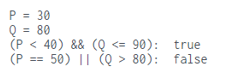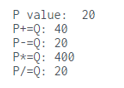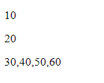Updated March 30, 2023
Introduction to ES6 Operator
Es6 operator is a symbol that instructs the system to carry out a specific operation. There is a large set of operators in JavaScript, and you may execute any task by utilizing certain operators. The operators are used to evaluate distinct operands in expressions; a statement that returns a value is known as an expression. The spread operator, which is made up of three dots, was introduced in ES6 (…). It allows an Iterable to expand where more than zero arguments are expected. In addition, it grants us access to an array of parameters.
What is the es6 operator?
- The syntax of the spread operator is similar to that of the rest parameter, but it is completely different.
- Below is the syntax of the es6 spread operator is as follows.
Var name_of_variable = […value]- At the time of declaring any variable, we need to put the var keyword before any variable. The name of the variable parameter shows that variable name.
- The spread operator targets full values in a variable, represented by the three dots (…), which is shown in the above syntax.
- The spread operator divides an array into its constituent elements.
- The spread operator debuted in JavaScript ES6. It decomposes the array into separate elements. As a result, it can be used to expand the array in areas where there should be zero or more elements.
Es6 operator
- JavaScript contains the below list of operators are as follows.
- Relational operator
- Arithmetic operator
- Assignment operator
- Logical operator
- Type operator
- Bitwise operator
- Miscellaneous operator
- In JavaScript, every expression evaluates the value, and it will contain the operator and operands.
Arithmetic operator
Below is the arithmetic operator is available in JavaScript is as follows.
- Addition (+): It will return the sum of two operand values. For example, if suppose A operand value is 5 and B operand value is 10, then the addition of two operands is 15.
- Subtraction (-): It will return the difference of two operand values. For example, if suppose A operand value is 15 and B operand value is 10, then the subtraction of two operands is 5.
- Multiplication (*): It will return the product of two operand values.
- Division (-): It will return the quotient of two operand values.
- Modulus (%) :It will return the remainder of two operand values.
Relational operator
Below is the relational operator available in JavaScript is as follows. The relational operator is defined as two entities’ relationship.
- Greater than operator (>) –
If A is 10 and B is 15, then (A>B) is false.
- Less than operator (<) –
If A is 10 and B is 15, then (A<B) is true.
- Greater than equal to operator (>=) –
If A is 10 and B is 15, then (A>=B) is false.
- Less than equal to operator (<=) –
If A is 10 and B is 15, then (A<=B) is true.
- Equal to operator (==) –
If A is 10 and B is 15, then (A==B) is false.
- Not equal to operator (!=) –
If A is 10 and B is 15, then (A!=B) is true.
Logical operator –
Below is the logical operator available in JavaScript is as follows. A logical operator is used to combine two or more conditions.
- Logical AND
- Logical OR
- Logical NOT
Bitwise operator –
Below is the bitwise operator available in JavaScript is as follows.
- Bitwise AND
- Bitwise OR
- Bitwise NOT
- Bitwise XOR
- Bitwise left shift
- Bitwise sign propagating right shift.
- Bitwise zero-fill right shift.
Assignment operator –
Below is the bitwise operator available in JavaScript is as follows.
- Simple assignment
- Add an assignment
- Subtract and assignment
- Multiply and assignment
- Divide and assignment
Miscellaneous operator
Below is the miscellaneous operator available in JavaScript is as follows.
- Negation operator
- String operator
- Conditional operator
- Typeof operator
- Spread operator
Es6 operator examples
Given Below is the example of the es6 operator:
Arithmetic operator example
Code –
var A = 100;
var B = 20 ;
console.log ("Addition of A and B is: " + (A + B));
console.log ("Subtraction of A and B is: " + (A - B));
console.log ("Multiplication is A and B is: " + (A * B));
console.log ("Division if A and B is: " + (A / B));
console.log ("Modulus of A and B is: " + (A % B));Relational operator example
Code –
var A = 25;
var B = 20;
console.log("A variable value is: " + A);
console.log("B variable value is: " + B);
var output = A > B;
console.log("A > B: " + output);
output = A < B;
console.log("A < B: " + output);
output = A >= B;
console.log("A >= B: " + output);
output = A <= B;
console.log("A <= B: " + output);
output = A == B;
console.log("A == B: " + output);
output = A != B;
console.log("A != B: " + output);Logical operator example
Code –
var P = 30;
var Q = 80;
console.log("P = " + P );
console.log("Q = " + Q );
var Output = ((P < 40) && (Q <= 90));
console.log("(P < 40) && (Q <= 90): ", Output);
var Output = ((P == 50) || (Q > 80));
console.log("(P == 50) || (Q > 80): ", Output);Assignment operator example
Code –
var P = 10;
var Q = 20;
P = Q;
console.log("P value: " + P);
P += Q;
console.log("P+=Q: " + P);
P -= Q;
console.log("P-=Q: " + P);
P *= Q;
console.log("P*=Q: " + P);
P /= Q;
console.log("P/=Q: " + P);Negation operator example
Code –
var A = 30;
var B = -A;
console.log("A value = " +A);
console.log("B value = " +B);Spread operator example
Code –
const num = [10, 20, 30, 40, 50, 60];
const [one, two, ...rest] = num;
document.write("<p>" + one + "</p>");
document.write("<p>" + two + "</p>");
document.write("<p>" + rest + "</p>");Output:
Conclusion
A statement is used to evaluate the value, which was referred to as an expression. Every sentence is made up of words. Operands are nothing but the variables which was used to represent the data. The operator is a component that performs actions on operands.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to ES6 Operator. Here we discuss What is es6 operator is and the list of operators which are available in JavaScript. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –