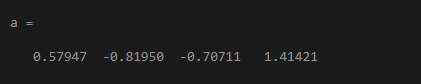Updated March 13, 2023
Introduction to fsolve in Matlab
Equations are defined as the expressions on the right and left-hand sides given by equal signs. There are various types of equations and one of them is a nonlinear equation. Nonlinear equations are defined as a set of expressions that have one of its variables in the equation greater than 1. Mathematically, there are various ways of solving nonlinear equations. In Matlab, fsolve is the function that is used to solve nonlinear equations. It solves the equations and returns a vector value for the objective function entered in the syntax.
Working of fsolve in Matlab with Syntax and Examples
In Matlab, the fsolve function is used to get the solutions of any nonlinear equations that are defined or declared in the environment. Please find the below syntaxes that are used while dealing with the fsolve function:
- a = fsolve(func,a0): This starts at an initial point a0 and continues to solve the equation where the function is equal to zero.
- a = fsolve(func,a0,options): This is used to solve the nonlinear equations using various options mentioned in syntax. optimoptions are used in Matlab to declare the required options.
- a= fsolve(problem): This is used to solve the nonlinear equations by the problem as mentioned in the syntax where it is specified as a structure.
- [a,fval] = fsolve(___) : This is used to find the value of the declared objective function in the input at the defined solution a.
- [a,fval,exitflag,output] = fsolve(___): This syntax is used when we want to display the output or exitflag .exitflag gives us the reason why fsolve algorithm stopped and output defines the process of optimization.
- [a,fval,exitflag,output,jacobian] = fsolve(___): This syntax is used to display the jacobian of the declared function.
The input and output arguments mentioned in the above syntax need to follow certain rules and criteria. ‘func’ is the first input argument that can be specified in the form of a function handle or a function name. It accepts its input as a vector and returns a vector quantity. If any of them is given in the form of arrays, then they are converted into vectors by the linear indexing method. The data types that are accepted are char, function handle, and string.’a0’ is another input argument that specifies the initial or starting point. fsolve uses the number of variables and size of the initial point (a0) to decide the number and size of variables that function should accept. It can be given in the form of a real vector or real array. The data type that is accepted by a0 is double. ‘problem’ is another input argument that is specified as a structure. It has various fields like objective (to declare the objective function), a0(to declare the initial point required in the algorithm), solver (fsolve to solve the equation), options (to change and modify the process of optimization in the whole process). ‘options’ is an input argument which has various options and it can be set by using optimoptions. Some of the options can be applied to all algorithms and some are not. Some of them are given below:
- Display Option: This is used to decide the levels of the display which are as follows:
- The ‘off’ option means there will no output display.
- ‘iter’ option means there will be output displayed for each iteration and provides the exit message(default).
- ‘iter-detailed’ option means there will be output displayed for each iteration with an exit message(technical).
- ‘final’ option means to display the final output of the whole iterative process and display the exit message(default) with it.
- ‘final-detailed’ means to display the final output of the whole iterative process and display the exit message(technical) with it.
- MaxFunctionEvaluations Option: This means the maximum number of evaluations that are allowed in the whole process. The default number of evaluations is 100 multiplied by the number of variables. It is given in the form of a positive integer only.
- MaxIterations Option: This means the maximum number of iterations that are allowed in the whole process. The default number of iteration is 400.
- Diagnostics Option: This option is used in some of the algorithms and it is used to display the diagnostic information about the function that is required to be solved or minimized. It can have two-valued i.e. ‘on’ and the default one is ‘off’.
Examples of fsolve in Matlab
Please find the below examples that show the use of the fsolve function in Matlab:
Example #1
To use fsolve in a matrix and find the value of fval and its exitflag value:
Code:
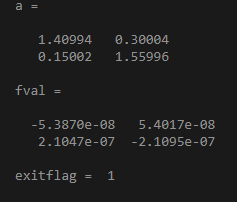
fun = @(a)a*a*a - [3,2;1,4];
a0 = ones(2);
[a,fval,exitflag,output] = fsolve(fun,a0);
a,fval,exitflag
Output:
Example #2
Code:
a0=[1,0,-2,1];
a=fsolve(@(a)[3*a(2)+3.*a(1).*a(4);2.*a(1)+a(2).*a(4);2.*a(3)+a(4);2-(a(1).^2)-0.5.*(a(3).^2)-a(4)],[a0])
Output:
Example #3
To find the value of the exit flag using the below objective function:
Code:
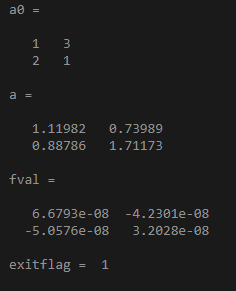
fun = @(a)a*a*a - [4,5;6,8];
a0 = [1,3;2,1]
[a,fval,exitflag,output] = fsolve(fun,a0);
a,fval,exitflag
Output:
The output arguments mentioned in the syntax section have also certain criteria like ‘a’ is an output argument that is returned in the form of a real vector or real array. The size of the solution ‘a’ is the same as the size declared for the initial point ‘a0’. Exitflag is another output argument that tells us the reason for the termination of the fsolve algorithm. It can have both positive and negative values like 1,2,3,4,0, -1, -2, -3 and each value has its own reason for termination. The output is another argument that contains the information about the whole optimization process and it can have several fields like iterations (displays the total number of iterations taken), funcCount (total number of function evaluations), message (to display the exit message, algorithm (name of the algorithm used in the optimization process).
If there are many variables then to save memory and time, then the algorithm option should be set to ‘trust-region’.
Conclusion
fsolve is widely used in Matlab, so it is important to understand it’s working. Certain limitations should be taken care of while dealing with the fsolve function, one of them is; the required function that should be solved must be continuous in nature and if the whole process is successful then the fsolve function gives only a single root.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to fsolve in Matlab. Here we discuss the Working of fsolve in Matlab with Syntax and Examples along with the codes and outputs. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –