Updated May 20, 2023
Introduction to Django JsonResponse
JSON is a format very flexibly preferred nowadays, so support for JSON is extended across all technology formats. This is because of the easy capability to reference and parse data in JSON objects. This parsing capability offers a large extent of preference for JSON objects. So, like other platforms, Django also provides support for JSON, and support is offered using JSON response. So when data is rendered like an HTML page, JSON objects can also be rendered. This rendering of JSON objects is depicted below.
Syntax:
from django.http import JsonResponse
JsonResponse(data,safe=TRUE/FALSE)How JsonResponse works in Django?
Understanding how JSON objects receive data involves actively working with the JSON format. The first and most significant element to ensure is to import the JsonResponse class from Django. HTTP library. This is a very critical step, only if the Django. HTTP library shares the JsonRespose class; then, the JSON-based rendering can be performed. The class will make the JSON response element to be available for the remaining of the program. Next, the data for rendering needs to be formulated. When formulating data, one must consider its source, whether from forms, random input, or databases. It is crucial to properly format the data to determine how it will be populated and which information will be involved. After this comes the key part of data rendering. The data rendering is the critical section where the JSON response will be rendered. This process involves depicting the data on the console. Furthermore, you must ensure to add the URL entry for the data.
Create a Django JsonResponse:
1. Changes in Models.py file: The JsonResponse charge at the same time as submitted ought to be stored, and at the same time as retrieved, it ought to be pulled from the database. Use the object created for the model, as explained in the following section of views.py, to complete this task.
models.py
from django.db import models
from django.contrib.auth.models import User
# Model variables
# Create your models here.
class Bride(models.Model):
JsonResponse_Example_name = models.CharField(max_length=200,null=True)
JsonResponse_Example_thegai = models.CharField(max_length=200,null=True)
JsonResponse_Example_State = models.CharField(max_length=50,null=True)
JsonResponse_Example_District = models.CharField(max_length=50,null=True)
JsonResponse_Example_Address = models.TextField(null=True)
JsonResponse_Example_Phone = models.BigJsonResponse_Example_Field(null=True)
JsonResponse_Example_profession = models.CharField(max_length=200,null=True)
JsonResponse_Example_salary = models.BigJsonResponse_Example_Field(null=True)
JsonResponse_Example_Under_Graduation_Degree = models.CharField(max_length=200,null=True)
JsonResponse_Example_Under_Graduation_college = models.CharField(max_length=400,null=True)
JsonResponse_Example_Post_Graduation_Degree = models.CharField(max_length=200,null=True)
JsonResponse_Example_Post_Graduation_college = models.CharField(max_length=400,null=True)
JsonResponse_Example_Rasi = models.CharField(max_length=200,null=True)
JsonResponse_Example_Nakshatra = models.CharField(max_length=200,null=True)
JsonResponse_Example_Creator = models.ForeignKey(User, null=True, on_delete=models.CASCADE)
def _str_(self):
return self.name2. Changes in Forms.py file:
We have made the following modifications to the forms.py file, which include adding the “bride” table and linking and declaring all of its fields within the forms.py file.
forms.py
from django import forms
from .models import Bride
from django.contrib.auth.forms import UserCreationForm
from django.contrib.auth.models import User
class Valueform(forms.ModelForm):
# Rasi = forms.ChoiceField(choices = Rasi_CHOICES)
class Meta:
model = Bride
fields = "__all__"3. Changes in Settings.py file:
Ensure that you correctly configure the values and database connections in the settings.py file to ensure smooth and flexible execution of the project.
Settings.py:
MIDDLEWARE = [
'django.middleware.security.SecurityMiddleware',
'django.contrib.sessions.middleware.SessionMiddleware',
'django.middleware.common.CommonMiddleware',
'django.middleware.csrf.CsrfViewMiddleware',
'django.contrib.auth.middleware.AuthenticationMiddleware',
'django.contrib.messages.middleware.MessageMiddleware',
'django.middleware.clickjacking.XFrameOptionsMiddleware',
]
ROOT_URLCONF = 'Matrimony.urls'
TEMPLATES = [
{
'BACKEND': 'django.template.backends.django.DjangoTemplates',
'DIRS': [Template_DIR,],
'APP_DIRS': True,
'OPTIONS': {
'render_dict_processors': [
'django.template.render_dict_processors.debug',
'django.template.render_dict_processors.request',
'django.contrib.auth.render_dict_processors.auth',
'django.contrib.messages.render_dict_processors.messages',
],
},
},
]4. Changes in url.py file:
To configure it correctly, you must instantiate the Media root and document root variables within the url.py file. Here are the steps you need to take to make the necessary adjustments to the url.py file.
url.py:
from django.contrib import admin
from django.urls import path
from django.conf.urls import url
from matrimony_pages import views
from django.conf import settings
from django.conf.urls.static import static
urlpatterns = [
url(r'^$',views.Welcome_page,name='Welcome_page'),
url(r'Mainpage/',views.Main_page,name='Main_page'),
url(r'form/',views.form_view,name='form_view'),
url(r"signup/", views.Sign_up_request, name="register"),
url(r"login/", views.login_request, name="login"),
path(r'profile//',views.JsonResponse_Example_page,name='profile'),
url(r'logout/',views.logout_request,name='logout'),
url(r'reg/',views.JsonResponse_Example_reg_user,name='reg'),
path(r'update//',views.form_update,name='update'),
path('admin/', admin.site.urls),
]+ static(settings.MEDIA_URL,document_root=settings.MEDIA_ROOT)5. Create a view for the form: The JsonResponse rate while submitted must be stored and retrieved from the database. Use the object you created for the model to complete this task. Refer to the views.py section provided below for instructions on how to do this.
views.py
from django.shortcuts import render, redirect
from django.http import HttpResponse
from .models import *
from .forms import NewUserForm,Valueform
from django.contrib.auth import login,authenticate,logout
from django.contrib import messages
from django.contrib.auth.forms import AuthenticationForm
from django.contrib.auth.models import User
from django.contrib.auth.decorators import user_passes_test,login_required
from django.core.paginator import Paginator
from django.http import JsonResponse
def form_view(request):
form = Valueform(request.POST or None)
if form.is_valid():
post = form.save()
post.Creator = request.user
print('Creator user stored',request.user)
post.save()
return render(request,'form.html', {"form": form})
@login_required
def JsonResponse_Example_page(request,pk):
Json_dict = {}
JsonResponse_key_variable_ = Bride.objects.get(id=pk)
JsonResponse_Example_name = JsonResponse_key_variable_.name
JsonResponse_Example_Age = Bride.objects.JsonResponse(first_name='Nalandan', last_name='Ranjan',defaults={'birthday': date(1990, 10, 9)})
JsonResponse_Example_Thegai = JsonResponse_key_variable_.thegai
JsonResponse_Example_state = JsonResponse_key_variable_.State
JsonResponse_Example_district = JsonResponse_key_variable_.District
JsonResponse_Example_Address = JsonResponse_key_variable_.Address
JsonResponse_Example_Phone = JsonResponse_key_variable_.Phone
JsonResponse_Example_Profession = JsonResponse_key_variable_.profession
JsonResponse_Example_Salary = JsonResponse_key_variable_.salary
JsonResponse_Example_UG = JsonResponse_key_variable_.Under_Graduation_Degree
JsonResponse_Example_UGC = JsonResponse_key_variable_.Under_Graduation_college
JsonResponse_Example_PG = JsonResponse_key_variable_.Post_Graduation_Degree
JsonResponse_Example_PGC = JsonResponse_key_variable_.Post_Graduation_college
JsonResponse_Example_UG = JsonResponse_key_variable_.Under_Graduation_Degree
JsonResponse_Example_UGC = JsonResponse_key_variable_.Under_Graduation_college
JsonResponse_Example_PG = JsonResponse_key_variable_.Post_Graduation_Degree
JsonResponse_Example_PGC = JsonResponse_key_variable_.Post_Graduation_college
JsonResponse_Example_Rasi = JsonResponse_key_variable_.Rasi
JsonResponse_Example_Nakshatra = JsonResponse_key_variable_.Nakshatra
Json_dict['Age'] = JsonResponse_Example_Age
Json_dict['name'] = JsonResponse_Example_name
Json_dict['thegai'] = JsonResponse_Example_Thegai
Json_dict['State'] = JsonResponse_Example_state
Json_dict['district'] = JsonResponse_Example_district
Json_dict['Address'] = JsonResponse_Example_Address
Json_dict['Phone'] = JsonResponse_Example_Phone
Json_dict['profession'] = JsonResponse_Example_Profession
Json_dict['Under_Graduation_Degree'] = JsonResponse_Example_UG
Json_dict['Under_Graduation_college'] = JsonResponse_Example_UGC
Json_dict['Post_Graduation_Degree'] = JsonResponse_Example_PG
Json_dict['Post_Graduation_college'] = JsonResponse_Example_PGC
Json_dict['Rasi'] = JsonResponse_Example_Rasi
Json_dict['Nakshatra'] = JsonResponse_Example_Nakshatra
return render(request,'Profilepage.html',Json_dict)
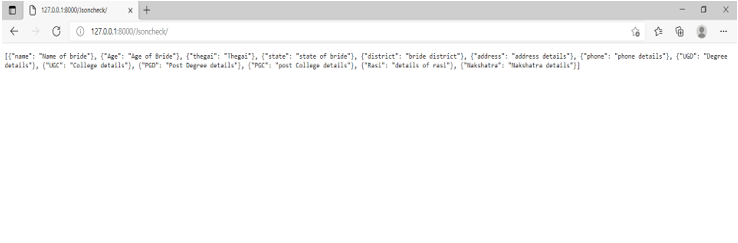
+def Json_Response(request):
jsondata = [{'name': 'Name of bride'},
{'Age': 'Age of Bride'},
{'thegai': 'Thegai'},
{'state': 'state of bride'},
{'district': 'bride district'},
{'address': 'address details'},
{'phone': 'phone details'},
{'UGD': 'Degree details'},
{'UGC': 'College details'},
{'PGD': 'Post Degree details'},
{'PGC': 'post College details'},
{'Rasi': 'details of rasi'},
{'Nakshatra': 'Nakshatra details'}
]
return JsonResponse(jsondata, safe=False)Output:
Conclusion
This guide explains how to claim JsonResponse area combos in Django, outlining the syntax and how JsonResponse relationships function in Django. It also provides a live website example, screenshots and highlights any updates made to Django-related documents.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “Django JsonResponse” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.