Updated March 31, 2023

Definition of Inner Class
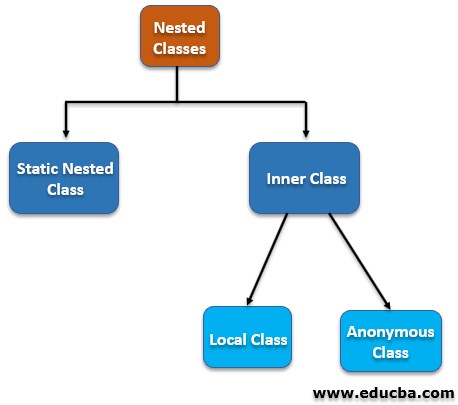
A class that is present inside another class or block and is treated as one of its members is known as an inner class. It is also known as a nested class and can easily access all the outer class/block members. This helps one declare a user-defined data type local to a block to implement a special type of relationship and helps to write more readable and maintainable code. It can be classified into 2 different categories:-
- Static Nested Classes: If a nested class is declared as static.
- Inner Classes: Non-static nested classes is known as an inner class.
Why do We Need Inner Class?
One needs to use inner class in the application when:-
- Local Class: If a class is used by only one other class, then it is more preferable to put the single-use class as a local inner class. Such embedding of a class with its helper class results in a better-streamlined package.
- Optimized Code: Such arrangement of code makes our code more optimized and more efficient memory usage wise.
- Readable and Maintainable Code: Such an arrangement of classes where a class is placed closer to the place where it is used results in easily readable code and looks maintained.
How does Inner Class Work in Programming languages?
Let’s understand each of the above one by one:-
1. Static Nested
This type of static class is declared inside another class and is treated as one of its members. Since it is static thus can be easily called by other static members without initiating the outer class. And being static, it does not have access to other non-static instance members of the outer class.
Syntax:
class Outer{
public static class Inner{
}
}
2. Method Local
This class type is declared inside a method and is treated similarly to its local methods and variables. And since it is a local member thus can not be accessed outside the method. To use it, one needs to create its instance inside the method itself.
Note: Here, instance variables of the Outer class are not accessible until they are declared as final upto JDk 1.7. In JDK 1.8, this flaw was overcome.
Syntax:
class Outer{
public int method1(){
//task to be performed
public class Inner{
//variables and methods of inner class
}
}
}
3. Anonymous
This type of classes is declared without a name. Such classes are used when one needs to override a method of a class or an interface. In this case, declaration of the class and instantiation needs to be implemented at the same time.
Syntax:
AnonymousInner an_inner = new AnonymousInner() {
public void my_method() {
........
........
}
};
4. Inner Class
This type of classes is implemented by declaring a class inside another class where the inner class has access to all the instance variables and the outer class’s methods. Since inner class here is associated with an instance, thus must never be defined as static members.
Syntax:
class Outer{
class Inner{
}
}
Examples of Inner Class
Following are the example are given below:
Example #1 – Static Nested
Code:
package Try;
public class Office {
static class Admin {
public void my_method() {
System.out.println("Admin name is Sarthak");
}
}
public static void main(String args[]) {
Office.Admin nested = new Office.Admin();
nested.my_method();
}
}
Output:
![]()
Example #2 – Method Local
Code:
package Try;
public class Office {
void my_Method() {
final int numOfDesk = 23;
class Inner {
public void print() {
System.out.println("Number of desk in Office = "+ numOfDesk);
}
}
Inner inner = new Inner();
inner.print();
}
public static void main(String args[]) {
Office outer = new Office();
outer.my_Method();
}
}
Output:
![]()
Example #3 – Anonymous
Code:
package Try;
abstract class MyInner {
public abstract void myMethod();
}
public class Office {
public static void main(String args[]) {
MyInner my_inner = new MyInner() {
public void myMethod() {
System.out.println(“Implementing myMethod named abstract method");
}
};
my_inner.myMethod();
}
}
Output:
![]()
Example #4 – Inner Class
Code:
package Try;
class Company {
class MyCEO {
public void show() {
System.out.println("CEO of this institute is Mr. Rakesh Kumar");
}
}
}
public class Office {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Company.MyCEO in = new Company().new MyCEO();
in.show();
}
}
Output:
![]()
Advantages
- Maintainable Code: It places a one-time use class inside the other class that enhances the readability and maintenance of the code; thus, our application becomes more maintainable.
- Enhances Encapsulation: Encapsulation is one of the properties of Object-Oriented Programming Languages where related variables and methods are encapsulated under one block named as a class and are referred to using an instance of that class. It is implemented as a part of the outer class and is treated as a member of the class, thus enhances encapsulation in our code, thus making it more efficient and maintainable.
- Improves Optimization: Using this in one’s application helps the compiler compile the class easily, thus enhancing the optimization of the code. Also, memory and CPU utilization by the compiler is reduced as less memory is utilized for a new class.
Conclusion
An inner or nested class is a way to place the classes used only at one place in our code closer. This enhances the code’s encapsulation and optimisation and makes our code more readable and maintainable as the members are made more accessible from other classes.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Inner Class. Here we also discuss how does inner classwork in programming languages? Along with different examples and their code implementation. you may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –

