Updated March 17, 2023

Introduction to for Loop in C Programming
Although writing C programs, we may experience a purpose to perform a comparable or exact group of instructions many times, for example, Printing numbers via 1 to 100 around the display screen, This with no usage of looping can be extremely tedious as well as, produce will make the program definitely not redistributable and never understandable. This problem came to be fixed by using looping.
Looping is known as a series of statements that are specific when as well as that can be performed several times. A collection of instructions will be carried out within the looping until some conditions to get termination with the loop have been reached.
Infinite Loops
Infinite loops can be a series of instructions that can be carried out forever. These types of loop happen whenever there simply no terminating condition offered or possibly a terminating condition that could never be fulfilled (just like 1==2 and so on.) or maybe occasionally due to a run time error. In the old system, infinite loops triggered the whole system to become irresponsible; however, in modern Operating Systems, these types of loops usually can be ended through the end-user.
A loop essentially includes 2 parts:
- The Control Declaration
- The loop Body
1. The Control Declaration
The control declaration checks the particular condition, and after that, it directs regular statements included in the body with the loop.
2. The Loop Body
The loop body features a group of instruction which will be carried out until some condition to get the termination with the loop has been reached. Loops being used through programming to repeat a particular block of code. When looking over this guide, you will understand to produce for loop in C programming. The for statement has three expressions within parentheses.
Syntax:
The syntax in for loop is –
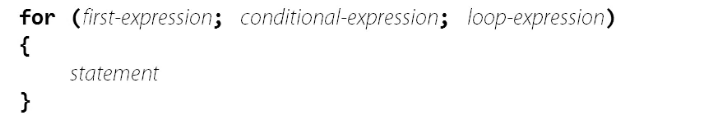
These works together to determine whether to execute the statement.
The first thing that happens is that the first expression is evaluated. Regardless of its outcome, this conditional expression is then evaluated. This expression defines some truth. If it evaluates to true or non-zero, then the statement is executed.
After the statement has been executed, the loop expression is evaluated only if the statement was executed. After the loop expression, the conditional expression is always executed to determine whether to execute the statement again.
Flow Diagram
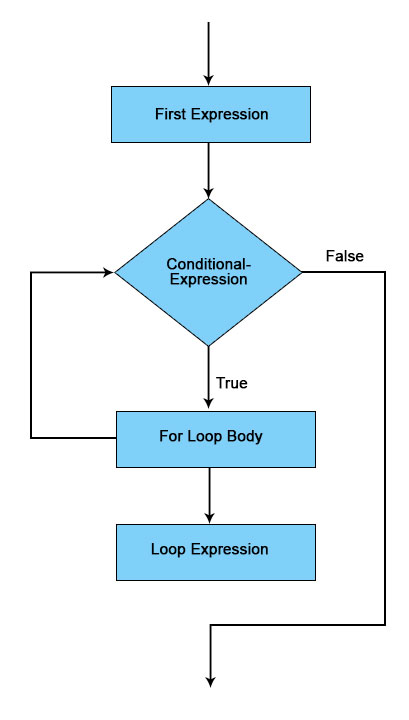
How for Loop Works in C?
- The initialization declaration is executed just once.
- After that, the conditional expression can be examined. If the test expression is false (0), for loop is ended. However, if the conditional expression is true (nonzero), codes within the body of for loop are performed, and the update expression is updated.
- This technique repeats before the test expression can be false.
- The for loop is usually applied if the quantity of iterations is well known.
- To find out more on conditional expression (once test expression is examined to nonzero (true) and 0 (false))
Examples
The most powerful iteration statement, but potentially also a source of bugs. Let’s get the loop variable initialized first.
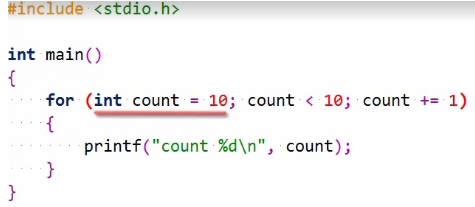
The loop condition is evaluated if its outcome is true.
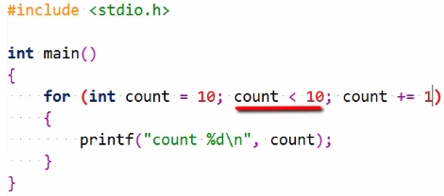
The body of the loop is executed.
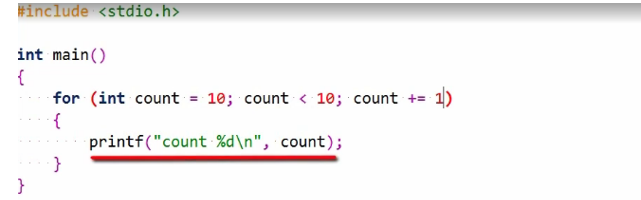
If not, execution continues following the for a statement after the body’s executed.
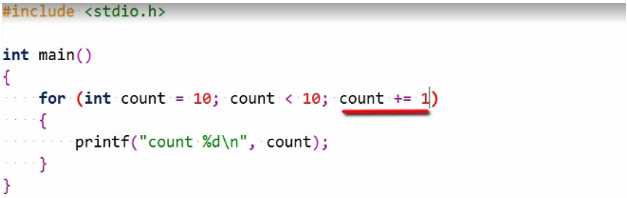
The expression updating the loop variable is executed, and the loop condition is again evaluated and so on, and this continues until the loop terminates. Of course, this loop will not execute its body since the count starts at 10, and this does not satisfy the condition.
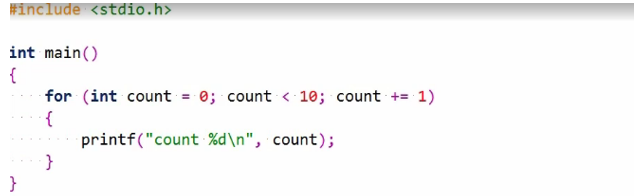
It’s easier to see such things at a glance with a for statement. So let’s change the initializer to 0 and take it for a spin, and there’s our count from 0 through 9 as expected.
Output:

An interesting thing about for statement is that any one of these may be omitted. We can, for example, use a loop variable declared elsewhere. This is fine and has the same effect.
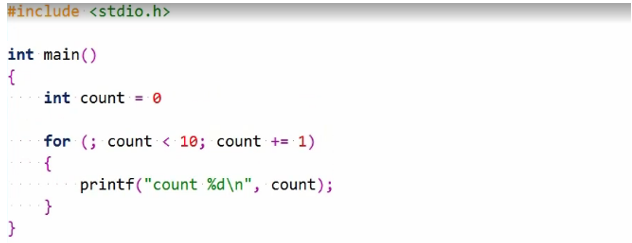
But now the count variable is visible beyond the for statement, again potentially a source of bugs. You should always try to keep a variable as limited and local as possible. Still, this is legal if you need it. You can also omit the expression by updating the loop variable.
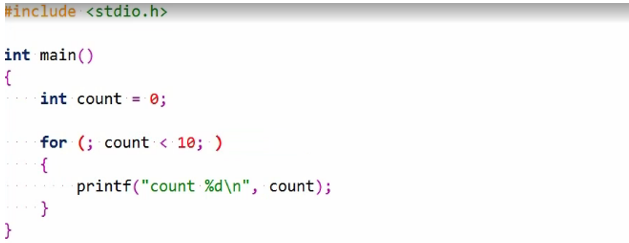
Again, this is fine, but what might be somewhat surprising is that you can even omit the loops condition expression itself.
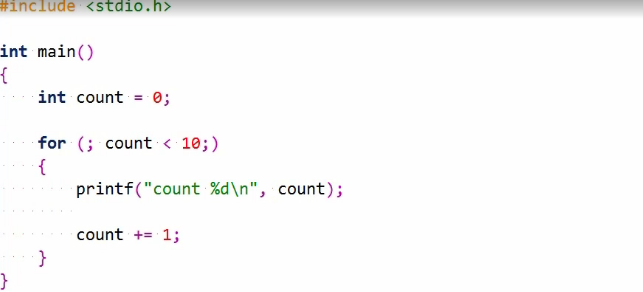
In that case, the condition is assumed to be true, and the loop will remain the same, so loop indefinitely or until you terminate it in some other way.
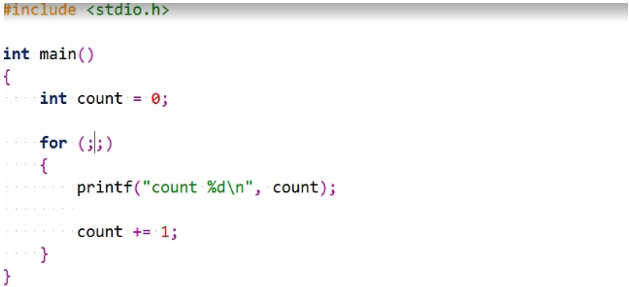
Here again, we are using the break statement. We first introduced with a switch statement.
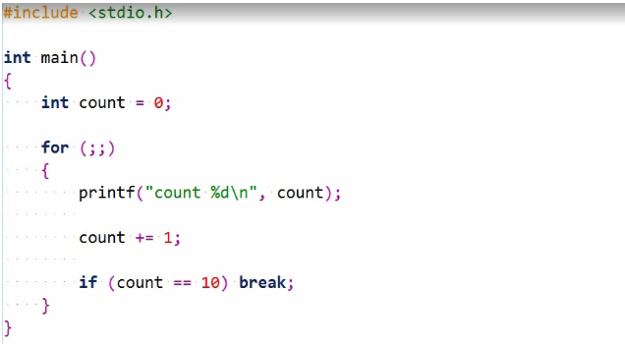
It can also be used to break out of the loop statement and causes execution to commence following the loop. This works just as well with a while statement, by the way. This now is again equivalent to the original while statement and the original for statement with three parts of the for statement neatly in line.
The main difference is that the loop condition is not actually checked upfront, although we know visually that the condition will hold at least once. The body is then executed, which includes the statement updating the loop variable and the if statement evaluating the loop condition manually.
Let’s give it a try. And sure enough, 0 through 9 again.

Conclusion – for Loop in C
- The primary statements are provided by the C programming language for selection and iteration.
- We considered the if statement the most widely used statement for selection or control flow.
- If some condition expression is true, then the associated statement or compound statement is executed. If not, execution continues at the next statement, if any.
- For statement gives you a lot of control over iteration in a more condensed syntax. There is nothing you cannot write with a while loop, but it is more convenient and safe in many cases since you can include a declaration which the other statements cannot, at least in C.
- The significance of loops in the different programming languages is enormous; they will enable us to minimize the number of lines within a program, producing our program more understandable and as well, effective.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to for Loop in C. Here we discuss the Introduction and how for loop works in C language with sample codes and output. You can also go through our other suggested articles –


