Introduction to Generative AI for Software Development
Generative AI is transforming how software gets built – faster, smarter, and more cost-efficient than ever. From writing code to automating testing and enhancing user experiences, it is helping teams deliver better products in less time. For business leaders, understanding generative AI for software development is not just a technical concern—it is a strategic advantage. By leveraging AI, companies can unlock innovation, scale efficiently, and gain a competitive edge.
This blog explores how generative AI is transforming the software development lifecycle, from idea to launch. It is not about replacing your teams, but empowering them with smarter tools to move faster and build better.
Key Highlights
- Popular generative AI tools used in software development.
- Generative AI acts as a co-developer by automating repetitive tasks, such as code generation, testing, and documentation.
- It speeds up prototyping, validation, and testing, resulting in faster iteration.
- By leveraging Gen AI, businesses can reduce technical debt, accelerate development cycles, and enable quicker product-market fit validation.
- Future trends in Gen AI include autonomous coding and testing agents, AI-driven full-stack environments, and low-code/no-code solutions.
Generative AI Tools in Software Development
When it comes to software development, there are several Gen AI tools. These tools simplify the task of developers and let them focus on more important things. Here are some key tools used:
- GitHub Copilot: OpenAI powers GitHub CoPilot. It assists developers by suggesting code snippets, functions, and even entire blocks based on the code’s context.
- Tabnine: This AI code completion tool helps developers by predicting and suggesting code. Tabnine learns from your coding patterns and preferences to improve suggestions over time.
- Codex: The primary functionality of this tool is that it can generate code in various programming languages. Developers do not have to write code manually for building applications.
- Kite: It is an AI-powered assistant. Kite provides autocompletion and documentation for Python and JavaScript.
- DeepCode: Bugs are likely in the codebase, which is why developers use this tool. DeepCode analyzes codebases for bugs and suggests improvements using machine learning.
The Strategic Shift: AI as a Co-Developer
AI is no longer just about automation, but it is stepping into the role of a true development partner. Generative AI can write functional code, suggest improvements, and even flag potential issues before your team runs into them. This is not about replacing developers. It is about freeing them up to focus on what really matters: architecture, innovation, and product strategy.
With AI co-developers handling boilerplate and routine tasks, iteration speeds up dramatically – what used to take days can now happen in hours. Prototyping speeds up, validation gets quicker, and your team has more room to experiment.
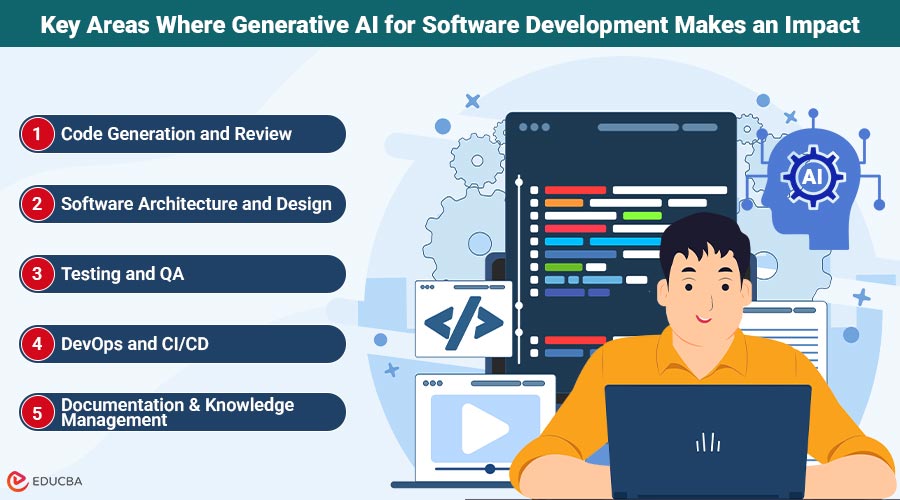
Key Areas Where Generative AI for Software Development Makes an Impact
Gen AI augments developers and reduces friction at each stage of the software lifecycle. Let us look at the areas where Gen AI is reshaping development in practice:
1. Code Generation and Review
Writing and maintaining code consumes significant time, and much of it is repetitive. Generative AI can shoulder this repetitive load and give your engineers adequate time for higher-value work.
- Code Generation: Developers can use AI to spin up entire functions, CRUD operations, or API connectors in minutes.
- Refactoring Legacy Systems: AI can scan older codebases, identify inefficiencies, and suggest optimized versions, which is a key aspect of refactoring. With AI-powered code refactoring, you can manage technical debt without months of manual rework.
- Smarter Code Reviews: It flags security vulnerabilities, code smells, or deviations from best practices. This way, AI adds consistency and coverage, especially across large or distributed teams.
Why this matters:
Your teams deliver faster while keeping code quality intact. Instead of firefighting bugs, your senior engineers can focus on system-level challenges.
2. Software Architecture and Design
Architectural decisions often determine scalability and cost efficiency. Previously, certain senior architects had the authority to make these decisions. However, things are no longer the same. AI is now beginning to support this function in meaningful ways.
- Blueprint Generation: Feed your business requirements into an AI model, and you will receive draft architecture diagrams or workflow outlines that provide your team with a solid starting point.
- Technology Recommendations: Based on constraints like scalability, compliance, or cloud provider, AI can suggest the most suitable frameworks or libraries.
- Scenario Simulation: AI tools can simulate “what if” scenarios, such as how different architectures will perform under sudden traffic spikes.
Why this matters:
You move from weeks of exploration to faster iterations and better-informed decisions. Your architecture becomes more responsive to business goals and less reliant on guesswork.
3. Testing and QA
Testing is usually the bottleneck in release pipelines. Gen AI helps compress this timeline while also improving coverage and accuracy.
- Automated Test Case Creation: AI can instantly generate functional, integration, and regression test cases directly from your requirements or user stories.
- Defect Prediction: AI can scrutinize historical bug data accurately. It highlights areas in your code that are most likely to break.
- Regression Maintenance: As the codebase evolves, AI keeps regression suites updated automatically. This reduces the manual overhead that QA teams face.
Why this matters:
Faster QA cycles, fewer production issues, and the ability to maintain release velocity without sacrificing reliability.
4. DevOps and CI/CD
In DevOps, every second of downtime or pipeline failure costs money and reputation. AI brings predictability and resilience into this space.
- Pipeline Automation: Whether you are using Jenkins, GitHub Actions, or GitLab CI, AI can generate CI/CD workflows tailored to your specific environment.
- Proactive Anomaly Detection: AI tools can detect unusual patterns in logs and metrics early. They warn you before failures happen.
- Self-Healing Operations: Systems can auto-trigger actions like restarting services, rerouting traffic, or reallocating cloud resources when disruptions occur.
Why this matters:
Reduced firefighting, higher uptime, and operational costs that scale down rather than escalate.
5. Documentation and Knowledge Management
Documentation has always been a weak spot in development. It is tedious, often outdated, and usually ignored. Generative AI turns this from a liability into an asset.
- Auto-Generated Docs: AI can generate API references, inline code explanations, and release notes directly from the codebase.
- Living Knowledge Bases: You can build internal AI-powered systems where developers ask questions in plain language (e.g., “How does the payment API handle retries?”) and instantly receive accurate answers pulled from your documentation and codebase.
- Onboarding Support: New hires can depend on AI-driven guides that explain code and architecture. This cuts down ramp-up time significantly.
Why this matters:
Knowledge no longer sits in silos or inside the heads of a few engineers. Documentation is accurate, accessible, and actively supports productivity.
6. Security and Compliance
AI-powered development introduces new opportunities, but also new risks. You need to ensure that AI-generated code, data handling, and system integrations do not expose your organization to vulnerabilities or regulatory breaches. Generative AI can help strengthen your security framework if applied thoughtfully.
- Secure Code Scanning: AI can review generated or existing code against known vulnerability databases (e.g., OWASP, CVE) in real-time.
- Compliance Mapping: Automatically check whether code or infrastructure decisions align with standards like GDPR, HIPAA, SOC 2, or ISO.
- Data Governance: AI can classify and monitor the usage of sensitive data and flag any misuse or mishandling of it.
- Threat Modeling: Generative AI can simulate attack scenarios to stress-test system resilience before deployment.
Why this matters:
Security becomes proactive instead of reactive. You gain continuous AI-driven monitoring and compliance checks embedded into the development lifecycle.
Business-Level Outcomes for CTOs
Gen AI is shifting the way you deliver value at the business level. The outcomes go beyond code efficiency. They impact how you manage teams, budgets, and strategic growth. Here is what you can expect:
- Efficiency Gains: By leveraging artificial intelligence in coding, testing, and documentation, you can accelerate development cycles. This allows you to achieve faster releases without stretching your resources.
- Talent Strategy: You will need smaller but sharper teams. AI reduces dependency on large developer pools by handling boilerplate code and routine QA. Your hiring focus shifts toward engineers who excel at architecture, domain knowledge, and AI governance.
- Innovation Speed: You can prototype new features, test product-market fits, and launch proofs of concept faster than before. You gain the flexibility to validate ideas quickly and scale only the ones that show business value.
- Risk Management: AI tools can help you detect vulnerabilities, enforce compliance, and standardize security checks. This forward-looking approach lowers the risk of expensive rework or compliance issues.
Challenges and Considerations
Software development with Generative AI is already delivering real value – but like any powerful tool, it comes with risks. Before scaling Gen AI across your engineering teams, here are a few key challenges to plan for:
1. Quality Control
AI can generate working code quickly – but speed does not always equate to quality. The output might not be optimized, maintainable, or aligned with your internal standards.
Solution: To keep technical debt in check, you will need strong validation processes: peer reviews, static analysis tools, and clear coding guidelines. This way, you can ensure AI-generated code meets the bar.
2. Security and Compliance
AI-generated code can sometimes introduce vulnerabilities or reuse snippets that conflict with licensing terms. Improperly governed prompts or training inputs can lead to the exposure of sensitive data.
Solution: Set strict data usage boundaries, enforce secure coding, and conduct regular compliance checks to prevent risks.
3. Cultural Shift
Your teams may feel threatened or uncertain about the role of AI in their day-to-day work. This can lead to resistance or shallow adoption.
Solution: You will need to show your teams that AI is not replacing them; it is freeing them up to focus on solving harder problems. Structured onboarding, hands-on training, and open conversations go a long way in building trust.
4. Governance
Without clear guardrails, AI adoption can quickly become messy and inconsistent.
Solution: Define clear ownership – who approves AI-assisted commits, who tracks model usage, and how compliance is measured. You may also introduce internal AI policies similar to coding standards to ensure ethical, consistent, and business-aligned adoption.
What’s Next in Generative AI for Software Development?
AI is transforming software development today, but this is just the start. You will soon see changes that go beyond productivity and reshape how software is designed, built, and managed. Here are the upcoming trends in Generative AI for software development:
- AI-Driven Full-Stack Environments: You can expect development platforms where AI supports every stage of the lifecycle – from writing code and generating tests to deployment and monitoring. These environments will streamline workflows, reduce tool-switching, and make end-to-end development more seamless than ever.
- Rise of Agentic AI: Autonomous coding and testing agents will take in requirements, generate working modules, run validations, and suggest improvements with minimal human input.
- Low-Code/No-Code Integration: Gen AI will make it easier for CTOs and product managers to build prototypes and workflows. Developers would not be sidelined; instead, they can focus on complex, high-impact work that drives innovation.
Key Reasons to Partner with a Gen AI Development Service
From automating code generation to next-gen chatbots, virtual assistants, content creation tools, predictive analytics, and even personalized product recommendations, the scope of Gen AI is wide and practical. However, building and scaling these solutions in-house can be complex and resource-heavy. By partnering with a Generative AI development service, you can accelerate adoption and minimize risks tied to cost, compliance, and delivery.
Here are the reasons to go with this approach:
- Access to specialized AI engineers, data scientists, and domain experts.
- Faster time-to-market with proven frameworks and pre-built accelerators.
- Reduced upfront investment compared to hiring and training full teams.
- Built-in compliance and data security practices aligned with regulations.
- Ability to scale development capacity on demand without long-term overheads.
- Ongoing support for model fine-tuning, updates, and maintenance.
- Strategic guidance to align AI solutions with your broader business goals.
Final Thoughts
Generative AI for software development is changing the way teams design, build, and deliver software. When applied thoughtfully, it helps accelerate development cycles, reduce repetitive work, and improve overall quality. The key is to introduce AI where it adds real value, while maintaining clear policies for compliance, security, and data handling. By treating AI as a strategic partner rather than a replacement, organizations can gradually integrate it to boost innovation and efficiency across their software development processes.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1. How can Generative AI accelerate software development?
Answer: Generative AI automates tasks like code generation, refactoring, and documentation. Since developers do not have to deal with these hassles, they can concentrate on the more complex aspects. As a result, teams can iterate more quickly, accelerate prototyping, and reduce the time-to-market for new features.
Q2. Will Generative AI replace developers in the future?
Answer: No, Generative AI is not replacing developers. Instead, it works like a co-developer that automates repetitive tasks. This is helping developers a lot since they have enough time to focus on high-value activities like architecture, innovation, and problem-solving.
Q3. What are the major bottlenecks when implementing Generative AI for software development?
Answer: Some challenges include maintaining quality control, managing security and compliance risks, uncertainty about AI’s role in software development, and a lack of proper governance. To overcome these hurdles, organizations need to be proactive in their approach.
Recommended Articles
We hope this guide on generative AI for software development helps you optimize your development processes. Explore these recommended articles for additional insights and strategies to enhance your software projects.