Updated March 24, 2023
Introduction to HOLAP
HOLAP stands for Hybrid Online Analytical Processing. As the name suggests, it is a hybrid model consisting of two different types of OLAP, such as Relational Online Analytical Processing (ROLAP) and Multidimensional Online Analytical Processing (MOLAP). OLAP is nothing but a method applied form business intelligence activities, like Managing and Analyzing the data in the Data Warehouse systems. In a HOLAP based Model, the system consists of tables and databases which are constructed using Relational and Multidimensional Database Management Systems. In other words, HOLAP permits to store data in both the relational type of databases and the multidimensional type of databases, with the use of its caching feature for a repeatedly used set of data and complex queries for multidimensional tables.
Architecture of HOLAP
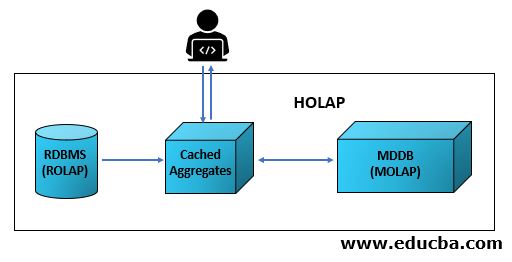
In a HOLAP system, the user can access the data from the relational database system and the multidimensional database system using simple queries for relational database and complex aggregate queries for a multidimensional database. As the querying process is complex and the same queries can be reused on a multidimensional system, it is efficient to build a cached data server just for the aggregates and repeatedly fetched data from the relational database. A Sample Model HOLAP Architecture can be pictured as
The User, that is the Analysts or Reporting professionals, queries the HOLAP for retrieving the required data. The querying involves both the relational database and the multidimensional database. The simple queries for the relational database bring the data to the cache system, and the complex queries themselves are saved in the cache system along with the data queried for the current flow. The data recovered from both the systems are then presented to the user, for the user to Analyze or create reports for business decision-making processes.
Since the multidimensional system is complex, caching needs to be maintained constantly, that is when every time an update is performed on the MDDB system. RDBMS doesn’t need any caching due to its simple structure. RDBMS uses the Cache system to combine the results with the results fetched from the MDDB. This model enables the dataflow to be more efficient, as the relational database is focused on the quantity of the data and MDDB focuses on the valuation of the data. When the aggregates are cached, the queries are stored, in order to not waste the effort of creating and applying the same queries repeatedly.
This helps in improving the performance of the HOLAP system while taking a huge amount of storage space. As HOLAP can have the advantages of both ROLAP & MOLAP, the sacrifice on storage space is a given.
Usability of HOLAP
HOLAP facilitates different combinations of ROLAP & MOLAP. The HOLAP Model can be designed based on the requirement provided by the project. This gives more creative options for the Database System Architects, unlike other OLAP systems available. Essentially, HOLAP can store data from both relational and multidimensional database systems. Accessing data from the combination of both the databases helps in fetching more accurate data, as the HOLAP system reduces redundancy. Due to this flexibility, the user can afford to relax the management of the desired data best suited for the given application.
HOLAP has another advantage while upgrading the existing databases as well. In cases of existing systems, if the existing system is a relational database, and if there is a new requirement for installing a multidimensional database for the same application, instead of applying these databases individually onto the same functional features of the application, it is more efficient to combine the databases. Hence converting the ROLAP & MOLAP systems into a single hub, that is HOLAP, brings in more efficiency and lesser processing time for the application.
HOLAP can have any number of ROLAP and MOLAP systems in it. A medium-size database that is applied to a smaller application can have reduced HOLAP systems. While a huge multi-level integrated application that uses multiple databases to fetch data usually will have different types of databases. Here, HOLAP will help to integrate all the databases and form a singular model with all types of databases in it. Caching will be a key feature that can simplify this kind of complex databases.
Advantages and Disadvantages of HOLAP
Here are the advantages and disadvantages of HOLAP mention below
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
| Better Accessibility in comparison to both ROLAP & MOLAP models. | Larger data volume, as both ROLAP and MOLAP are combined to form HOLAP. |
| Faster querying as the Caching feature helps in not going back and forth often. | It occupies a lot of storage space, as it consists of the data from relational databases and multidimensional databases. |
| Moderate query performance, faster than ROLAP & slower than MOLAP. | Processing can be slow when querying involves more of the relational databases, as ROLAP contains all the categorical data. |
| Cubes are smaller than MOLAP since only precise data is fetched for processing. | System processing needs to be done every time data is updated, inserted or deleted in the database. |
| The best solution when data volume is expected to increase over time. | Cache needs to be updated whenever an update happens in the database associated with the stored queries and relational data |
| Higher processing ability, when related to ROLAP and MOLAP systems. | Maintenance is complex, as the updates can be expected quite often. |
| Volume to occupy huge data, as it has a relational database inside HOLAP. | Difficulty in finding a balance in storage and performance while designing the HOLAP system. |
Conclusion
HOLAP was invented as a solution to avoid the confusion of choosing between ROLAP & MOLAP, as both have their own advantages. As the relational database is the best solution for the larger volume of data, but the multidimensional database is the finest for high performance, combining both can be advantageous. If the project demands easy accessibility of data and good performance, even with the large volume of data, HOLAP will be the best solution. Or, if the legacy application has a relational database with a large amount of data and the new features need multidimensional accessibility, then a new MOLAP can be added to the existing ROLAP to form a HOLAP system.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to HOLAP. Here we discuss the architecture and usability of HOLAP along with the advantages and disadvantages. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –