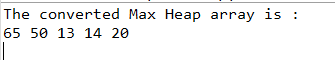Updated March 13, 2023
Introduction to Heap data structure in Java
The following article provides an outline for Heap data structure in Java. The heap is a special type of tree-based data structure where the tree is a complete binary tree. On the other hand, the binary tree is a tree in which each node can have a maximum of two children. Therefore, we must first understand the full binary tree before understanding more about the heap data structure.
The root node of a heap data structure is compared to its children and ordered according to the order. If x is a root node and y is one of its children, the property key (x)>= key (y) will produce a maximum heap. The “Heap Property” refers to the relationship between the root and the child node mentioned property key (x)>= key (y).
The heap can be one of two kinds, depending on the order of parent-child nodes:
1. Max-Heap –
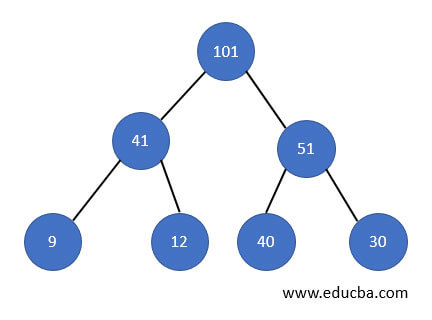
The root node key in a Max-Heap is the greatest of all the keys in a heap. Therefore, it should be ensured that all sub trees in a heap have the same property recursively.
Below is an illustration of a Min-heap tree. The root node is greater than its children, as we can see.
2. Min-Heap –
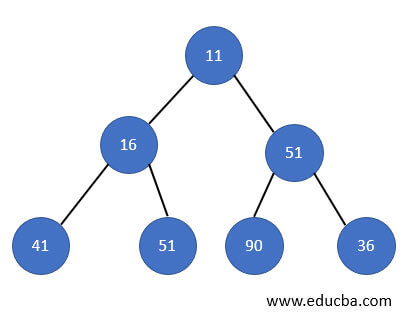
The root node key in a Min-Heap is the smallest or least significant of all the other keys in a heap. This property should be recursively valid in all other subtrees in a heap, just as it is in the max heap.
Below is an illustration of a Min-heap tree. The root key is the smallest of all the keys in a heap, as we can see.
The time complexity of the max heap is O(logn) because the tree’s height determines the maximum number of comparisons available in the max heap. Thus, the full binary tree’s height is always logn.
A straightforward method for implementing a heap data structure in Java –
A heapify is the method of converting a binary tree into a heap data structure. A Min-Heap or a Max-Heap can be made with it.
- Accept an input array.
- From the array, create a complete binary tree.
- Begin with the first index of a non-leaf node, whose index is n/2 – 1.
- Make the current element I the biggest.
- The index of the left child is 2i + 1, and 2i+2 is the index of the right child.
Set leftChildIndex to largest if leftChild is greater than currentElement (i.e. element at ith index).
Set rightChildIndex to largest if rightChild is greater than the element in largest.
- Replace the largest element with the currentElement.
- Steps 3 to 7 should be repeated before the subtrees are heapified as well.
The algorithm of the heap data structure –
Heapify ( arr, size, i)
Step 1: make i the largest
Step 2: lChild = 2i + 1
Step 3: rChild = 2i + 2
Step 4: if lChild > arr[largest]
set lChildIndex as largest
Step 5: if rChild > arr[largest]
set rChildIndex as largest
Step 6: swap arr[i] and arr[largest]
To create a Max-Heap:
MaxHeap(array, size)
loop from the non-leaf node’s first index to zero
call Heapify
Return value – The return value of this algorithm is the max heap.
Examples for the heap data structure in java
Example for max heap data structure in java to insert an element in the max heap –
Program example 1 –
package jex;
import java.util.ArrayList;
class Heap {
void heapify(ArrayList <Integer> mh, int i) {
int size = mh.size();
int largest = i;
int lc = 2 * i + 1;
int rc = 2 * i + 2;
if (lc < size && mh.get(lc) > mh.get(largest))
largest = lc;
if (rc < size && mh.get(rc) > mh.get(largest))
largest = rc;
if (largest != i) {
int temp = mh.get( largest );
mh.set( largest, mh.get(i) );
mh.set( i, temp );
heapify(mh, largest);
}
}
void insert(ArrayList <Integer> mh, int n) {
int size = mh.size();
if (size == 0) {
mh.add( n );
} else {
mh.add( n );
for (int i = size / 2 - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
heapify( mh, i);
}
}
}
void printHeap(ArrayList<Integer> a, int size) {
for (Integer i : a) {
System.out.print(i + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
public static void main(String args[]) {
ArrayList <Integer> a = new ArrayList <Integer>();
int size = a.size();
Heap h = new Heap();
h.insert(a, 13);
h.insert(a, 14);
h.insert(a, 65);
h.insert(a, 50);
h.insert(a, 20);
System.out.println("The converted Max Heap array is : ");
h.printHeap(a, size);
}
}An output of the above code is –
As in the above program, the Heap class is created which contains heapify(), insert() and printHeap() functions. The heapify() function is used to create the max heap from the passed ArrayList by setting the leftchild or rightchild largest based on the condition. The insert() function is used to insert the number into the max heap, and the printHeap() function is used to print the max heap. Then, in the main function, the ArrayList of an integer is created, and also the Heap class object is created. Next, insert the element into the heap object by calling the insert() function on the heap object. After inserting all the elements calling the printHeap() function which prints the max heap, as we can see in the above output.
Conclusion
The heap is based on the complete binary tree data structure. The binary tree is a tree in which each node can have a maximum of two children. Thus, there are two kinds of heap which are max heap and min-heap. The time complexity of the max heap is O(logn).
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Heap data structure in Java. Here we discuss the full binary tree before understanding more about the heap data structure. You may also look at the following articles to learn more –