Updated April 6, 2023
Introduction to Function Prototype in C
A function prototype is one of the most important features of C programming which was originated from C++. A function prototype is a declaration in the code that instructs the compiler about the data type of the function, arguments and parameter list. As we all know that a block of code which performs a specific task is called as a function. In the same way, a function prototype is a function which specifies return type, function name and its parameter to the compiler so that it can match with the given function calls when required.
Syntax:
returntypefunctionname( datatype paramter1 , datatype paramter2 , datatype paramter3..);Example:
Code:
intaddition(int a, int b);In the above example addition is the name of the function of integer data type is the return type and a and b are the argument of two arguments of type int passed to the function. Note that we can pass as many arguments we want in our function based on the requirement. Also in the same program we can define as many prototype we want but they should differ in either name or argument list. All you have to do is define a prototype in the code and then call it anytime by using the function name.
Examples of Function Prototype in C
Given below are the examples mentioned:
Example #1
Code:
#include <stdio.h>
int Num_addition( int i , int j );// prototype for the function
int main()
{
int num1,num2,total;
printf( " Please enters the 2 numbers you want to add : " ) ;
scanf( "%d %d" , &num1 , &num2 ) ;
total = Num_addition( num1 , num2 ) ; // calling the function
printf( " The total of the given numbers is = %d " , total ) ;
return 0 ;
}
int Num_addition( int i , int j ) // function definition for prototype
{
int results;
results = i + j ;
return results ;
}Output:

As you can see in the above code, initially we are declaring the function prototype for the addition of two numbers with name “ Num_addition ” of integer return type with two integer arguments named as i and j into the function. In the main class, we defined three integers num1, num2, and total. After that, we are taking input from the users then storing the addition results of the two given numbers in total. To call the function “ Num_addition“ function is used again. At last in the function definition you can see we are giving the logic to perform addition and store it in results.
Example #2
Code:
#include <stdio.h>
intNum_subtraction( inti , int j ); // prototype for the function
intmain()
{
int num1 , num2 , output ;
printf( " Please enters the 2 numbers you want to subtract : " ) ;
scanf( "%d %d" , &num1 , &num2 ) ;
output = Num_subtraction( num1 , num2 ) ;
printf( " The subtraction of the given numbers is = %d " , output ) ;
return 0 ;
}
intNum_subtraction( inti , int j )// function definition
{
intresults ;
results = i - j ;
return results ;
}Output:
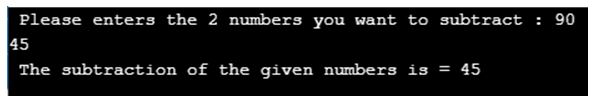
As you can see in the above code, initially we are declaring the function prototype for the subtraction of two numbers with name “ Num_subtraction ” of integer return type with two integer arguments named as i and j into the function. In the main class, we defined three integers num1, num2, and output. After that, we are taking input from the users then storing the subtraction results of the two given numbers in output. To call the function Num_subtraction function is used again. At last in the function definition you can see we are giving the logic to perform subtraction and store it in results.
Example #3
Code:
#include <stdio.h>
intNum_multiplication( inti , int j );// prototype for the function
intmain()
{
int num1 , num2 , output ;
printf( " Please enters the 2 numbers you want to multiply : " );
scanf( "%d %d" , &num1 , &num2 ) ;
output = Num_multiplication( num1 , num2 );// calling the function
printf( " The multiplication of the given numbers is = %d " , output );
return 0 ;
}
intNum_multiplication( inti , int j )// function definition
{
intresults ;
results = i * j ;
return results ;// return statement to return results to user
}Output:

As you can see in the above code, initially we are declaring the function prototype for the multiplication of two numbers with name “ Num_multiplication ” of integer return type with two integer arguments named as i and j into the function. In the main class, we defined three integers num1, num2, and output. After that, we are taking input from the users then storing the multiplication results of the two given numbers in output. To call the function Num_multiplication function is used again. At last in the function definition you can see we are giving the logic to perform multiplication and store it in results.
Conclusion
Defining a function prototype in C helps is saving a huge amount of time in debugging and when it comes to overloading the function, prototypes help in figuring out which function to call in the given code which is really helpful in avoiding ambiguity and other programming problems.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Function Prototype in C. Here we discuss the introduction to Function Prototype in C along with respective examples for better understanding. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –


