Updated April 5, 2023
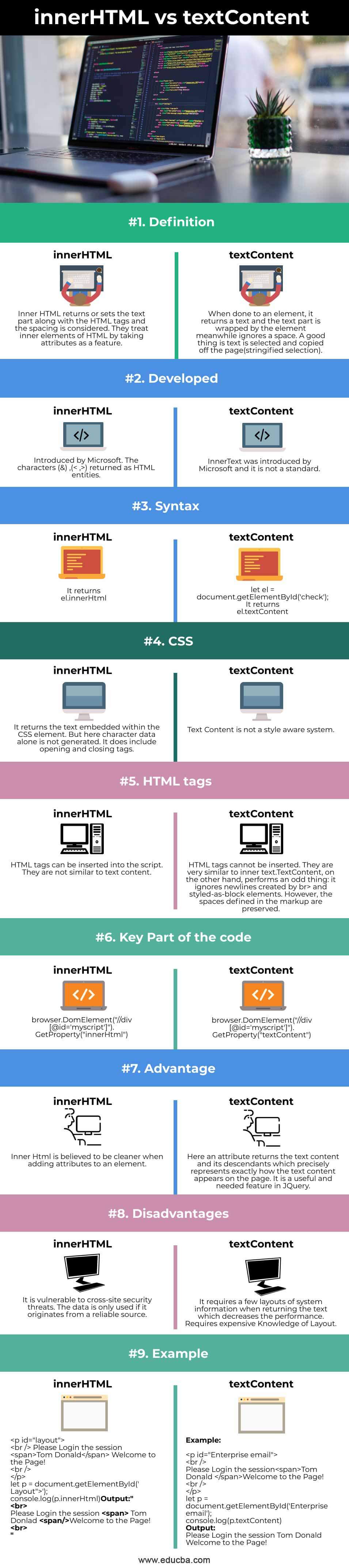
Definition of innerHTML vs textContent
All text included by an element, as well as all of its children, is referred to as text contents and Whitespace in texts is consistently reduced across all supported browsers when accessed via the text contents attribute of an element. whereas inner HTML returns all the text along with the HTML tag which is enclosed by an element. This property changes the text content inside an element. Unlike the text Content property, inner HTML returns everything inside the element precisely as it is, including HTML.
Head to Head Comparison Between innerHTML vs textContent (Infographics)
Below are the top 9 differences between innerHTML vs textContent:
Comparison Table of innerHTML vs textContent
The below table gives the comparison between the inner HTML and text Content. Let’s get started.
| S.NO | Text Content | Inner HTML |
| Definition | When done to an element, it returns a text and the text part is wrapped by the element meanwhile ignores a space. A good thing is text is selected and copied off the page(stringified selection). | Inner HTML returns or sets the text part along with the HTML tags and the spacing is considered. They treat inner elements of HTML by taking attributes as a feature. |
| Developed | InnerText was introduced by Microsoft and it is not a standard. | Introduced by Microsoft. The characters (&) ,(< ,>) returned as HTML entities. |
| Syntax |
It returns el.textContent
|
It returns el.innerHtml |
| CSS | Text Content is not a style aware system.
|
It returns the text embedded within the CSS element. But here character data alone is not generated. It does include opening and closing tags. |
| HTML tags | HTML tags cannot be inserted. They are very similar to inner text.TextContent, on the other hand, performs an odd thing: it ignores newlines created by br> and styled-as-block elements. However, the spaces defined in the markup are preserved. | HTML tags can be inserted into the script. They are not similar to text content. |
| Key Part of the code |
|
|
| Advantage | Here an attribute returns the text content and its descendants which precisely represents exactly how the text content appears on the page. It is a useful and needed feature in JQuery. | Inner Html is believed to be cleaner when adding attributes to an element. |
| Disadvantages | It requires a few layouts of system information when returning the text which decreases the performance. Requires expensive Knowledge of Layout. | It is vulnerable to cross-site security threats. The data is only used if it originates from a reliable source. |
| Example | Example:
Output: Please log in the session Tom Donald Welcome to the Page! |
|
Key differences of innerHTML vs textContent
1. The element’s innerHTML attribute obtains or sets the element’s HTML content. Because the textContent element does not automatically encode and decode text, we can only operate with the content portion of the element.
2. text content simply allows you to write plain texts as strings, but innerHTML provides a direct and easier way to create HTML templates as strings and insert them into the DOM.
3. Although innerHTML isn’t fully safe in all situations, it can be useful in others, such as adding static data on a website that doesn’t capture user input.
4. Text content removes child nodes when does alter. Text content has good performance has its value is not parsed. And it prevents XSS attacks.
5. text content, unlike innerText, is unaware of CSS styling and will not cause reflow. Only HTMLElement objects have innerText, while all Node objects have textContent.
6. InnerHtml is supported in Internet Explorer while textContent property is not supported in IE.
Let’s get started with some sample HTML script that will show how each property works.
Example:
Example #1
demo.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
<p id="click" onclick="myclick()">Place cursor on the Text.</p>
<script>
function myclick() {
document.getElementById("click").textContent = "Changed Content!";
}
</script>
</body>
</html>Explanation
The Script says to click the phrases and the content is changed to the text and the output is shown as:
Output:
Example #2
air.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
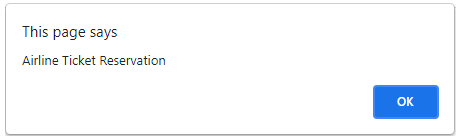
<span id="exid">Airline <span style="display:none;">Ticket Reservation</span></span>
<button onclick="reservation();">inner</button>
<button onclick="cancel();">textContent</button>
<script>
function reservation()
{
var elt = document.getElementById("exid");
alert(elt.innerText);
}
function cancel()
{
var ele1 = document.getElementById("exid");
alert(ele1.textContent);
}
</script>
</body>
</html>Explanation
The Above example code shows both the innerHTML and text Content formats. So when a button is submitted the page directs to the dialog box displaying the text Content.
Output:
After Clicking on inner button
After Clicking on textContent button
Example #3
edu.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>
HTML textContent Property Demo
</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>This is EDUCBA</h1>
<h2>Button Press for Text Content</h2>
<button id = "edu" onclick = "Myeducba()">
Press
</button>
<p id = "exam"></p>
<script>
function Myeducba() {
var tt =
document.getElementById("edu").textContent;
document.getElementById("exam").innerHTML = text;
}
</script>
</body>
</html>Explanation
The Text Content returns the concatenated text of all text nodes in the Script that is stripping out the markup tags. In the above script when a button is clicked it displays the text in the HTML tags, not the markup tags. Therefore, the output looks like this:
Output:
Example #4
page.html
<html>
<body>
<p>
Learning is a precious gift <strong>Is a lifelong process</strong>,
and <em> boost mental ability</em> and a <a href="#">page</a>.
</p>
<p></p>
</body>
<script>
const a1 = document.querySelectorAll("p")[0];
const a2 = document.querySelectorAll("p")[1];
a2. textContent = a1.textContent;
</script>
</html>Explanation
We can see that the formatting from the top paragraph has been removed from the bottom paragraph when we execute the example above. This says that we won’t be able to replace text with HTML using textContent.
Output:
Conclusion
Therefore, in this article, we have learned how to use The JavaScript properties of inner Html and text content to get the text nodes and Html elements and their descendants. InnerHTML is more versatile since it allows be more creative. If the user merely wants to return text content, textContent is the way to go. As we have more JavaScript properties which we had discussed in the previous article, it depends on the situation of the property we should prefer.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to innerHTML vs textContent. Here we discuss innerHTML vs textContent key differences with infographics and comparison table, respectively. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –