Updated July 31, 2023
Gordon Growth Model Formula (Table of Contents)
- Gordon Growth Model Formula
- Examples of the Gordon Growth Model Formula (With Excel Template)
- Gordon Growth Model Formula Calculator
Gordon Growth Model Formula
The term “Gordon Growth Model” refers to the method of stock valuation based on the present value of the stock’s future dividends, irrespective of the current market conditions.
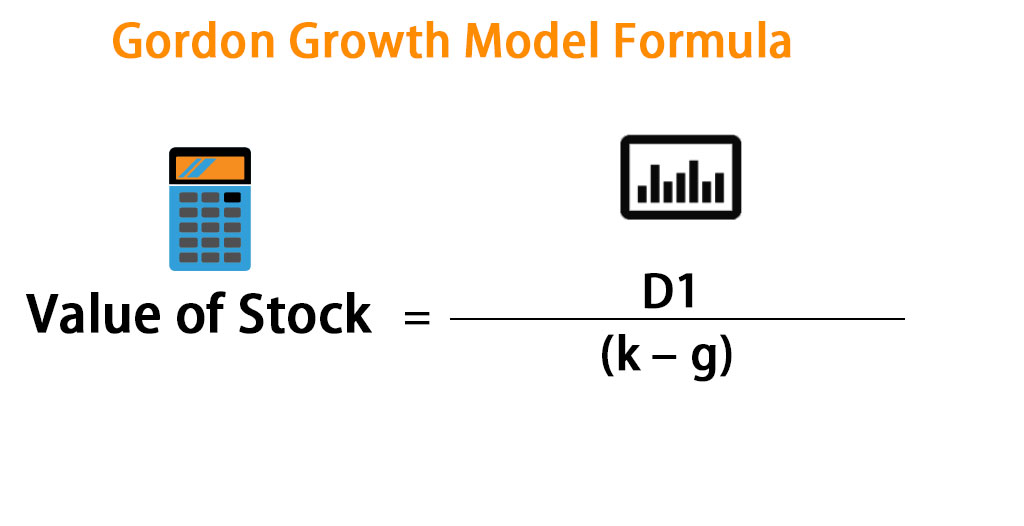
The Gordon Growth Model is also referred to as the dividend discount model. The formula is applicable for dividend-paying stocks only and the formula for the stock valuation is computed by dividing the next year’s dividend per share by the difference between the investor’s required rate of return and dividend growth rate. Mathematically, it is represented as,
where,
- D1 = Expected dividend per share to be paid next year
- k = Investor’s required rate of return
- g = Expected dividend growth rate
There are basically two forms of the model:
- Stable model: As per the model, the dividends are assumed to grow at the same rate.
- Multistage growth model: The above assumption is not realistic as the expected dividend growth rate changes over the period of time which is captured in this model.
Examples of the Gordon Growth Model Formula (With Excel Template)
Let’s take an example to understand the calculation of the Gordon Growth Model formula in a better manner.
Gordon Growth Model Formula – Example #1
Let us take the example of ABC Ltd that has planned to pay out a dividend of $2.00 per share next year and as per the market, the dividend is expected to grow by 6% per year thereafter. Also, the required rate of return of the investor is 9%. Currently, the stock ABC Ltd is trading in the market at $50 per share. Determine the intrinsic value of the stock based on the above formula.
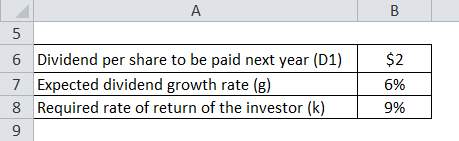
Using the formula of the Gordon growth model, the value of the stock can be calculated as:
Value of stock = D1 / (k – g)
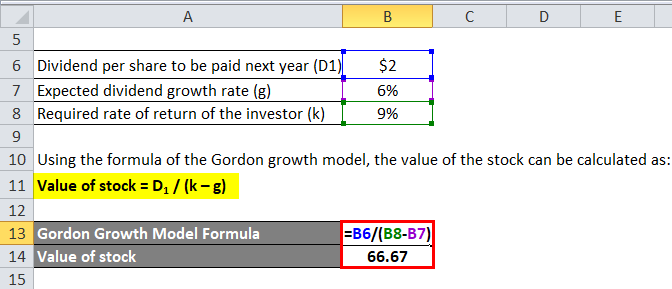
- Value of stock= $2 / (9% – 6%)
- Value of stock = 66.67
Therefore, the intrinsic value of the stock is higher than the market value of the stock. As such, it is advisable to purchase the stock of ABC Ltd as the market value is expected to go up to its intrinsic value.
Gordon Growth Model Formula – Example #2
Let us take the example ABC Ltd again and assume that the company will increase the dividends rapidly during the next few years and then stabilize the growth rate. So, in the current year, the dividend paid is $1.82 per share, but the dividends will grow by 10% and 12%, in the subsequent two years and then steadily increase by 6% thereafter. The required rate of return of the investor continues to be 9%. Determine the intrinsic value of the stock based on the above formula while incorporating the impact of unusual dividend growth.
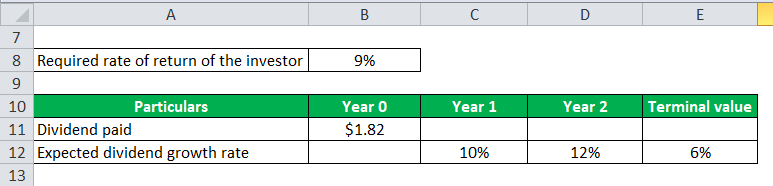
Dividend per share is calculated as:
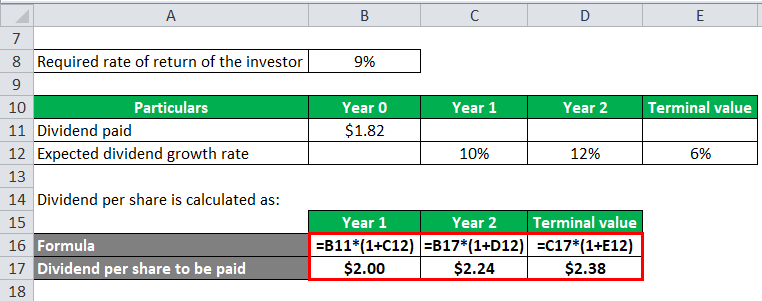
- Dividend per share to be paid in year 1, D1 = $1.82 * (1 + 10%) = $2.00
- Dividend per share to be paid in year 2, D2 = $2.00 * (1 + 12%) = $2.24
- Dividend per share to be paid in year 3, D3 = $2.24 * (1 + 6%) = $2.38
Terminal value is calculated as:
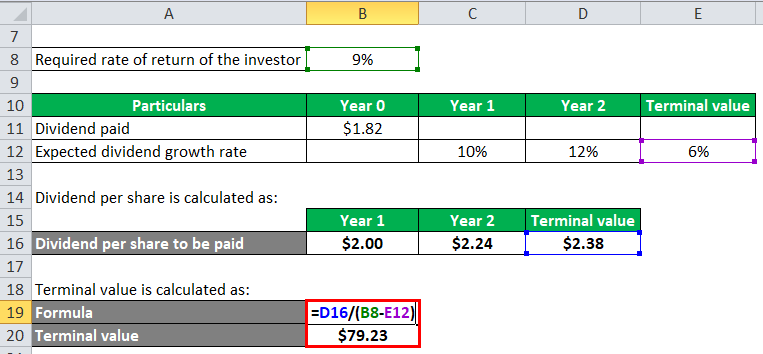
- Terminal value = $2.38 / (9% – 6%)
- Terminal value = $79.23
Present Value is calculated as:
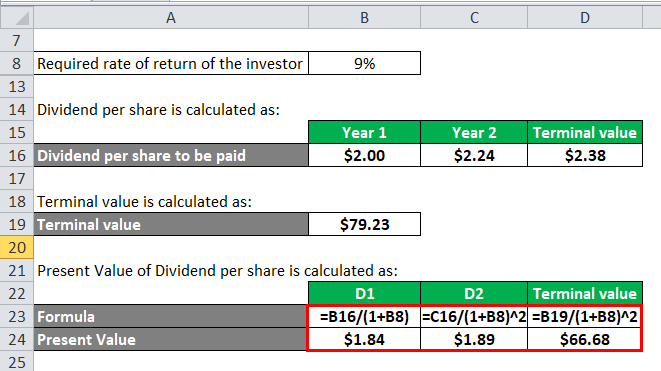
- PV of D1 = $2.00 / (1 + 9%) = $1.84
- PV of D2 = $2.24 / (1 + 9%)2 = $1.89
- PV of terminal value = $79.23 / (1 + 9%)2 = $66.68
Therefore, value of the stock under the multi growth model can be calculated as,
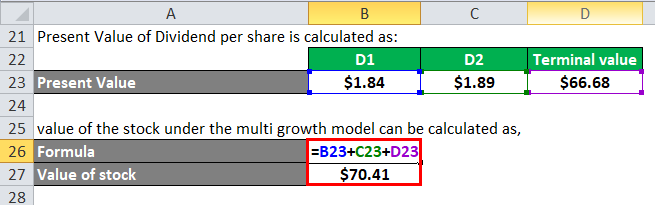
- Value of stock = $1.84 + $1.89 + $66.68
- Value of stock = $70.41
Therefore, the intrinsic value of the stock is $70.41.
Explanation of the Gordon Growth Model Formula
The formula for the Gordon Growth Model is calculated by using the following steps:
Step 1: Firstly, determine the dividend that is going to be paid next year. The information is likely to be received from the corporate strategy of a particular company. Say the company declared that next year the dividend (D1) will grow by x% and the current dividend is D0. Then, the expected dividend next year is,
D1 = D0 * (1 + x%)
Step 2: Next, the required rate of return expected by the investor from the stock investment is determined based on the risk appetite of the investor and the ongoing market condition. It is denoted by k.
Step 3: Next, the dividend growth is determined based on the company’s earnings projection and market situation. In some cases, a single model has more than one dividend growth rate i.e. multistage growth model. It is denoted by g.
Step 4: Finally, the formula for Gordon Growth Model is computed by dividing the next year’s dividend per share by the difference between the investor’s required rate of return and dividend growth rate as shown below.
Value of stock = D1 / (k – g)
Relevance and Uses
It is very important to understand that the Gordon Growth Model can be used to determine a clear relation between valuation and return, despite the fact that the valuation is very sensitive to changes in the discount rate. Nevertheless, the model suffers from a major problem with the assumption that a company grows at a constant rate since it is highly impractical for a company. Further, the model’s sensitivity to the growth rate and discount factor is also another drawback.
Gordon Growth Model Formula Calculator
You can use the following Gordon Growth Model Calculator.
| D1 | |
| k | |
| g | |
| Value of Stock | |
| Value of Stock= |
| |||||||||
|
Recommended Articles
This has been a guide to Gordon Growth Model formula. Here we discuss How to Calculate the Gordon Growth Model along with practical examples. We also provide the Gordon Growth Model Calculator with downloadable excel template. You may also look at the following articles to learn more –

