What is Financial Regulation?
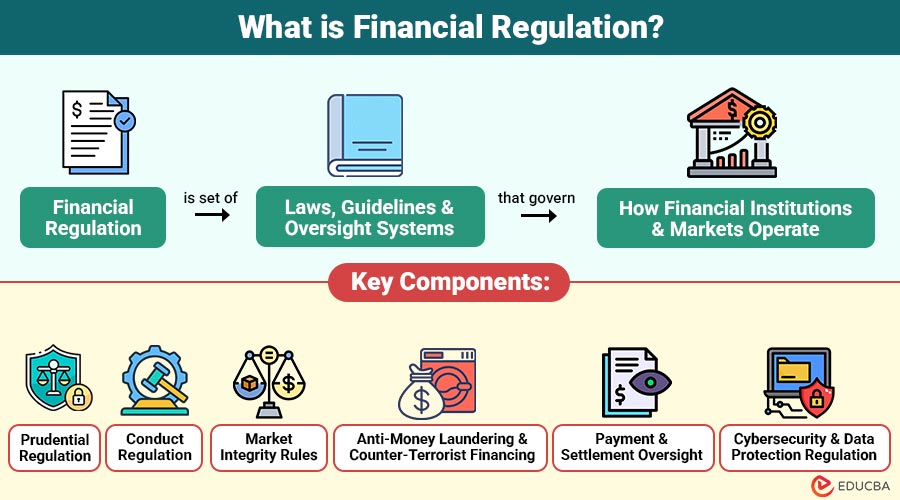
Financial regulation is the set of laws, guidelines, and oversight systems that govern how financial institutions and markets operate. These regulations are enforced by regulatory authorities such as central banks, securities commissions, and specialized financial oversight agencies.
Core Goals:
- Promote financial stability
- Protect consumers and investors
- Prevent market manipulation and fraud
- Maintain trust in the financial system
- Reduce systemic risk
- Ensure responsible lending and investment practices
Table of Contents:
Key Takeaways:
- Financial regulation establishes structured oversight, ensuring fair financial practices and strengthened confidence across global markets.
- Well-designed regulatory systems minimize economic disruptions by managing risks and promoting long-term financial system resilience.
- Regulatory frameworks encourage ethical conduct, improve transparency, and safeguard public interests and financial market stability.
- Modern regulations evolve continuously to address emerging technologies, new risks, and increasingly complex financial activities.
Why is Financial Regulation Important?
Here are the key reasons why financial regulation plays an crucial role in modern financial systems.
1. Protects Consumers
Regulation shields consumers from mis-selling, hidden fees, unfair lending practices, fraud, and identity theft in financial markets.
2. Prevents Risky Behavior
Rules restrict excessive leverage, speculative activities, and inadequate capital reserves to minimize systemic risks and instability.
3. Ensures Market Integrity
Regulations prevent insider trading, fraud, and manipulation, ensuring fair, transparent financial markets that maintain investor trust.
4. Enhances Economic Stability
Strong regulation promotes sustainable growth, prevents financial crises, reduces systemic vulnerabilities, and strengthens overall economic resilience.
5. Encourages Fair Competition
Regulation prevents monopolies, supports innovation, protects small institutions, and ensures all firms compete fairly in markets.
Key Components of Financial Regulation
Here are the key components that ensure financial systems operate safely, fairly, and transparently.
1. Prudential Regulation
Ensures institutions remain financially stable by maintaining capital strength, liquidity buffers, and strong internal risk management systems.
Examples:
- Capital adequacy requirements
- Liquidity coverage ratios
- Risk management guidelines
- Stress testing
2. Conduct Regulation
Sets rules for fair customer treatment through transparent pricing, responsible lending, and strict consumer protection standards.
Examples:
- Transparency in pricing
- Responsible lending rules
- Customer protection laws
- Product disclosure requirements
3. Market Integrity Rules
Prevents market manipulation, fraud, and insider trading by enforcing strict monitoring, reporting, and transparency requirements.
Examples:
- Insider trading prohibitions
- Market manipulation surveillance
- Fair disclosure rules
- Trade monitoring systems
4. Anti-Money Laundering & Counter-Terrorist Financing
Requires customer verification, transaction monitoring, and reporting suspicious activity to prevent financial crimes and illegal funding.
Examples:
- KYC (Know Your Customer) checks
- Suspicious transaction reports (STR)
- Enhanced due diligence
- Transaction monitoring tools
5. Payment and Settlement Oversight
Ensures payment systems operate safely through standards governing clearing, settlement accuracy, digital transaction security, and reliability.
Examples:
- Real-time gross settlement systems (RTGS)
- Automated clearing houses (ACH)
- Digital payment regulations
- Settlement finality rules
6. Cybersecurity and Data Protection Regulation
Protects financial data by enforcing encryption, cyber-risk assessments, breach reporting, and strong controls against unauthorized system access.
Examples:
- Data encryption standards
- Multi-factor authentication
- Cyber risk audits
- Mandatory breach reporting
Major Global Financial Regulatory Frameworks
Here are the most influential international frameworks shaping modern financial regulation worldwide.
1. Basel Accords (Basel I, II, III, IV)
Global banking standards establish capital adequacy, stress testing, and liquidity rules to strengthen international financial stability.
2. Dodd-Frank Act (USA)
Comprehensive U.S. legislation reducing excessive risk-taking, increasing transparency, and protecting consumers after the 2008 financial crisis.
3. MiFID II (Europe)
European framework improving investor protection, regulating securities markets, enhancing transparency, and strengthening operational standards for firms.
4. GDPR (Europe)
European data protection law requires strict privacy safeguards, controls over consent, and the secure handling of customer financial information.
5. FATF (Financial Action Task Force)
International body establishing global AML and CTF standards, guiding countries on preventing financial crime and terrorism financing.
6. Solvency II (Europe)
Regulatory regime for European insurers setting capital requirements, governance rules, and risk management standards to protect policyholders.
Challenges in Financial Regulation
Despite its importance, financial regulation faces several ongoing challenges:
1. Rapid Technological Advancements
Financial technologies like blockchain, fintech, and digital payments evolve faster than regulators can adapt oversight frameworks.
2. Regulatory Gaps
Cross-border financial activities often bypass national regulations, creating loopholes that weaken global oversight and systemic stability.
3. Compliance Costs
Small institutions struggle with expensive, complex compliance requirements, increasing operational burdens, and reduced competitive capabilities.
4. Shadow Banking Risks
Lightly regulated non-bank intermediaries create systemic vulnerabilities, increasing risks outside traditional financial supervision structures.
5. Data Privacy Concerns
Balancing transparency, customer protection, and data-sharing requirements becomes difficult as digital financial ecosystems rapidly expand.
6. Cybersecurity Threats
Growing cyberattacks demand stronger regulations, advanced security measures, and continuous vigilance to protect global financial systems.
Real-World Use Cases of Financial Regulation
Here are practical use cases showing how financial regulation protects markets, consumers, and the overall economy.
1. Preventing Bank Collapses
To assess banks’ capacity to endure economic shocks and preserve financial stability in times of crisis, regulators perform stress tests.
2. Consumer Protection in Lending
Regulations restrict predatory lending, enforce fair terms, and cap interest rates to protect borrowers from financial exploitation.
3. Safeguarding Online Payments
Payment gateways must follow strict security standards, such as PCI-DSS, to ensure safe, secure, and fraud-free digital transactions.
4. Stopping Insider Trading
Regulators and exchanges monitor suspicious trading activity, enforce disclosure rules, and prosecute offenders to maintain market fairness.
5. Preventing Money Laundering
Banks use AML tools to detect unusual transactions, verify identities, and report suspicious activity to regulatory authorities.
Examples of Financial Regulation in Action
Here are examples of how financial regulations operate in real-world scenarios:
1. Capital Adequacy Rules
Banks maintain required capital ratios to absorb unexpected losses and ensure long-term financial system stability.
2. KYC Requirements
Banks verify customer identity during onboarding to prevent fraud, enhance security, and comply with regulatory guidelines.
3. Trading Restrictions
Regulators keep an eye on high-speed trading programs to make sure they don’t cause big price swings, cheat the system, or disrupt the smooth functioning of the market.
4. Deposit Insurance
Insurance schemes like FDIC guarantee customer deposits up to regulated limits, increasing trust and financial system stability.
5. Consumer Data Privacy
Financial institutions must obtain explicit consumer consent before sharing personal data, thereby protecting privacy and ensuring responsible use.
Final Thoughts
Financial regulation is the backbone of a secure and trustworthy financial ecosystem. It ensures that institutions operate responsibly, markets function smoothly, and consumers remain protected. As technology, digital finance, and global markets evolve, regulation must continuously adapt. Whether you are an investor, consumer, policymaker, or financial professional, understanding financial regulation is crucial to navigating the modern financial world.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1. Who regulates financial institutions?
Answer: Depending on the country: central banks, securities regulators, insurance supervisory bodies, and international agencies.
Q2. How does financial regulation protect consumers?
Answer: By enforcing fair practices, preventing predatory lending, and ensuring transparency in financial products.
Q3. What happens if a financial institution violates regulations?
Answer: Penalties may include fines, suspension, corrective actions, or revocation of licenses.
Q4. How does technology affect financial regulation?
Answer: AI, digital payments, and cryptocurrencies require new rules to protect customers and maintain stability.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “Financial Regulation” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.

