Updated April 12, 2023

Introduction to Function Pointer in C++
Function pointer in C++ is a variable that stores the address of a function. We know that a pointer is a variable that stores the address of another variable, similarly function pointer stores the address of a function which can later be called through the function pointer and even we can pass the variable or pointer as a parameter to the function through a function pointer. Even the function pointer can pass as an argument and also can be returned from another function. The applications of function pointer are callbacks, in the event-driven application, storing functions in an array, etc.
The function pointer points to code, not data of the function. It stores the start address of executable code.
Syntax of Function Pointer in C++
The following is the syntax for the declaration, initialization, and call of a function pointer.
void myFunc(int x)
{
//some code of myFun() function
}
int main()
{
//declare function pointer
void (*funcPtr)(int);
/*Initialize function pointer(which stores the address of myFunc function)*/
funcPtr = &myFunc;
//call myFunc(note that no need to call (*foo)(2))
funcPtr( 4 );
//also can be called as
(*funcPtr)( 4 );
return 0;
}An in above syntax the function is declared. We know that function is not simple as variable, so function pointers have parameter list and return type as function. As in the above syntax for declaration “void (*funPtr)(int);”, first we provide the return type, and then pointer name(as funcPtr) enclosed by the brackets which proceed by the pointer symbol(*). And, then provide the list of the parameter as (int).
As in above syntax for initialization is “funcPtr = &myFunc;”, the function pointer(funcPtr) is initialize by the address of function(myFun).
As in above syntax to call function is “funcPtr( 4 );” or “(*funcPtr)( 4 );”, where the function pointer(funcPtr) is call as funcPtr(4) and pass the parameter 4.
Working and Examples of the Function Pointer in C++
Next, we write the C++ code to understand the function pointer working more clearly with the following example where we use function pointer to call a function indirectly through the pointer, as below –
Example #1
Code:
#include<stdio.h>
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
void square(int x)
{
cout<<"The square of a number is "<<x*x<<endl;
}
int main()
{
// declare funPtr pointer
void (*funPtr)(int);
// initialize funPtr pointer
funPtr = □
// the above two line is equivalent to void (*fun_ptr)(int) = &fun;
funPtr(20);
return 0;
}Output:
![]()
As in the above code, the function pointer is declared, as void (*funPtr)(int) and then initialize by storing the address of the square() function in funPtr, which means funPtr is pointing to function square(). So, by using the funPtr(function pointer) we can call to square function as in code funPtr(20).
Next, we write the C++ code to understand the function pointer working more clearly where we use function pointer to point or store the address of the function and call a function trough function pointer by another way as not above, as below –
Example #2
Code:
#include<stdio.h>
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
void square(int x)
{
cout<<"The square of a number is "<<x*x<<endl;
}
int main()
{
// declare funPtr pointer
void (*funPtr)(int);
// initialize funPtr pointer
funPtr = □
cout<<"The address of square function is ="<<&square<<endl;
cout<<"The function pinter funPtr=&square pointing to ="<<funPtr<<endl;
//also initialize as
funPtr = square;
cout<<"The function pinter funptr=square pointing to ="<<funPtr<<endl;
funPtr(20);
return 0;
}Output:
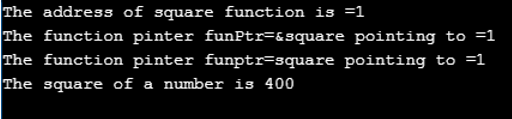
As in the above code, the address of a square() function is displaying. The address of a square() function printing as mention the name of the function proceed by & and also printed by the function pointer. If we see in the output, both addresses are the same. Therefore the funPtr is pointing to square() function.
Next, we write the C++ code to understand the function pointer working more clearly where we use function pointer to point a function and call a function by passing the array trough function pointer, as below –
Example #3
Code:
#include<stdio.h>
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
void disp(char *str)
{
cout << "Your Name is :" <<str<< endl;
}
int main()
{
char array[50];
// declare funPtr pointer
void (*funPtr)(char*);
// initialize funPtr pointer
funPtr = &disp;
cout<<"Enter Your Name : "<<endl;
cin>>array;
funPtr(array);
return 0;
}Output:
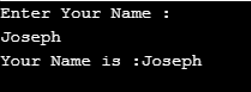
As in the above code, the disp() function is defined which accepts the parameter as char pointer. In main() function the function pointer funPtr is declare as “void (*funPtr)(char*)” and assign the address of disp() function as funPtr=&disp. So, by using the funPtr we can call to disp() function as in code funPtr(array) and pass the array as a parameter.
Next, we write the C++ code to understand the function pointer working more clearly where we use function pointer to point a function and call a function by Passing a function pointer as a parameter, as below –
Example #4
Code:
#include<stdio.h>
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
void dispFun(char *str)
{
cout << "Your Name is :" <<str<< endl;
}
void disp(void (*funPtr)(char*)) // declare funPtr pointer and initialize funptr
{
char array[50];
cout<<"Enter Your Name : "<<endl;
cin>>array;
funPtr(array);
}
int main()
{
disp(dispFun);
return 0;
}Output:
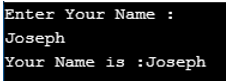
As in the above code, the two function are define, the dispFun() function is define which accepts the parameter as char pointer and the disp() function which accept function pointer that is funPtr as “void disp(void (*funPtr)(char*))”. In main() function the disp() function is calling as “disp(dispFun)”, which means the address of dispFun() function is assign or pass to funPtr function pointer parameter.
Conclusion
The function pointer in C++ is a variable that can be used to stores the address of a function and when the function needs to be called we can call indirectly through the function pointer.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Function Pointer in C++. Here we discuss the working and examples of the Function Pointer in C++ along with the programming examples. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –


