What is E-Learning?
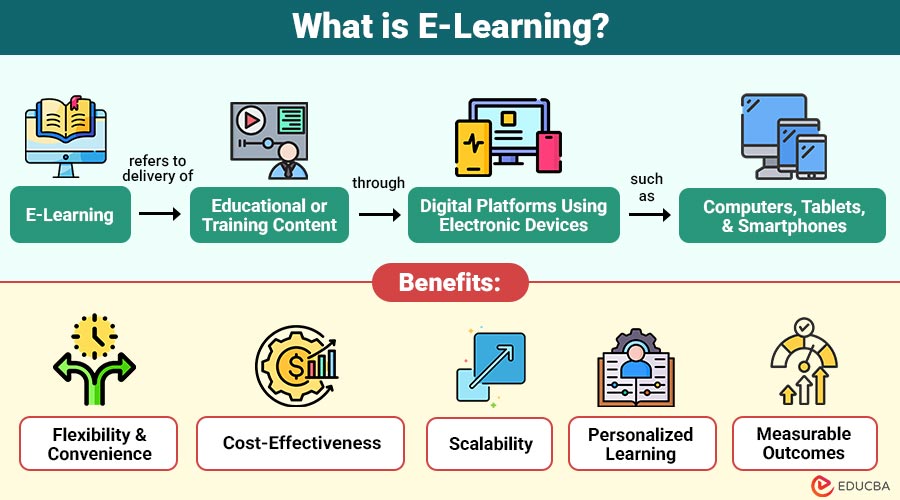
E-Learning refers to the delivery of educational or training content through digital platforms using electronic devices such as computers, tablets, and smartphones. It can include videos, interactive modules, quizzes, simulations, virtual classrooms, and collaborative tools.
Unlike traditional face-to-face learning, e-learning removes geographical and time constraints, allowing learners to engage with content remotely. It may be self-paced or instructor-led and can be used independently or blended with in-person instruction.
Table of Contents:
Key Takeaways:
- E-learning enables flexible, scalable education through digital platforms, supporting diverse learners across locations, schedules, and preferences.
- Multiple formats address diverse needs, ranging from real-time collaboration to self-paced, mobile, and microlearning experiences.
- Effective e-learning depends on robust LMS infrastructure, high-quality content, assessments, feedback, and meaningful learner collaboration.
- When designed well, it saves money, can be personalized, shows clear results, and supports ongoing learning across the organization.
Types of E-Learning
It takes several forms, each designed to meet different learning needs and contexts.
1. Synchronous E-Learning
Provides real-time instruction in which learners and instructors interact in virtual classes, webinars, discussions, and feedback sessions.
2. Asynchronous E-Learning
Enables learners to access materials at any time via recorded lectures, forums, self-paced courses, and email communication.
3. Blended Learning
Blended learning integrates face-to-face classroom instruction with online modules, assessments, and digital resources to provide flexible learning experiences.
4. Mobile Learning
5. Microlearning
Microlearning provides short, focused learning units that target specific objectives, enabling rapid knowledge acquisition and just-in-time application for professionals.
Key Components of an E-Learning System
An effective e-learning ecosystem relies on several core components working together.
1. Learning Management System
A learning management system is the backbone. It manages course content, user enrollment, progress tracking, assessments, and reporting. Popular LMS platforms support analytics, certifications, and integrations with other tools.
2. Learning Content
Content includes videos, presentations, readings, simulations, and interactive exercises. High-quality content is engaging, well-structured, and aligned with learning objectives.
3. Assessment and Feedback
Quizzes, assignments, exams, and surveys help evaluate learner understanding and performance. Automated and instructor-led feedback ensures continuous improvement and knowledge retention.
4. Collaboration Tools
Discussion forums, chats, group projects, and virtual classrooms foster social learning and peer interaction, which are essential for deeper understanding and engagement.
Benefits of E-Learning
It offers numerous benefits for learners, organizations, and educational institutions.
1. Flexibility and Convenience
Students can better balance their education with their personal and professional duties by accessing content from anywhere, at any time.
2. Cost-Effectiveness
Reduces expenses related to travel, accommodation, physical infrastructure, and printed materials. Organizations can train large audiences at a lower cost.
3. Scalability
Digital courses can be delivered to thousands of learners simultaneously without compromising consistency or quality.
4. Personalized Learning
Learners can advance at their own pace, according to their unique requirements and skills, through adaptive learning paths, self-paced courses, and data-driven recommendations.
5. Measurable Outcomes
Platforms show clear information about how learners are doing, such as progress, completion, test scores, and activity, helping teachers and organizations make better decisions.
Challenges of E-Learning
Despite its advantages, it also presents certain challenges.
1. Limited Human Interaction
The absence of face-to-face communication can reduce social engagement and motivation if not addressed through collaborative activities.
2. Technology Barriers
Access to reliable internet, devices, and technical support is essential. Technical issues can disrupt the learning experience.
3. Learner Self-Discipline
Needs good time management and self-motivation. Without proper guidance, some students may struggle to stay focused and organized.
4. Content Quality and Design
Ineffective learning results and disengagement can result from poorly designed courses. A key component of success is instructional design.
Use Cases of E-Learning
It is widely adopted across various sectors.
1. Corporate Training
Organizations use e-learning for onboarding, compliance training, leadership development, and technical skill enhancement. It ensures consistent delivery of training across locations.
2. Academic Education
Schools, colleges, and universities offer online courses, degree programs, and virtual classrooms to reach diverse learner populations.
3. Professional Development
Professionals use platforms to learn new technologies, obtain certifications, and maintain their competitiveness.
4. Government and Public Sector
Supports large-scale training initiatives, awareness programs, and capacity building for public servants and citizens.
Best Practices for Effective E-Learning
To maximize the impact, consider the following best practices:
1. Clear Goals & Structured Design
Define measurable learning objectives aligned with the goals and apply rigorous instructional design to ensure clarity.
2. Engaging & Interactive Content
3. Assessment, Feedback & Improvement
Include regular assessments and timely feedback, and continuously update content using learner insights.
4. Collaboration & Social Learning
Promote discussions, group activities, and peer learning to enhance understanding and motivation.
Final Thoughts
E-learning has transformed education and training by making learning more accessible, flexible, and scalable. While it presents challenges, thoughtful design, appropriate technology, and learner-centric approaches can unlock its full potential. As digital transformation accelerates, e-learning will remain a key enabler of continuous learning and professional growth in the years to come.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1. Is e-learning as effective as classroom learning?
Answer: Yes, when well designed, e-learning can be as effective as or more effective than traditional learning, offering flexibility, personalization, and measurable outcomes.
Q2. What skills are required for e-learning?
Answer: Basic digital literacy, time management, self-discipline, and willingness to engage with online tools are essential.
Q3. Can e-learning be used for practical skills?
Answer: Yes, through simulations, virtual labs, videos, and blended learning approaches.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “E-Learning” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.
