Introduction to Galaxy Schema
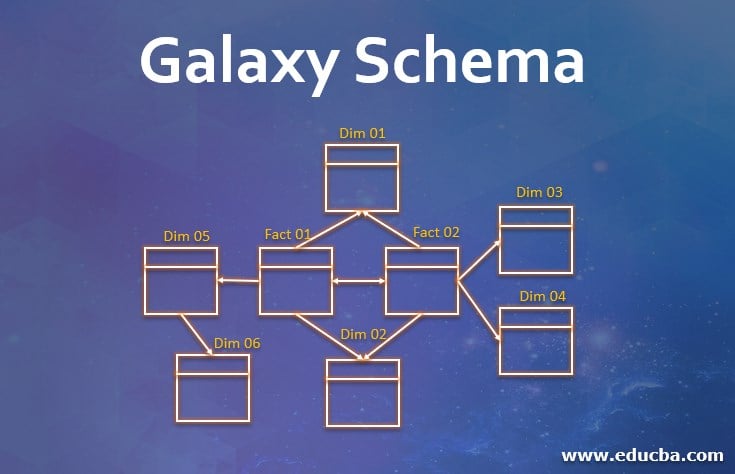
Galaxy Schema is also known as fact constellation schema, as the name suggests, appears like a galaxy in the space. The design involves more than one fact table, which are connected further with multiple dimension tables that are completely normalized. The fact table contains all the facts, while the dimension table contains the objects and properties, where the dimension tables are connected to the fact tables using the Foreign key from each dimension table.
Essentially, Galaxy schema can be derived as a collection of star schemas interlinked and completely normalized, to avoid redundancy and inaccuracy of data. It can also be a meaningful association of a Snowflake schema with a Star schema, where the fact tables of both schemas can be linked. The Dimension tables from both structures can be linked as per the requirement. The resulting system appears in the structure like a Constellation of stars, wherein fact tables are the stars here. This explains the name Galaxy schema. This type of schema is also called as ‘Fact constellation’ schema, as it has multiple fact tables.
Since this can have both star and snowflake schemas in it, Galaxy Schema is completely normalized. Normalization is nothing but breaking down of information into further more levels, so as to facilitate a meaningful relationship between the fact and dimension tables. This ensures accurate, organized and well-defined data in the system.
Reasons to Choose Snowflake Schema
Usually, the Schema type is chosen based on multiple parameters that are thought to be important for any given Project, by the Project Management team. Here are the basic characteristics of the Galaxy Schema that can help in making the choice,
- This model can involve more than one fact table and many dimension tables
- All the dimension tables are normalized until there is no more space for further normalization.
- Galaxy Schema makes it possible for the data in the Database to be more distinct, in contrast to star schema but similar to snowflake schema.
- The Fact Table will have all the facts/ measures, while the Dimension Tables will have foreign keys to connect with the Fact Table.
- Galaxy Schema allows the Dimension Tables to be linked to other Dimension tables, including the Dimension Tables in the first level.
- This Multidimensional nature makes it easy to implement on complex Relational Database systems, thus resulting in effective Analysis & Reporting processes.
- In terms of Accessibility, Complex multiple levels of Join queries are required to fetch aggregated data from the center fact table, using the foreign keys to access all the required Dimension tables, as the system itself is more complex.
- Multiple Dimension tables, which are created as a result of normalization, serve as lookup tables when querying with complex multi-level Join queries.
- The process of breaking down all the Dimension tables into multiple small Dimensions until it is completely normalized takes up a lot of storage space compared to other schemas.
- As the system and querying process is multifaceted, the speed of Data Retrieval from the database systems is by very slow.
- Different fact tables are explicitly assigned to each of the dimensions available. This is advantageous for facts associated with the given dimension table, and also for other facts that can have a deeper dimension level.
Workflow of Galaxy Schema
Here we will discuss the Workflow of Galaxy Schema by explaining how to create Galaxy Schema along with the pros and cons.
How to Create a Galaxy Schema?
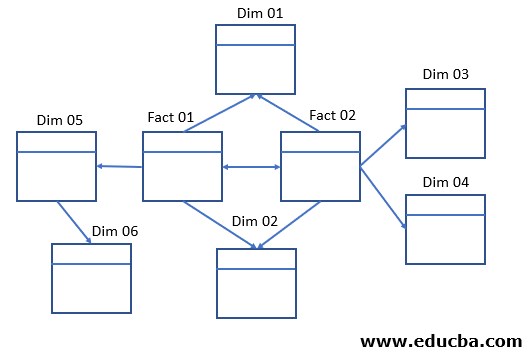
When the system consists of the fact tables A & B that is connected to the Dimension tables C, D, E, F, G, H, I, Galaxy Schema can be structured. Given the rules, fact tables can be connected with one another, and dimension tables can be connected with any fact table and dimension table inside the system, the below example will help in better understanding the underlying concept of a Galaxy Schema.
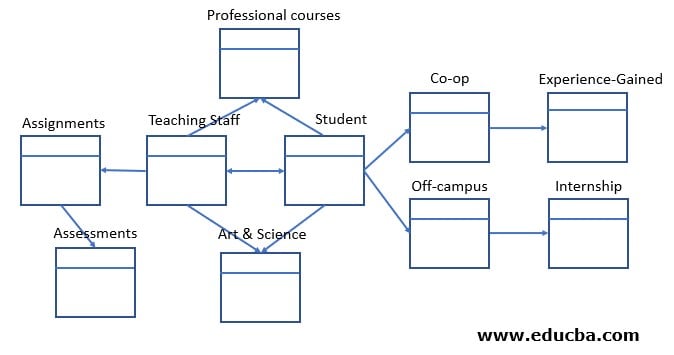
In this example, the student database has two fact tables – students & Teaching staff. Both the fact tables can have common dimensions – Professional courses, Arts & Science, based on their respective departments. From the student dimension, furthermore, normalization applied to derive co-op and offcampus jobs. This can be further broken down to mention the experience types and internships.
On the other side, the teaching staff will have assignments for students. And, these assignments dimension table can be further normalized to define assessment details. All these dimension tables can be further normalized based on the limitations of the information provided for the designing team by the project.
Pros and Cons of Galaxy Schema
The following pros and cons are mention below –
Pros:
- Its multidimensional nature helps in structuring complex Database systems efficiently.
- Minimum or no redundancy, as a result of Normalization.
- This is a flexible Schema, considering the complexity of the system.
- Data Quality will be fine, as Normalization provides the advantage for well-defined tables/ data formats.
- When queried with Joins, clear & accurate data can be extracted.
- High Data quality & accuracy helps in creating exceptional Reporting & Analytical results.
Cons:
- Galaxy schema can be Complex in structure.
- Working on this schema is tedious, as the complexity in both Schema and database system makes it more intricate all together.
- Data retrieval is done with multi-level joins combined with conditional expressions.
- The number of levels of normalization is expected, depending on the depth of the given database.
- Maintenance and support tasks get difficult as Galaxy schema is applied for larger database systems with complex structures.
- Large storage space is required for its larger design arrangement and detailed querying process.
- The analysis gets difficult, as it has no limitation on how many fact and dimension tables it can have.
Conclusion
When the project team is provided with more than one fact tables, than has both individually connected dimensions and dimensions shared amongst the fact tables, Galaxy Schema can be a well-organized solution. Most of the advanced applications might need multiple fact tables to share dimension tables, and Galaxy Schema is a given in such cases. If the requirement comes with consent for more storage space, acceptance for low performance, structures with more than one fact tables & more than one dimension tables, time & space for normalization, Galaxy Schema will be the best solution for that particular Database system.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Galaxy Schema. Here we discuss the workflow of Galaxy Schema by explaining how to create Galaxy Schema? the pros and cons respectively. You can also go through our other suggested articles to learn more –