What is Human Augmentation?
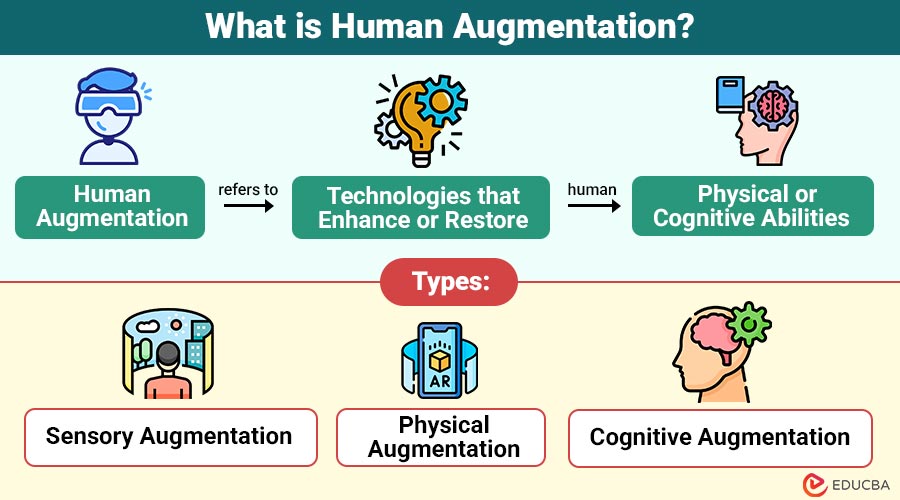
Human Augmentation refers to technologies that enhance or restore human physical or cognitive abilities. It involves integrating devices or systems with the human body to improve strength, intelligence, perception, or health.
It encompasses a broad spectrum, from wearable devices like smartwatches to more complex innovations like brain-computer interfaces (BCIs). The goal is to either augment a normal human function or compensate for a lost one.
Table of Contents:
- Meaning
- Types
- Key Techologies
- Applications
- Benefits
- Key Challenges
- Ethical Considerations
- Real World Examples
- Future
Key Takeaways:
- Human augmentation combines biology and technology to improve or restore physical, sensory, and mental capabilities.
- It plays an important role in transforming lives through innovative applications in healthcare, education, defense, and daily living.
- Technological drivers like AI, BCIs, and robotics are accelerating the development and adoption of enhancement tools.
- Future developments may lead to deeper integration between humans and machines, reshaping how we live, learn, and work.
Types of Human Augmentation
Human augmentation can be categorized into three primary types:
1. Sensory Augmentation
Sensory augmentation enhances human perception by improving or restoring the five senses through advanced technologies, enabling users to experience the world in new ways.
2. Physical Augmentation
Physical augmentation boosts human bodily abilities such as strength, mobility, and stamina, often using mechanical or electronic devices to extend or restore physical performance.
3. Cognitive Augmentation
Cognitive augmentation strengthens mental functions like memory, focus, and decision-making by integrating technology or substances that enhance brain activity and cognitive performance.
Key Technologies Driving Human Augmentation
A variety of cutting-edge technologies powers human augmentation:
1. Artificial Intelligence
AI powers smart systems by enabling real-time data analysis, adaptive learning, and personalized experiences in brain-computer interfaces, wearables, and cognitive enhancement tools.
2. Brain-Computer Interfaces
Through direct brain-machine contact made possible by BCIs, individuals can communicate with machines or control external devices via neural impulses and mental patterns.
3. Robotics
Robotics enhances human mobility and physical capabilities through advanced prosthetics, robotic limbs, and exoskeletons designed for rehabilitation, physical augmentation, and industrial applications.
4. Augmented Reality and Virtual Reality
AR and VR provide immersive environments that improve training, healthcare, education, and entertainment through simulated experiences and enhanced human-computer interaction.
5. Biotechnology and Genetic Engineering
Genetic tools like CRISPR allow precise DNA modification for enhancing traits, preventing diseases, and enabling regenerative medicine, opening possibilities for biological augmentation.
6. Nanotechnology
Nanotechnology introduces microscopic machines capable of targeting and repairing tissues, improving drug delivery, boosting healing, and potentially enhancing cognitive and physical functions.
Applications of Human Augmentation
The applications of human augmentation span multiple domains:
1. Healthcare and Rehabilitation
With the use of technology such as cochlear implants, neurostimulators, prosthetic limbs, and smart eyeglasses, human augmentation enhances medical care, promoting rehabilitation and improving patients’ quality of life.
2. Military and Defense
Augmented exoskeletons and enhanced vision systems increase physical capabilities, endurance, and situational awareness of soldiers, leading to more effective and safer military operations.
3. Workplace and Industry
Wearable devices such as exosuits and AR headsets reduce physical strain and assist workers with real-time information for complex industrial tasks and maintenance.
4. Education and Learning
Immersive learning through AR/VR, AI tutors, and brain-enhancing apps creates more engaging, personalized, and effective educational experiences across all age groups.
5. Consumer Lifestyle
Every day, users benefit from smart wearables, health trackers, digital assistants, and brain-training apps that promote health monitoring, productivity, and cognitive improvement.
6. Sports and Fitness
Athletes use augmentation tools like smart wearables, biomechanical sensors, and AI-based performance analysis to optimize training, reduce injury risk, and enhance performance.
Benefits of Human Augmentation
Here are the key benefits that human augmentation offers across various aspects of life and work:
1. Improved Quality of Life
Human augmentation helps individuals regain lost functions—like movement or hearing—enabling those with disabilities or chronic conditions to live more independent, fulfilling, and empowered lives.
2. Enhanced Productivity
Wearable exosuits, AR devices, and assistive tools enable workers to perform physically demanding or complex tasks more efficiently, with reduced fatigue, error, and physical strain.
3. Better Health Monitoring
Smart wearables monitor oxygen levels, heart rate, sleep patterns, and other parameters, facilitating better long-term wellness management, tailored interventions, and early health problem diagnosis.
4. Increased Accessibility
Assistive technologies like speech-to-text, eye-tracking systems, and mobility aids make digital interfaces, public spaces, and work environments more inclusive and easier to navigate.
5. Revolutionized Learning and Interaction
AR/VR technologies, brain-training apps, and AI tutors help people learn better by making lessons more interesting, improving memory and focus, and customizing the content based on how each person learns best.
Key Challenges of Human Augmentation
Here are the major key challenges that must be addressed as human augmentation technologies evolve:
1. Equity and Accessibility
Human augmentation may create societal divides, favoring those who can afford enhancements, leading to inequality and the rise of a privileged “biotechnological elite.”
2. Privacy and Data Security
Implants and wearables collect sensitive health data, exposing users to hacking, surveillance, and misuse, raising major concerns over informed consent and data protection.
3. Health and Safety Risks
4. Dependency on Technology
Overuse of augmentation may cause people to lose natural abilities, becoming dependent on devices for cognitive, sensory, or physical function over time.
5. Workplace Discrimination
Employers may prefer augmented workers, creating pressure on others to adopt risky technologies just to compete or maintain their job positions.
6. Regulatory Gaps
Laws and bioethics have not kept pace with augmentation, lacking clear regulations and global standards to manage risks, safety, and accountability.
Ethical Considerations of Human Augmentation
Here are the key ethical issues that arise as we integrate technology deeper into the human body and mind:
1. Fairness and Equity
2. Informed Consent
Users might not fully understand long-term risks or implications, raising concerns about exploitation, coercion, or misinformed decision-making.
3. Privacy Invasion
4. Identity and Humanity
Excessive augmentation may blur the line between human and machine, challenging societal norms around identity, personhood, and natural evolution.
5. Ethical Use in Military
Using human upgrades in war could create super soldiers, make fights more dangerous, and raise serious moral questions about fairness and harm to civilians.
Real World Examples
Here are notable real-world applications of human augmentation technologies currently making an impact:
1. Neuralink
Founded by Elon Musk, Neuralink is developing brain-machine interfaces that could one day allow people to control digital devices through thought.
2. Ekso Bionics
This company makes wearable exoskeletons that help people with spine injuries and support workers doing heavy physical tasks.
3. Second Sight
Provides retinal implants, such as the Argus II, to help people with specific types of blindness regain some of their vision.
4. Hearing Aids with AI
Modern hearing aids like Oticon and Starkey use AI to reduce background noise and improve speech recognition.
Future of Human Augmentation
The future of human augmentation looks transformative. Here are a few likely developments:
1. Integration with the Internet of Things
Smart implants can connect to the internet, so doctors can check your health live, control the implant from far away, and use AI to give you personal tips and make the implant work better.
2. Genetic Enhancements
Gene-editing technologies could enhance memory, strength, and immunity, offering tailored biological upgrades through precise genomic alterations and disease resistance.
3. Full-Cybernetic Replacements
Advanced prosthetics and organs may mimic natural functions completely, responding to neural signals and powered by intelligent artificial systems.
4. Mind-Machine Symbiosis
Brain-computer interfaces may enable direct thought-to-digital interaction, merging cognitive processes with external devices for seamless mental extension.
Final Thoughts
Human augmentation is redefining human potential—restoring lost abilities and enhancing natural ones. As this convergence of biology and technology accelerates, we must balance innovation with ethical responsibility. Regulation, equitable access, and informed public discourse are essential. The future is not just about what we can enhance, but how wisely and fairly we choose to shape humanity’s next evolution.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1. Is human augmentation safe?
Answer: Most forms of augmentation undergo rigorous testing and are generally safe. However, risks depend on the type—implants involve surgical risks, while wearables have fewer health implications.
Q2. Can human augmentation be reversed?
Answer: Some forms, like exoskeletons or wearables, are temporary. Implants and genetic enhancements may be irreversible.
Q3. Are there laws regulating human augmentation?
Answer: Regulations exist, especially in healthcare, but laws around cognitive and genetic augmentation are still evolving globally.
Q4. Is human augmentation only for disabled individuals?
Answer: No. While initially developed for medical use, augmentations are now used in lifestyle, sports, military, and industrial sectors.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “Human Augmentation” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.
