry. It includes digital tools and platforms that streamline operations, personalize products, automate claims, and enhance customer experience.
Imagine buying car insurance using an app that tracks your driving behavior. If you drive safely, your premium goes down automatically. That is insurtech in action, using technology to offer dynamic, user-friendly insurance.
Table of Contents
Key Features of Insurtech
| Feature | Description |
| Digitization | Insurtech allows customers to buy, manage, and renew policies entirely online, removing the need for physical paperwork or in-person meetings. |
| Personalization | It uses behavioral data, location data, and lifestyle metrics to tailor insurance products to individual customer needs and risk profiles. |
| Automation | Processes such as underwriting, claims approvals, fraud detection, and customer queries are increasingly handled through AI, robotic process automation (RPA), and chatbots. |
| Risk Assessment Tools | Devices such as wearable fitness trackers or connected car sensors help insurers collect real-time data to offer dynamic pricing and assess risk more accurately. |
| Blockchain Integration | Through smart contracts and decentralized data management, blockchain enhances transparency, reduces fraud, and facilitates faster claims resolution. |
These features combine to make insurance more responsive, cost-effective, and aligned with modern consumer expectations.
Benefits of Insurtech
1. Improved Customer Experience
Traditional insurance often involved complex documentation and long waiting times. Insurtech platforms now offer user-friendly digital interfaces, self-service portals, and 24/7 chat support, creating a seamless and intuitive experience for customers. Features like instant policy issuance and mobile claims submission reduce friction and boost satisfaction.
2. Cost Reduction
It reduces operational expenses by automating manual tasks, eliminating middlemen, and improving process efficiency. This allows insurers to lower premiums and pass savings on to customers. Startups can operate with leaner structures, often needing fewer employees and physical offices compared to legacy insurers.
3. Faster Claims Processing
With machine learning models and AI algorithms, insurtech platforms can process, approve, or flag claims within minutes. Fraud detection systems use predictive analytics to identify suspicious patterns, reducing loss ratios and improving trust between insurers and customers.
4. Access to Underserved Markets
It democratize access to insurance by offering microinsurance products, pay-as-you-go plans, and mobile-first platforms for populations in rural or emerging markets. These inclusive models allow people with limited income or digital infrastructure to obtain protection for health, life, crops, or property.
5. Data-Driven Decision-Making
Real-time analytics derived from various sources (e.g., wearables, telematics, weather sensors, customer feedback) allow insurers to understand emerging risks, refine pricing strategies, and improve product innovation. This data-centric approach leads to smarter risk pooling, dynamic underwriting, and customizable coverage.
Emerging Trends in Insurtech
1. Usage-Based Insurance (UBI)
UBI models tailor insurance premiums based on actual usage or behavior. For example, in auto insurance, telematics devices monitor speed, mileage, and braking habits to offer dynamic pricing. This model rewards safer drivers with lower premiums and encourages responsible behavior, lowering accident rates.
2. Embedded Insurance
E-commerce platforms, travel booking sites, and mobile banking apps increasingly integrate insurance into their services. For instance, when booking a flight, customers can add travel insurance with one click. This “invisible insurance” trend improves convenience and boosts penetration by meeting customers at the point of need.
3. AI and Predictive Analytics
AI systems analyze vast data points to predict customer churn, detect fraud, and estimate potential claims. These insights allow insurers to optimize underwriting, enhance risk profiling, and create preemptive service strategies like early fraud alerts or wellness nudges in health plans.
4. Blockchain Integration
Blockchain ensures tamper-proof data storage and instant verification, making it valuable for claims documentation and policyholder identification. Smart contracts meet predefined conditions and then automatically execute claims payments, speeding up settlements and reducing disputes.
5. On-Demand Insurance
Customers increasingly demand flexible, short-term coverage for specific activities or timeframes, such as travel, drone usage, freelance work, or car rentals. These on-demand products offer coverage by the hour or day and are activated via apps, making insurance more adaptable to the gig economy and modern lifestyles.
Real-World Examples of Insurtech
| Company | Country | Description |
| Lemonade | USA | Uses AI to underwrite renters and homeowners policies, settling claims in minutes and donating unused premiums to charities. |
| Root Insurance | USA | Offers auto insurance based on driving behavior tracked via a smartphone app; safer drivers pay less. |
| Trōv | USA | Provides on-demand, item-level insurance (e.g., for laptops, bikes) with instant activation and cancellation. |
| ZhongAn | China | Fully digital insurer offering millions of low-cost, high-volume policies across gadgets, health, and e-commerce. |
| Bima | Global | Delivers mobile-based microinsurance and health services to low-income populations in Africa, Asia, and Latin America. |
These companies showcase the breadth and versatility of insurtech, ranging from high-tech AI solutions in urban markets to life-changing mobile insurance in remote villages.
Challenges Facing Insurtech
Despite its growth, insurtech faces several hurdles:
- Regulatory Compliance: Navigating varying legal frameworks across countries can slow down adoption. Regulators often struggle to keep pace with new technology, leading to unclear rules and compliance issues.
- Data Privacy and Security: Collecting and processing personal data (health, location, financial) raises serious concerns about cybersecurity and consumer trust. Insurtechs must comply with GDPR, HIPAA, and other privacy regulations.
- Integration with Legacy Systems: Many traditional insurers still rely on outdated IT infrastructure, making it difficult to adopt modern tools without costly overhauls or significant downtime.
- Customer Skepticism: A segment of the population still prefers personal interaction with brokers or agents and may be hesitant to trust digital-only insurers or bots with sensitive matters.
The Future of Insurtech
The insurtech revolution is still unfolding. In the future, expect to see:
- Hyper-personalized policies tailored to your lifestyle, health status, and risk profile.
- Decentralized insurance ecosystems, where users can choose policies from multiple providers through a single platform.
- AI-driven claims adjudication that evolves in real-time.
- Global expansion of mobile-first insurance into developing markets.
- Sustainability-linked insurance offers incentives for eco-friendly behaviors, such as lower premiums for electric vehicle drivers or energy-efficient homes.
The convergence of technologies will make insurance smarter, more adaptive, and ultimately more human-centric, even if algorithms power it.
Final Thoughts
Insurtech fundamentally transforms how insurers create, deliver, and manage insurance. By embracing AI, big data, IoT, and blockchain, the industry is changing from a slow-moving sector into a dynamic, customer-focused ecosystem. As it continues to evolve, it holds the potential to make insurance more inclusive, transparent, and relevant to a digital-first world.
Whether you are an insurer, investor, or consumer, understanding insurtech is key to navigating the future of financial protection.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1. How does insurtech differ from traditional insurance?
Answer: While traditional insurance relies on manual processes, in-person interactions, and standardized policies, insurtech uses digital platforms, automation, and data analytics to deliver faster, more personalized, and customer-centric insurance solutions.
Q2. Can insurtech companies operate without being licensed insurers?
Answer: Some insurtech startups operate as technology partners or intermediaries, providing platforms or analytics while partnering with licensed insurance providers. Others are fully licensed digital insurers. Regulatory requirements vary by country and business model.
Q3. Is insurtech only for large insurance companies, or can small businesses benefit too?
Answer: Small insurance agencies and brokers can benefit greatly from insurtech by using tools like cloud-based CRMs, automated quote engines, and digital policy management systems to enhance their services, improve efficiency, and compete with larger firms.
Q4. What types of insurance are most impacted by insurtech?
Answer: Insurtech has made the biggest impact in auto, home, health, and travel insurance due to high customer interaction and data availability. However, innovations are also emerging in life insurance, agriculture, and cybersecurity insurance.
Q5. How secure is customer data in insurtech platforms?
Answer: Reputable insurtech companies implement robust data protection measures, including encryption, multi-factor authentication, and compliance with regulations like GDPR and HIPAA. Still, users should ensure the platform follows industry security standards before sharing sensitive information.
Recommended Articles
We hope this detailed guide on Insurtech was helpful. You may also want to explore related articles on:
