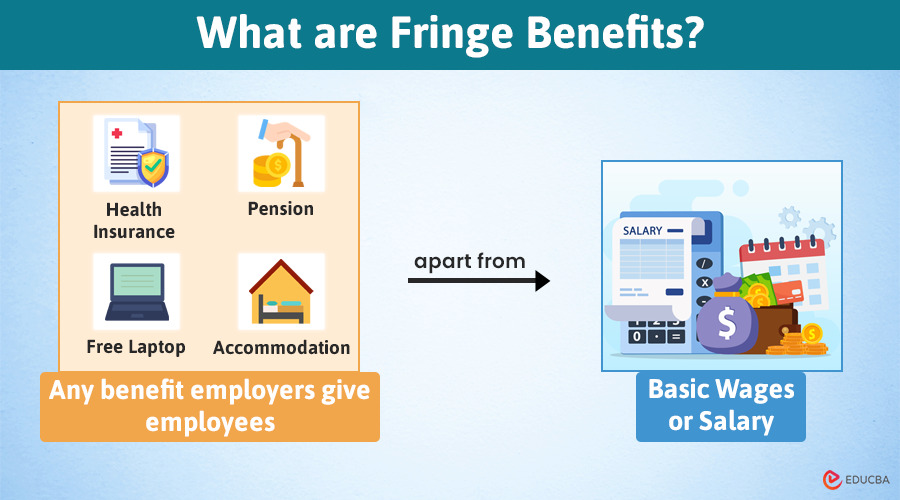
Definition of Fringe Benefits
Fringe benefits are advantages that the employer provides to an employee over and above the normal salary and wages, which may be in the form of cash support or assistance in daily needs of life or financial support for retirement age, or any other form to retain the high-quality people within the organization.
Explanation
- Everyone on this planet appreciates receiving something extra beyond what is expected, such as oregano and chili flakes with Domino’s Pizza. That “extra” principle applies a lot in the employment field.
- Fringe Benefits is “that extra” component. You are getting a salary for your service, no doubt. But won’t you like to get appreciated for your performance? Won’t you like to get pampered in your time of need? Some of the things are valued beyond salary. That’s what a fringe benefit is all about.
- The later part of the article will follow the examples, types, advantages, importance, and all sorts of stuff. But what’s very important to understand that these benefits may be temporary or permanent. You may get the benefits under your current employment but may not get changed employment. Getting the most out of the facilities is of the utmost essential.
Objectives of Fringe Benefits
- In the earlier days of businesses, the only way to retain employees was to hike the current salary. Days moved ahead, and only those employees retained who were honest on their job profiles. In the modern world today, the retention of employees is served by giving them extra benefits for their long service with the organization.
- Since many companies provide fringe benefits, it is also a compulsion for the remaining companies if they want to stay competitive in the environment.
- To attract talented employees, organizations give ample salaries and different fringe benefits because if they don’t give them, others (i.e., competitors) will grab them in no time.
- The organization has observed that many talented employees leave if they don’t receive sufficient benefits to incentivize long-term retention.
How does it Work?
- The fringe benefits differ from employer to employer. Employees are at the discretion to choose the fringe benefits.
- Employees choose those options at which they are at maximum benefit.
- Retail businesses provide employees with benefits such as discounts on electronic items, sales at cost benefits, and rewards for increasing the number of customers.
- Fringe benefits are dual-sided swords. On one side, it gives happiness and a feeling of satisfaction to the employees; on the other, it gives confidence in retention to the employer at a minimal cost.
- Uniqueness is always appreciated. The same is the case with the benefits. Employees like to continue with those employers who offer unique benefits.
Examples of Fringe Benefits
Examples of fringe benefits are explained below:
|
Sr. No |
Benefits |
Explanation |
| 1 | Meals | Many employers provide this essential benefit through meal vouchers or discounted coupons at partner restaurants. |
| 2 | Contributions for retirement | This benefits the employees who had served a long term with the employer & now, at retirement age, they get financial support from retirement schemes. |
| 3 | Health Assistance | The most essential thing in today’s world is health. So many employers provide free of cost gym memberships. The employer voluntarily arranges free meditation campaigns, yoga campaigns, aerobics, Zumba, etc., for the employees’ mental health. |
| 4 | Educational Assistance | Some employees want to study more in the area of their interest. Employers support the said cause. This also helps the employer to uplift the talent of the employees. With financial support, employers also let the employees work fewer hours for a few months. |
| 5 | Insurance Coverage | This is the most common benefit around the globe. The life of employees is at stake by the employer during working hours, and hence, insurance coverage is provided by the employer. |
| 6 | Cultural benefits | To support the broad culture followed by various employees within the organization, employers arrange for cultural programs to bring the feeling of one organization |
| 7 | Official reimbursements | Employers give cash benefits for the employee’s local conveyance, food, or travel expenses, which the employee incurs for official purposes during working hours. |
| 8 | Concessional Rental accommodation | Many employees come from different cities. So, the employer allows such employees to stay at company-owned premises at concessional rent till they find a suitable flat in the city. |
Types of Fringe Benefits
The benefits are explained below:
Category I: Fringe benefits that are required by law
- The federal government mandates these benefits, considering their importance and the employees’ needs.
- Such benefits are medical support, financial support, retirement benefits, insurance benefit, unemployment insurance, etc.
- The primary intent behind such benefits is that these are life-saving & life-supporting benefits.
- Each business entity must provide these benefits due to the provision in labor laws.
Category II: Voluntary benefits
- These benefits are not mandated by law but are given out of courtesy by the employer at his discretion.
- The moral intent behind such benefits is giving personal space to employees, letting them grow within the organization, helping them generate finance for the future, etc.
- Since these benefits are voluntary, many are taxable with certain exemptions.
- Voluntary benefits include employee stock options, educational support, leave salary, rent-free accommodation, investment advisory, free laptop, etc.
Fringe Benefit Tax
- Coming from the tax perspective, there is no free lunch. The IRS considers fringe benefits as part & parcel of employee compensation & thus, these benefits are taxable.
- Not all benefits are taxable. IRS specifies three categories of benefits, viz., non-taxable benefits, partially taxable benefits & tax-deferred benefits.
- For paying tax, we need to know the value of the benefit multiplied by the tax rate. The IRS specifies the tax rate, but the real task lies in valuing the benefits.
- The valuation is majorly based on the fair value principle.
- In a few instances, the IRS allows the value to taxes as fair value less than the amount recovered from employees.
A few of the non-taxable benefits are listed below:
- Retirement contributions
- Employee stock options
- Education assistance up to the specific limit
- Discounts from retail-employer
- Meals
- Conveyance expense
- Amenities provided by the employer
Reasons for Fringe Benefits
Many employees are always attracted to employers who provide additional benefits over and above the salary. Once the organization gains a reputation for its positive approach toward employees, its market reputation increases. An employee’s health is related to the revenue earned by the organization.
The organization cannot employ employees who fall ill or get injured and cannot work. Thus, fringe benefits in the form of personal health care help employees stay fit & active during working hours. So, some organizations around the globe also arrange for the mini-dance program at intervals of 3 hours during the day. In this case, all the employees dance at their respective bays.
Satisfied employees are retained in the long term. Satisfaction is not necessarily in terms of money but personal life. Thus, many employers offer paid leaves, encashment, travel with family benefits, etc.
Advantages and Disadvantages
Below listed are some advantages and disadvantages:
Advantages
- Fringe benefits motivate the employee. Motivation leads to more work in a lower time frame, saving the cost of an organization.
- The organization ensures the health of its employees. Health employees are productive in their work.
- Fringe benefits show the caring approach of the employer toward the employees. It increases the self-image of the organization.
- It reduces employee turnover and increases loyalty to work.
- Due to education support, the knowledge base of the employee increases. The employer can give the employees task related to newer skills they acquired. This lets the employer earn from no additional cost of hiring new people.
Disadvantages
- Some employees need a larger cash salary than the combination of salary + benefits. Such employees do not stay for long with the organization.
- For managing the equal flow of benefits within the organization, administrative costs increase to that extent.
- Few benefits are compulsion by law & thus, any non-compliance leads to paying fines and penalties to the government. Thus, to comply with labor laws, the employer must also bear the cost of a professional expert.
- Companies standardize fringe benefits in nature. Given the large mob of the organization, customization becomes difficult, and therefore, it is impossible to keep each employee satisfied.
- For a few organizations, the cost of providing fringe benefits is also high. The employer needs to cover the cost through an increase in revenue or the selling price of his products.
Conclusion
When talking about benefits, who does not like the same? As said earlier, there is no free lunch. In some way or another, your employer recovers 5 to 10 times the cost of extra benefits given to you, using use own skill set for the job. Employee retention is a big task in the modern-moving world. Every organization intends to continue with the same people with great potential to serve the company. Companies want to retain good employees at all possible costs. Even for employees, it shows courtesy of the employer towards them.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Fringe Benefits. Here we discuss the introduction and objectives of fringe benefits along with advantages and disadvantages. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –