Updated March 22, 2023
Difference Between Git ReBase vs Merge
The following article provides an outline for Git ReBase vs Merge. In this article, we will be discussing two such tools Rebase and Merge and their difference. GIT is one of the most commonly used distributed version controller DVCS among the programmers because of its dynamic nature and vast tool availability to handle the versions. There are two ways with which we can send our changes from one branch to another. One is by using Rebase, and the other is Merge which is quite popular.
Head to Head Comparison Between Git ReBase vs Merge (Infographics)
Below are the top 5 comparisons between Git ReBase vs Merge:
Key Differences Between Git ReBase vs Merge
Let’s discuss the key difference between Git ReBase vs Merge:
1. Git Rebase
Git Rebase begins its work from a common commit between the two branches. Master and feature, from here, compare both and captures the snapshot of the difference done in one of the branches and then adds it to others.
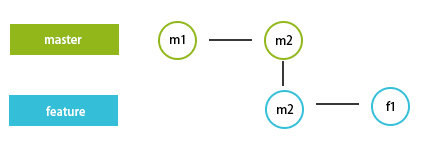
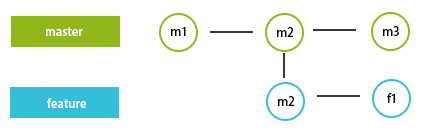
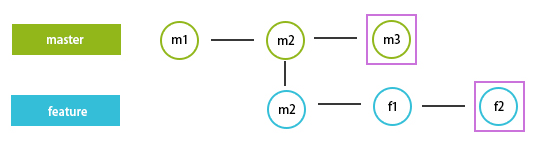
Let us imagine that we have a master branch and the latest commit to it, m2, as shown in the above screenshot. We create a feature branch from this commit, and we did some modifications and commit with the f1 message. Now let’s consider someone has merged his work to master, and now the latest commit of the master is m3, not m2, as shown below.
And we also continue to work on the feature branch to add its latest commit to be f2, as shown below.
As seen from the above screengrab, we have mastered the latest commit, m3 and we a have feature that is not up to date with the master as it was created from the m2 commit snapshot, which has the latest commit as f3. Now to combine these efforts with the master to generate is shown below.
Now we need to integrate the above changes, which can be done in two ways, one with merge and the other with rebase. Here we will look at how to integrate with rebase.
$ git checkout feature
Switched to a new branch 'feature'
$ git rebase master
From the above rebase command, we will try to look for a common commit from both master and feature, and in this case, it is m2. And then, since we have to rebase master, it will look for additions that were done with master and take snapshot m3 and rebase feature from m2 to m3. So now we have a feature with m3 (in place of m2), f1,f2 commits. Now I can apply to rebase on the feature to make the master branch updated with the feature changes. One thing to remember is any change to master must be audited.
$ git checkout master
Switched to a new branch 'master'
$ git rebase feature
Now in this, we will apply the latest commit feature branch that is f2 to master, and the latest commit snapshot of the master will be f2. You can list the commits by using the git log command, but we need to check out first to which branch we need to see the log like below.
$ git checkout feature
Switched to a new branch 'feature'
$ git log
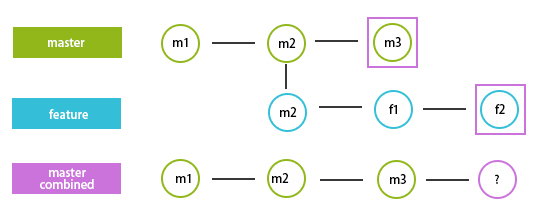
Now with rebase, we have integrated the updates of a feature to master. Let us try to achieve this by merge.
2. Git Merge
We will use the above screenshot for reference here, and we can achieve the same what we achieved with rebase and merge.
Git merge commits the last commit that we had in the feature branch, and in here, the case is with f2 commit, which gathers all the changes and merges it with the latest commit that we have in the master branch, m3 here. This looks complicated but can be easily performed by the merge command. We can either do a direct merge or squash merge and the difference in both.
$ git checkout master
Switched to a new branch 'master'
$ git merge feature
The above command will take all the commits of the feature and add them in the master’s log. To avoid that, we can use squash so that in the log of the master, we will after m3 only one commit and that’s is of update.
$ git checkout master
Switched to a new branch 'master'
$ git merge –squash feature
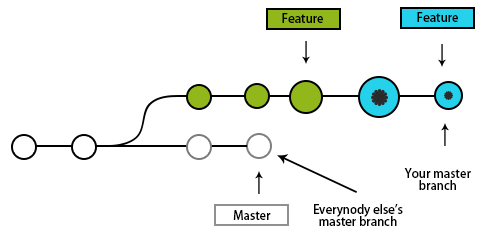
One should be careful while using git rebase and try to avoid it. The golden rule is to avoid it using public branches.
Just look at the above scenario. This can happen when u try to rebase master on top of your feature branch, and our master branch is public; now the master branch is updated, but everybody else is working on an older version of master. Since rebasing will result in brand new commits, git can think that the history of the master branch has diverged from everybody else. The only way to solve this will be to synchronize both the master by merging them back together and have a resultant set of commits that will be confusing.
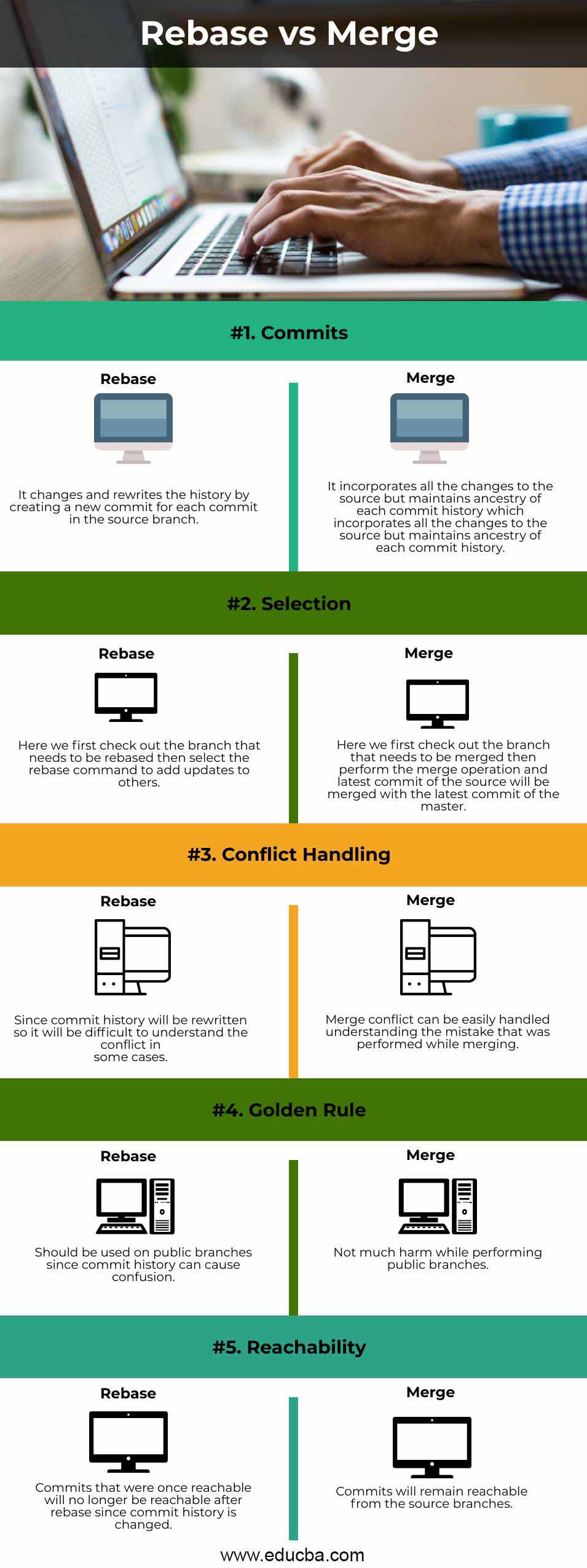
Comparison Table of Git ReBase vs Merge
The table below summarizes the comparisons between Git ReBase vs Merge:
| Basis of Comparison | Rebase | Merge |
| Commits | It changes and rewrites the history by creating a new commit for each commit in the source branch. | It incorporates all the changes to the source but maintains ancestry of each commit history incorporates all the changes to the source but maintains ancestry of each commit history. |
| Selection | Here we first check out the branch that needs to be rebased, then select the rebase command to add it updates to others. |
Here first check out the branch that needs to be merged first. Then perform the merge operation and latest commit of the source will be merged with the latest commit of the master. |
| Conflict Handling | Since commit history will be rewritten to understand the conflict will be difficult in some cases. |
Merge conflict can be easily handled, understanding the mistake that was performed while merging. |
| Golden Rule | Should to use on the public branches since commit history can cause confusion. | No much harm while performing public branches. |
| Reachability | Commits that were once reachable will no longer be reachable after rebase since the commit history is changed. | Commits will remain reachable from the source branches. |
Conclusion
Merge and Rebase are a couple of two powerful tools of Git, and both are used to incorporate the changes to the branches, but we must be a bit careful with rebase since it will rewrite the history of commits and using them on public branches can hamper the work of others causing them confusion. Whereas you can use the merge option as its commits are reachable from the source branch and can easily resolve merge conflicts if we have proper understanding.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to the top difference between Git ReBase vs Merge. Here we also discuss the key differences with infographics and comparison table. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –