Updated April 6, 2023

Introduction to Expression in C
An expression in C is defined as 2 or more operands are connected by one operator and which can also be said to a formula to perform any operation. An operand is a function reference, an array element, a variable, or any constant. An operator is symbols like “+”, “-“, “/”, “*” etc.
Let’s observe this example:
A*B
In the above expression multiplication symbol (*) is said to be an operator and A and B are said to be 2 operands.
Types of Expression in C
There are 4 types of expressions:
- Arithmetic expressions
- Relational expressions
- Logical expressions
- Conditional expressions
Every expression of these 4 types takes certain types of operands and used a specific type of operators. The result of this expression operation produces a specific value.
Example:
addition=(12/5)+(A-B);
From this line after equal operator(=) is an expression((12/5)+(A-B)) and total line is said to be a statement(addition=(12/5)+(A-B);).
How does Expressions works in C?
Expressions in C are built from combinations of operators, let’s see them as described below.
1. Arithmetic Expressions
Addition (+), Subtraction(-), Multiplication(*), Division(/), Modulus(%), Increment(++) and Decrement(–) operators are said to “Arithmetic expressions”. This operator works in between operands. like A+B, A-B, A–, A++ etc.
Syntax:
A+B;
A-B;
A*B;
A/B;Example:
Code:
//used to include basic C libraries
#include <stdio.h>
//main method for run c application
int main()
{
//declaring variables
int a,b,result;
//Asking the user to enter 2 numbers
printf("Enter 2 numbers for Arithmetic operation \n");
//Storing 2 numbers in varaibles a and b
scanf("%d\n%d",&a,&b);
//Arithmetic operations and its result displaying
result = a+b;
printf("================ARITHMETIC EXPRESSIONS==============\n");
printf("Addition of %d and %d is = %d \n",a,b,result);
result = a-b;
printf("Subtraction of %d and %d is = %d \n",a,b,result);
result = a*b;
printf("Multiplication of %d and %d is = %d \n",a,b,result);
result = a/b;
printf("Division of %d and %d is = %d \n",a,b,result);
result = a%b;
printf("Modulus(Remainder) when %d divided by %d = %d \n",a,b,result);
int c=a;
result = a++;
printf("Post Increment of %d is = %d \n",c,result);
result = ++a;
printf("Pre Increment of %d is = %d \n",c,result);
result=a--;
printf("Post decrement of %d is = %d \n",c,result);
result=--a;
printf("Pre decrement of %d is = %d \n",c,result);
printf("==========================================");
return 0;
}Output:

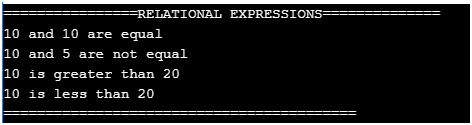
2. Relational Expressions
== (equal to), != (not equal to), != (not equal to), > (greater than), < (less than), >= (greater than or equal to), <= (less than or equal to) operators are said to “Relational expressions”.This operators works in between operands. Used for comparing purpose. Like A==B, A!=B, A>B, A<B etc.
Syntax:
A==B;
A!=B;
A<B;
A>B;Example:
Code:
//used to include basic C libraries
#include <stdio.h>
//include boolean library in c
#include <stdbool.h>
//main method for run c application
int main()
{
//declaring variables
int a,b;
bool result;
//Realational Expressions and its result displaying
printf("================RELATIONAL EXPRESSIONS==============\n");
//equal expression
a=10, b=10;
result=(a==b);
if(result)
{
printf("%d and %d are equal\n",a,b);
}
//not equal expression
a=10, b=5;
result=(a!=b);
if(result)
{
printf("%d and %d are not equal\n",a,b);
}
//greater expression
a=10, b=20;
result=(a<b);
if(result)
{
printf("%d is greater than %d\n",a,b);
}
//lesser expression
b=10, a=20;
result=(a>b);
if(result)
{
printf("%d is less than %d\n",b,a);
}
printf("==========================================");
return 0;
}Output:
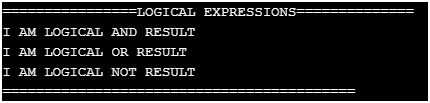
3. Logical Expressions
&&(Logical and), ||(Logical or) and !(Logical not) operators are said to “Logical expressions”. Used to perform a logical operation. This operator works in between operands. Like A&&B, A||B,A!B etc.
Syntax:
A&&B;
A||B;
A!B;Example:
Code:
//used to include basic C libraries
#include <stdio.h>
//include boolean library in c
#include <stdbool.h>
//main method for run c application
int main()
{
//declaring variables
int a,b;
bool result;
//Logical Expressions and its result displaying
printf("================LOGICAL EXPRESSIONS==============\n");
//logical and(&&) expression
a=10, b=20;
result=(a>5&&b>10);
if(result)
{
printf("I AM LOGICAL AND RESULT\n");
}
//logical or(||) expression
a=10, b=5;
result=(a>10||b>4);
if(result)
{
printf("I AM LOGICAL OR RESULT\n");
}
//logical not(!) expression
a=10, b=5;
result=(!(a==20));
if(result)
{
printf("I AM LOGICAL NOT RESULT\n");
}
printf("==========================================");
return 0;
}Output:
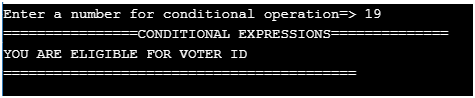
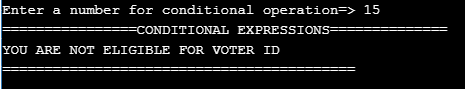
4. Conditional Expressions
?(Question mark) and :(colon) are said to “Conditional expressions”. Used to perform a conditional check. It has 3 expressions first expression is condition. If it is true then execute expression2 and if it is false then execute expression3. Like (A>B)?”A is Big”:”B is Big”.
Syntax:
(X+2=10)?'true':'false';Example:
Code:
//used to include basic C libraries
#include <stdio.h>
//include boolean library in c
#include <stdbool.h>
//main method for run c application
int main()
{
//declaring variables
int a,b;
char result;
//Asking the user to enter a number
printf("Enter a number for conditional operation=>");
//Storing a number in varaibles a
scanf("%d",&a);
//Realational Expressions and its result displaying
printf("================CONDITIONAL EXPRESSIONS==============\n");
//conditional expression
result=(a>=18)?'Y':'N';
if(result=='Y')
{
printf("YOU ARE ELIGIBLE FOR VOTER ID\n");
}
else
{
printf("YOU ARE NOT ELIGIBLE FOR VOTER ID\n");
}
printf("==========================================");
return 0;
}Output:
Conclusion
Expression in C is said to be a formula which is formed 2 or more operands and one operator. Arithmetic expressions, Logical expressions, Conditional expressions and Relational expressions are some of the expressions in C.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Expression in C. Here we discuss the Introduction to Expression in C and its types along with the different examples and code implementation. You can also go through our other suggested articles to learn more –


