Updated March 17, 2023
Introduction to Functions in PHP
IN PHP, many functions are used such as built-in functions and user-defined functions. Each and every function has its own functionality and properties. A function is a set of statements written in the program that can be used multiple times in the code anywhere needed. A function call is required to execute the statements written inside the function. It is a piece of code that takes one or more inputs as a parameter and processes it and returns a value. Programmers simply have to create a function and then call that function in the program wherever required.
Types of Functions in PHP
In PHP, mainly two functions are used by the programmers. They are:
1. User-Defined
These functions are used when the developer or programmer has to execute their own logic of code. These functions are defined using the keyword function and inside the function, a set of statements will be written to execute it when a function call occurs. The function call can be made by just simply calling the function like functionname(), and the function will get executed.
2. Built-in
These functions provide us with built-in library functions. PHP provides these functions in the installation package itself which makes this language more powerful and useful. To use the properties of the function we just need to call the function wherever required to fetch the desired result.
There are many built-in functions used in PHP such as Date, Numeric, String, etc.
- String Functions: These functions have a predefined functionality in PHP to work with strings. PHP has various string functions such as strpos(), strncmp(), strrev(), strlen(),
- Date Function: These functions are predefined functionality in PHP where the format is a UNIX date and time which is a human-readable format.
- Numeric Functions: These functions have their own predefined logic provided by PHP which is used for numeric operations. It will return the result either in Boolean form or in the numeric form. Some of the numeric functions include is_number(), number_format(), round() ,etc.
Why we should Use Functions in PHP?
Below are the points explain why should we use functions in php:
- Reusability: In any of the programming languages, a function is used to reduce the lines of code to be written multiple times. This will reduce the time and effort of the developer or programmer. If a common code has to be used in multiple areas then we can simply contain it in a function and call it wherever and whenever required. This can be achieved by calling the functions either in the same program or to be used in some different programs.
- Easier Error Detection: Since the code is not written as bulk but split or divided into functions, the error occurred if any can be easily detected and the error can be fixed fast and easily.
- Easily Maintained: As functions are used in the program, so if any function or any lines of code needs to be changed, we can change it easily in the function and the change will be reflected. Hence, it is easy to maintain anywhere.
How Functions are Used in PHP?
As we discussed earlier, in PHP we have two functions i.e. built-in and user-defined. Let’s understand more about these functions:
Example #1
For String Functions
Code:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
<?php
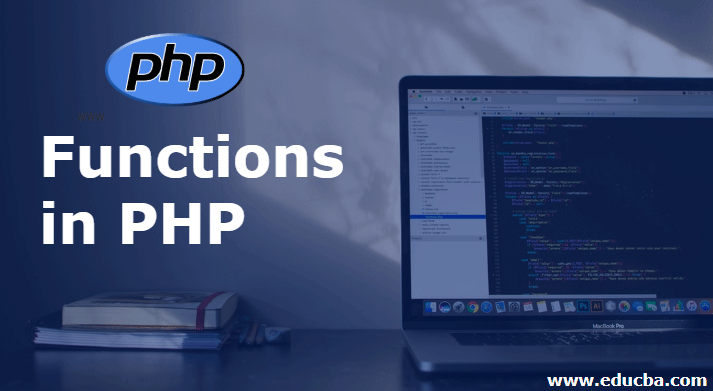
print_r(str_split("Hi This is a test sample"));
?>
</body>
</html>Output:
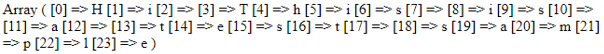
The explanation for the above program: In the above example, the string that we passed inside the function str_split(), splits the string on to a single character and produces the output.
Example #2
Code:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
<?php
echo strcmp("Hi this is test","Hi this is test");
?>
<p>If this function returns 0, the two strings are same.</p>
</body>
</html>Output:
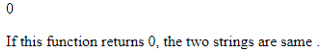
The explanation for the above program: In the above example, the function strcmp () will compare the strings and if the strings are the same it will return zero and if the strings are not equal then it will return some other number.
Example #3
Code:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
<?php
echo strpos("I love coding, I love php too!","coding");
?>
</body>
</html>Output:
![]()
The explanation for the above program: This function strpos() will check the position of the string that is passed as a parameter.
Example #4
Code:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
<?php
echo strrev("Hi world!");
?>
</body>
</html>Output:
![]()
The explanation for the above program: In the above example, the function strrev() will reverse the string passed as a parameter and provides the desired output.
Example #5
Code:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
<?php
echo str_word_count("Hello this is the new world!");
?>
</body>
</html>Output:
![]()
The explanation for the above program: In the above example, the str_word_count() function will count the number of strings passed as a parameter and provides the desired output.
Example #6
Code:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
<?php
echo strlen("Hello this is the test sample!");
?>
</body>
</html>Output:
![]()
The explanation for the above program: In the above example, the strlen() function will count the number of characters present in the string and provides the count as the desired output.
Example #1
For Numeric Functions
Code:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
<?php
echo(abs(5.8) . "<br>");
echo(abs(-5.8) . "<br>");
echo(abs(-2) . "<br>");
echo(abs(3));
?>
</body>
</html>Output:
The explanation for the above program: In the above example, the numeric function abs() will provide us the absolute value of the number that is passed as a parameter to the function.
Example #2
Code:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
<?php
echo(round(0.65) . "<br>");
echo(round(0.75) . "<br>");
echo(round(0.30) . "<br>");
?>
</body>
</html>Output:
![]()
Example #3
Code:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
<?php
echo(sqrt(0) . "<br>");
echo(sqrt(7) . "<br>");
echo(sqrt(2) . "<br>");
echo(sqrt(0.45) . "<br>");
echo(sqrt(-3));
?>
</body>
</html>Output:

The explanation for the above program: In the above example, the parameters passed to the function sqrt() fetches the result by calculating the square root of the number and produces the desired output.
Example #4
Code:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
<?php
// Check if the type of a variable is integer or not
$x = 456;
var_dump(is_int($x));
echo "<br>";
// Check whether the type of variable is integer or not
$x = 66.58;
var_dump(is_int($x));
?>
</body>
</html>Output:
![]()
The explanation for the above program: In the above example, the var_dump() function will check the data type of a particular number passed as a parameter. In the above screenshot, the output is printed as true or false in the condition that the number should be an integer. If the number is not an integer it will return false else true.
Example #5
Code:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
<?php
// Invalid calculation will return a NaN value
$x = acos(10);
var_dump($x);
?>
</body>
</html>Output:
![]()
The explanation for the above program: In the above example, the function var_dump() will check the datatype of the number passed as a parameter. In this example, the function acos() cannot calculate the number specified as a parameter and hence produces the output NAN which means that the calculation is incorrect.
Example #6
Code:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
<?php
$x = 11.35;
var_dump(is_float($x));
?>
</body>
</html>Output:
![]()
The explanation for the above program: In the above example, the function is_float() will check whether the number passed as a parameter is of float datatype. This function always returns a Boolean value. If the result is positive then it will return true and if the result is negative it will return false.
Example #1
For User-defined functions
Code:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
<?php
function Writefunction() {
echo "Hello world!";
}
Writefunction();
?>
</body>
</html>Output:
![]()
Example #2
Code:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
<?php
function employee($ename) {
echo "$ename Patil.<br>";
}
employee("Akshay");
employee("Leela");
employee("Sharda");
employee("Subhadra");
employee("Akash");
?>
</body>
</html>Output:
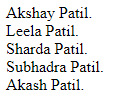
Example #3
Code:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
<?php
function Employee($ename, $id) {
echo "employee name is $ename. Employee id is $id <br>";
}
Employee("Heetal","778456");
Employee("Clark","567890");
Employee("Mohit","567894");
?>
</body>
</html>Output:

The explanation for the above program: In the above example, the employee names along with the employee id’s can be displayed by just calling the function employee () where the user wants to print the employee details. This user-defined functions can be used when the organization has a huge data and has to print all the employee details all together at a single go.
Example #4
Code:
<?php
function addNumbers(int $a, int $b) {
return $a + $b;
}
echo addNumbers(5, "13 days");
// since strict is NOT enabled "5 days" is changed to int(5), and it will return 10
?>Output:
![]()
The explanation for the above program: In the above example, we have seen that the user-defined functions have their own properties and also the user can give his own inputs to get the desired output. User-defined functions are used by a programmer or developer to make his own changes in the code rather than use built-in functions. The main motive of using this function type is that the developer can make his own logic such as calculation of area of the circle, measurement of height, employee details, etc. PHP has loosely typed language where the datatypes are not set in a strict way, we can add the integer and string datatype values to fetch the output. In the example above the integer and string “5 and 13” are added together and the output is fetched as 18. This feature makes an advantage to the user.
Conclusion
In this article, we discussed the types of functions in PHP and also its characteristics. The developers and programmers try to develop the code using these two functions as they don’t have to write it again and also the code are easy to test as it is written based on the type of task it has to perform.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Functions in PHP. Here we discuss the types of function in php and how to use the function in php with the different examples. You can also go through our other related articles to learn more-


