Updated March 22, 2023

Introduction to Hierarchical Clustering Algorithm
The hierarchical clustering algorithm is an unsupervised Machine Learning technique. It aims at finding natural grouping based on the characteristics of the data. The hierarchical clustering algorithm aims to find nested groups of the data by building the hierarchy. It is similar to the biological taxonomy of the plant or animal kingdom. Hierarchical clusters are generally represented using the hierarchical tree known as a dendrogram.
Types of Hierarchical Clustering Algorithm
Hierarchical clustering algorithms are of 2 types:
- Divisive
- Agglomerative
1. Divisive
This is a top-down approach, where it initially considers the entire data as one group, and then iteratively splits the data into subgroups. If the number of a hierarchical clustering algorithm is known, then the process of division stops once the number of clusters is achieved. Else, the process stops when the data can be no more split, which means the subgroup obtained from the current iteration is the same as the one obtained from the previous iteration (one can also consider that the division stops when each data point is a cluster).
2. Agglomerative
It is a bottom-up approach that relies on the merging of clusters. Initially, the data is split into m singleton clusters (where the value of m is the number of samples/data points). Two clusters are merged into one iteratively thus reducing the number of clusters in every iteration. This process of merging clusters stops when all clusters have been merged into one or the number of desired clusters is achieved.
At level 1, there are m clusters that get reduced to 1 cluster at level m. Those data points which get merged to form a cluster at a lower level stay in the same cluster at the higher levels as well. Eg., suppose there are 8 points x1..x8, so initially, there are 8 clusters at level 1. Suppose points x1 and x2 get merged into a cluster at level 2, then till level 8, they stay in the same cluster.
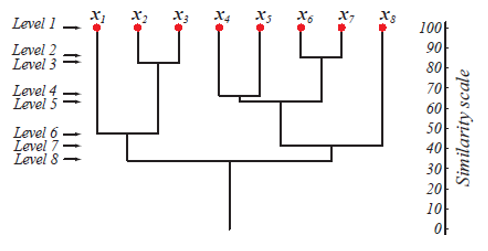
The above figure shows a dendrogram representation of the agglomeration clustering approach for 8 data points as well as the similarity scale corresponding to each level. The levels of clusters give us an idea of how similar the data points in the clusters are. As shown in fig 1, earlier the data points get merged into a cluster, the similar they are. So, the data points within a cluster at level 2 (eg. x2 and x3) are more similar than those data points in a cluster at level 6 (eg. x1 and x2).

The above figure shows the Set or Venn diagram representation of the agglomerative clustering approach of the above-mentioned 8 data points. Both dendrograms and set representations can be used for clustering. However, a dendrogram is usually a preferable asset representation that cannot quantitatively represent the cluster similarities.
Steps for Hierarchical Clustering Algorithm
Let us follow the following steps for the hierarchical clustering algorithm which are given below:
1. Algorithm
Agglomerative hierarchical clustering algorithm.
- Begin initialize c, c1 = n, Di = {xi}, i = 1,…,n ‘
- Do c1 = c1 – 1
- Find nearest clusters, say, Di and Dj
- Merge Di and Dj
- Until c = c1
- Return c clusters
- End
This algorithm begins with n clusters initially where each data point is a cluster. With each iteration, the number of clusters reduces by 1 as the 2 nearest clusters get merged. This process continues until the number of clusters reduces to the predefined value c.
How to Decide Which Clusters are Near?
That is defined using several distance metrics which are as follows:
- The minimum distance between the clusters dmin(Di,Dj). Useful for single.
- The maximum distance between the clusters dmax(Di,Dj). Useful for complete.
- The average distance between the clusters davg(Di,Dj).
What is Single Linkage and Complete Linkage?
- When dmin(di,dj) is used to find the distance between two clusters, and the algorithm terminates if the distance between the nearest clusters exceeds a threshold, then the algorithm is called a single linkage algorithm.
- When dmax(Di,Dj) is used to find the distance between two clusters, and the algorithm terminates if the distance between the nearest clusters exceeds a threshold, then the algorithm is called a complete linkage algorithm.
- Let us consider each data point as a node of a graph. There is an edge between two data points if they belong to the same cluster. When two nearest clusters are merged, an edge is added. It is called a single linkage because there exists a unique path from one node to the other.
- The complete linkage algorithm merges two clusters by minimizing the distance between the two farthest points.
- A single linkage algorithm generates a spanning tree. However, this algorithm is susceptible to noise. A complete linkage algorithm generates a complete graph.
What is Time Complexity of the Algorithm?
Suppose we have n patterns in d-dimensional space, and we use dmin(Di,Dj) to form c clusters. We need to calculate n(n − 1) inter-point distances — each of which is an O(d2) calculation — and place the results in an inter-point distance table. The space complexity is O(n2). Finding the minimum distance pair (for the first merging) requires that we step through the complete list, keeping the index of the smallest distance.
Thus for the first agglomerative step, the complexity is O(n(n − 1)(d2 + 1)) = O(n2d2). For another arbitrary agglomeration step (i.e., from c1 to c1 − 1), we merely step through the n(n − 1) – c1 “unused” distances in the list and find the smallest for which x and x’ lie in different clusters. This is, again, O(n(n−1)−c1). The total time complexity is thus O(cn2d2), and in typical conditions n >> c.
2. Visualization
Once the data is split into clusters, it is a good practice to visualize the clusters so as to get an idea of how does the grouping look. But visualizing this high-dimensional data is difficult. Hence we use Principal Component Analysis (PCA) for visualization. After PCA, we obtain the data points in the low dimensional space (generally 2D or 3D) which we can plot to see the grouping.
3. Evaluation
One of the methods for the evaluation of clusters is that the distance of the points between the clusters (inter-cluster distance) should be much more than the distance of the points within the cluster (intracluster distance).
Conclusion
The hierarchical clustering algorithm is used to find nested patterns in data Hierarchical clustering is of 2 types – Divisive and Agglomerative Dendrogram and set/Venn diagram can be used for representation Single linkage merges two clusters by minimizing the minimum distance between them. It forms a spanning Complete linkage merges two clusters by minimizing the maximum distance between It forms a complete graph. The total time complexity of the hierarchical clustering algorithm is O(cn2d2), where c is the predefined number of clusters, n is the number of patterns and d is the d- dimensional space of the n patterns.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to the Hierarchical Clustering algorithm. Here we discuss the types and steps of hierarchical clustering algorithms. You may also look at the following articles to learn more-

