Updated July 12, 2023
Definition of Insolvency
Insolvency can be defined as a situation when the company or an individual is unable to meet his / their financial obligation due to insufficient cash flow. It also refers to a state where the assets of an individual/company are not enough to settle for their liabilities.
If insolvency is not treated on time, then it can become bankrupt. Therefore, the individual/company should take the necessary steps to rectify the insolvency; otherwise, it will become bankrupt.
Example of Insolvency
Bata co. Ltd has branches all over the U.S. One of its branches has taken a loan due on the 5th of this month, but due to some cash flow crunch, the debt payment could not be processed even though the company’s assets were more than its liabilities. If this situation persists, the company will become insolvent.
Kingston and company manufacture shoes in the U.S. They have 3 big dealers who used to buy shoes from them and sell them in the market. Kingston and company were doing fairly well in their business, and the products were also in great demand. In month of September, a new company started manufacturing shoes of the same quality but lesser price than Kingston Company. The three big dealers located another company, terminated their contract with the Kingston Company and initiated their business with the new company due to the lower prices. The Kingston Company has to endure significant losses as its major dealers are no longer affiliated. They could not meet the company’s daily needs, and unfortunately, the Company went through insolvency. The management of Kingston Company should plan to get more reliable clients to avoid this insolvency situation.
Types of Insolvency
Below are the different types:
1. Personal Insolvency
It means when the individual is trapped with his liabilities and cannot pay off his debt irrespective of having assets in their books.
2. Commercial Insolvency
It is when the company is in the urge of liquidation but cannot pay off the debt obligations on time, even when it has assets in its books.
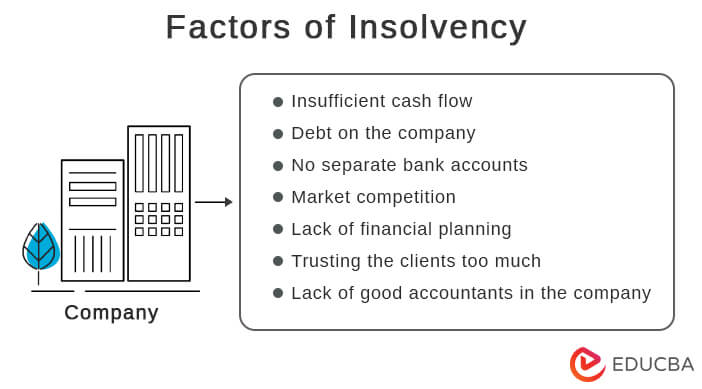
Factors of Insolvency
There are certain factors that the company or an individual has to suffer.
- Insufficient cash flow: When the company faces that its liabilities are less than its assets, but still the company cannot pay off its debts, it is known as insufficient cash flow. This is a rare situation but may occur and finally lead to insolvency.
- Debt on the company: Whenever a company takes too much debt and is unable to pay them off, then insolvency occurs. The company should plan its debt accordingly to avoid insolvency.
- No separate bank accounts: This is one of the most common reasons for insolvency. The company sometimes has a common bank account, which makes the company’s and the individual’s liabilities the same, and thus, if the debts are not paid off, then insolvency may occur.
- Market competition: Market competition also plays a vital role for the company. Sometimes it can be very useful, and sometimes it is not that good and healthy for the company since the company may take huge debts or invest in some places, which may be a nightmare. Therefore the company should invest and take loans very wisely.
- Lack of financial planning: The Company suffers from insolvency due to poor financing planning. The company should take all necessary steps to plan well before any investment or loan decisions.
- Trusting the clients too much: Now, this is a practical situation that leads to insolvency. For example, the company sometimes tries to maintain good customer relations by giving them credit. Sometimes, they may not pay in full, but the company continues their services. Another situation is that the company relies on some big clients, and in case they stop taking services from the company, it has to suffer insolvency.
- Lack of good accountants in the company: Many companies compromise in hiring a good accounting team for their company. A good accounting team can help the management understand their expected budgets and how much they can spend. If the budgets are not prepared properly, the company may indulge in overspending, and thus the entire budget may get disturbed; if this is in huge money terms, the company will suffer insolvency.
Consequences
Insolvency can be very frustrating for the top management or the company’s directors. The creditors initiated the demand for their money, and legal proceedings also involved the directors. Some companies’ management decides to take voluntary liquidation of the company. This decision relies upon the company and is different for different companies. In some cases, Mergers and Acquisitions also occur, and thus, the management has to suffer these consequences whenever insolvency occurs. If the company is LLP (Limited Liability Partnership), the business will be liquidated, but the partner’s liability is saved in this case.
Key Takeaways
Insolvency occurs when the company cannot pay off debts they have taken. It is a type of financial distress that is very unfortunate but can be avoided by proper planning. The company goes into liquidation, and the identity of the company comes to an end. If the company is an LLP (Limited Liability Partnership), then the property of the promoters will not get attached.
Conclusion
Insolvency occurs when the company takes too many loans but cannot pay off the same. As a result, the company’s identity suffered because the company went for liquidation. The top management should take all necessary steps to avoid the consequences of insolvency. In some situations, the company has assets but cannot pay off its liabilities; thus, insolvency occurs.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Insolvency. Here we discuss the definition, example, types, and factors of Insolvency and its Consequences. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –